宁夏网站建设优化/外包公司值得去吗
文章目录
- 线性表
- 顺序表
- 顺序表与数组
- 本质
- 优点
- 缺陷
- 解决办法
- SeqList.h
- Test.c
- 实现
- 初始化与销毁
- 扩容
- 尾插头插
- 打印
- 尾删头删
- 查找
- 中间插入/删除
- 修改
- 链表
- 优点
- 缺点
- 单链表
- 逻辑结构&物理结构
- 链表组合
- 实现
- 定义
- 创建节点
- 打印
- 查找
- 尾删
- 头删
- 头插
- 尾插
- pos后插入
- pos前插入
- pos后擦除
- 双向链表
- 头文件
- 初始化
- 创建节点
- 尾插
- 头插
- 尾删
- 头删
- 查找
- 插入
- 擦除
- 是否为空
- 计算大小
- 摧毁
- 练习
- [27. 移除元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/)
- [26. 删除有序数组中的重复项](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
- [989. 数组形式的整数加法](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-to-array-form-of-integer/)
- [88. 合并两个有序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/)
- [189. 轮转数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-array/)
- [203. 移除链表元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
- [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- [876. 链表的中间结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
- [剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lian-biao-zhong-dao-shu-di-kge-jie-dian-lcof/)
- [21. 合并两个有序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/)
- 链表分割
- VS下调试链表的题目
- 链表的回文结构
- [160. 相交链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
- [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
- [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- [138. 复制带随机指针的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
- [147. 对链表进行插入排序](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insertion-sort-list/)
- 删除链表中重复的结点
线性表
常见的线性表:顺序表,链表,栈,队列,字符串
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,(连续的一条直线)
但是在物理结构不一定是连续的
逻辑结构
物理结构
顺序表
顺序表与数组
由于顺序表结构的底层实现借助的就是数组,因此对于初学者来说,可以把顺序表完全等价为数组,但实则不是这样。数据结构是研究数据存储方式的一门学科,它囊括的都是各种存储结构,而数组只是各种编程语言中的基本数据类型,并不属于数据结构的范畴。
本质
顺序表:本质就是数组,动态增长,并且要求里面存储的数据必须是从左往右连续的
数组可以只存1 3 5位置,顺序表不行
数组是静态的利用malloc和realloc
优点
- 按下标进行随机访问
- 空间地址连续,CPU高速缓存命中率比较高
CPU访问数据时,数据在缓存,命中;
不在缓存,不命中
假设不命中时,一次性加载16字节
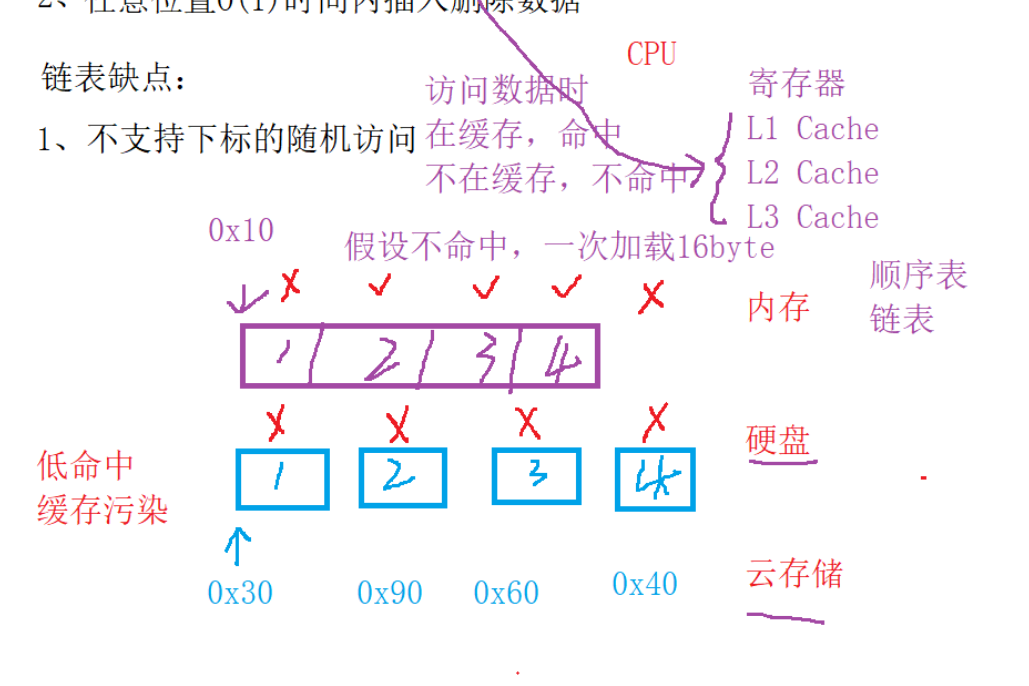
缺陷
- 动态增容有性能消耗,通常伴随着空间浪费
- 头部或中间插入/删除数据,需要挪动数据,效率比较低
解决办法
链表
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#define N 100
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>静态顺序表(不推荐)
//struct SeqList
//{
// int a[N];
// int size;
//};typedef int SeqDataType;//利用typedef插入任意类型数据typedef struct SeqList
{SeqDataType* a;//指向动态开辟的数组int size;//有效数据个数int capacity;//容量
}SeqList,SEQ;//初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* pseq);
//销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* pseq);
//打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* pseq);//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* pseq, SeqDataType x);
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* pseq, SeqDataType x);
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* pseq);
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* pseq);
//查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* pseq,SeqDataType x);
//中间插入
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* pseq, int pos, SeqDataType x);
//中间擦除
void SeqListErase(SeqList* pseq, int pos);
//修改
void SeqListModify(SeqList* pseq, int pos, SeqDataType x);
Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"void TestSeqList()
{SeqList s;SeqListInit(&s);//必须传址SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);SeqListPushFront(&s, 0);SeqListPushFront(&s, 0);SeqListPushFront(&s, 0);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopFront(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopFront(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListDestory(&s);
}void TestSeqList2()
{SeqList s;SeqListInit(&s);SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListInsert(&s, 0, 30);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListErase(&s, 0);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListModify(&s, 0, -1);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListDestory(&s);}
int main()
{TestSeqList2();return 0;
}
实现
Tips:不要先写菜单,把接口都调正确了再写菜单
//静态顺序表(不推荐)
struct SeqList
{int a[N];int size;
};
初始化与销毁
//初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* pseq)
{assert(pseq);pseq->a = NULL;pseq->capacity = 0;pseq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* pseq)
{assert(pseq);free(pseq->a);pseq->a = NULL;pseq->capacity = pseq->size = 0;
}
扩容
void SeqCheckCapacity(SeqList* pseq)
{//满了需要增容if (pseq->size == pseq->capacity){//一开始要赋予初识空间int newcapacity = pseq->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pseq->capacity * 2;//通常增加2倍SeqDataType* newA = realloc(pseq->a, sizeof(SeqDataType) * newcapacity);/*if (newA == NULL){printf("SeqListPushBack::%s\n", strerror(errno));}*///或者if (newA == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);}pseq->a = newA;pseq->capacity = newcapacity;}
}
尾插头插
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* pseq, SeqDataType x)
{/*assert(pseq);SeqCheckCapacity(pseq);pseq->a[pseq->size] = x;pseq->size++;*/SeqListInsert(pseq, pseq->size, x);
}//头插需要从后往前挪动
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* pseq, SeqDataType x)
{/*assert(pseq);SeqCheckCapacity(pseq);int end = pseq->size - 1;while (end >= 0){pseq->a[end + 1] = pseq->a[end];--end;}pseq->a[0] = x;pseq->size++;*/SeqListInsert(pseq, 0, x);
}
打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* pseq)
{assert(pseq);for (int i = 0; i < pseq->size; i++){printf("%d ", pseq->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
尾删头删
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* pseq)
{/*assert(pseq);assert(pseq->size > 0);--pseq->size;*/SeqListErase(pseq, pseq->size - 1);
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* pseq)
{/*assert(pseq);assert(pseq->size > 0);//必须从前往后挪动int begin = 0;//挪到begin == size-1就停止while (begin < pseq->size - 1){pseq->a[begin] = pseq->a[begin+1];begin++;}pseq->size--;*/SeqListErase(pseq, 0);
}
查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* pseq, SeqDataType x)
{assert(pseq);for (int i = 0; i < pseq->size; i++){if (pseq->a[i] == x){return i;}return -1;}
}
中间插入/删除

//中间插入
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* pseq, int pos, SeqDataType x)
{assert(pseq);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= pseq->size);//=size时表示的就是尾插SeqCheckCapacity(pseq);//从后往前挪动int end = pseq->size - 1;while (end>=pos){pseq->a[end + 1] = pseq->a[end];--end;}pseq->a[pos] = x;pseq->size++;
}
//中间擦除
void SeqListErase(SeqList* pseq, int pos)
{assert(pseq);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < pseq->size);//不能=size,=size时没有元素的int begin = pos;while (begin <= pseq->size-1){pseq->a[begin] = pseq->a[begin + 1];++begin;}pseq->size--;
}
修改
void SeqListModify(SeqList* pseq, int pos, SeqDataType x)
{assert(pseq);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < pseq->size);pseq->a[pos] = x;
}
链表
优点
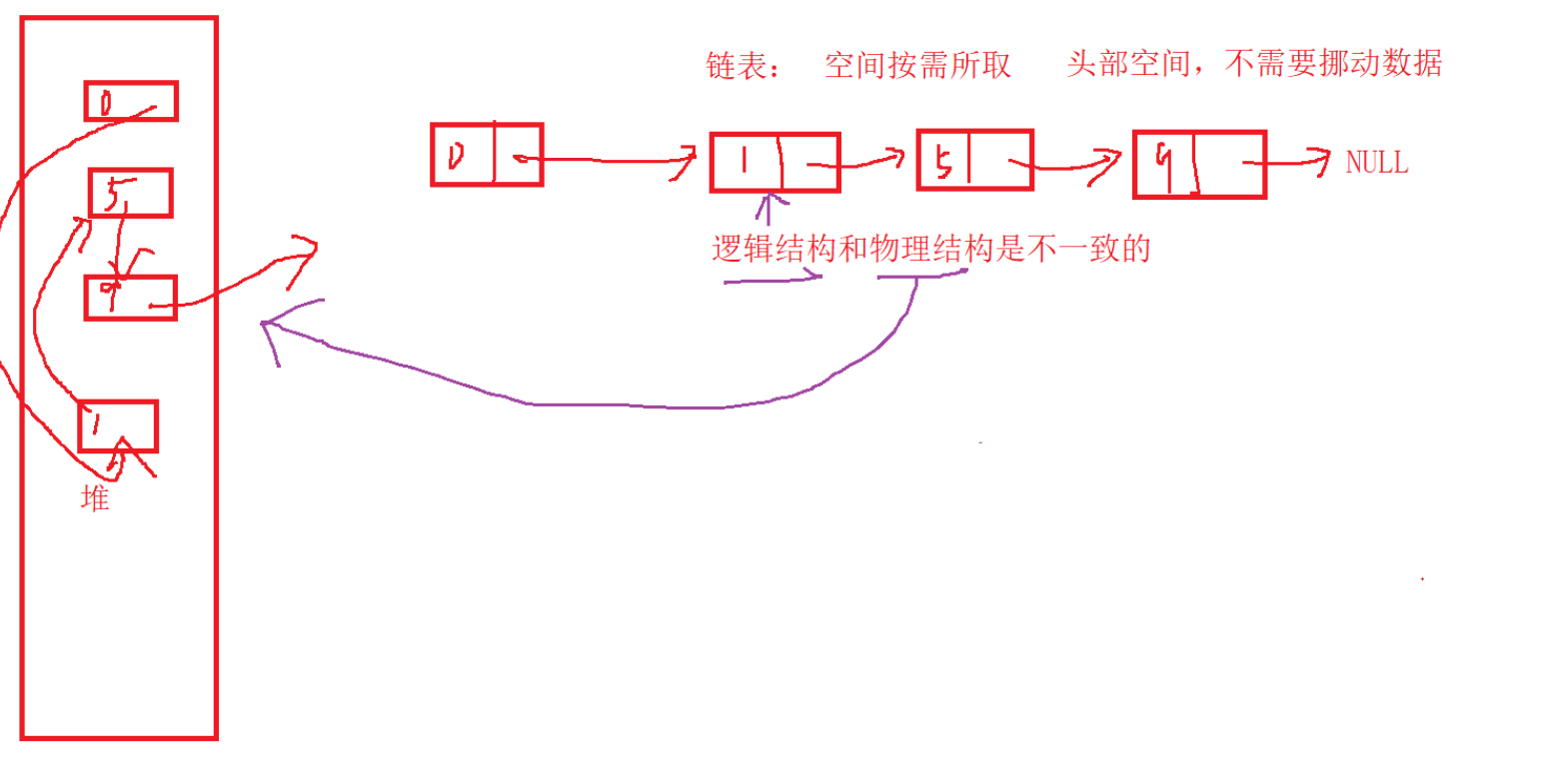
- 按需申请内存,不存在空间浪费
- 任意位置O(1)时间插入删除数据
缺点
- 不支持下标的随机访问
总结:顺序表和链表相辅相成,使用要看具体应用场景
单链表
struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
};
void Test()
{struct SListNode* node1 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));struct SListNode* node2 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));struct SListNode* node3 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));struct SListNode* node4 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));printf("%p\n", node1);printf("%p\n", node2);printf("%p\n", node3);printf("%p\n", node4);
}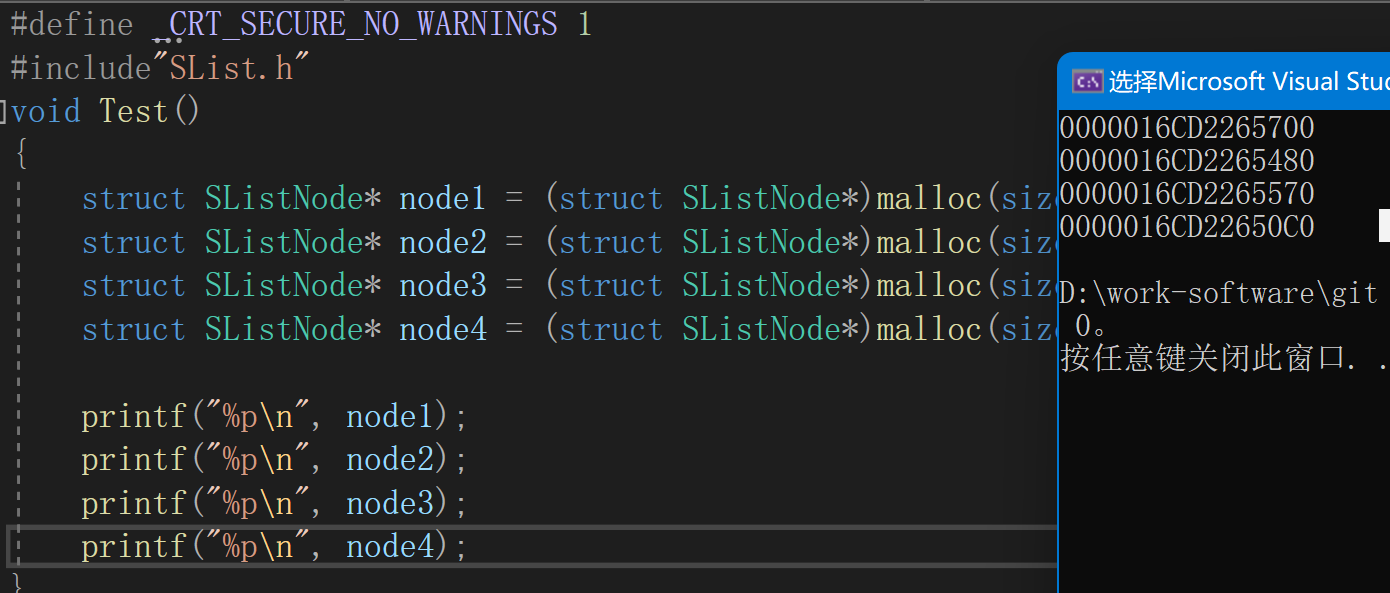
地址均不连续,堆上使用的空间地址由高到低
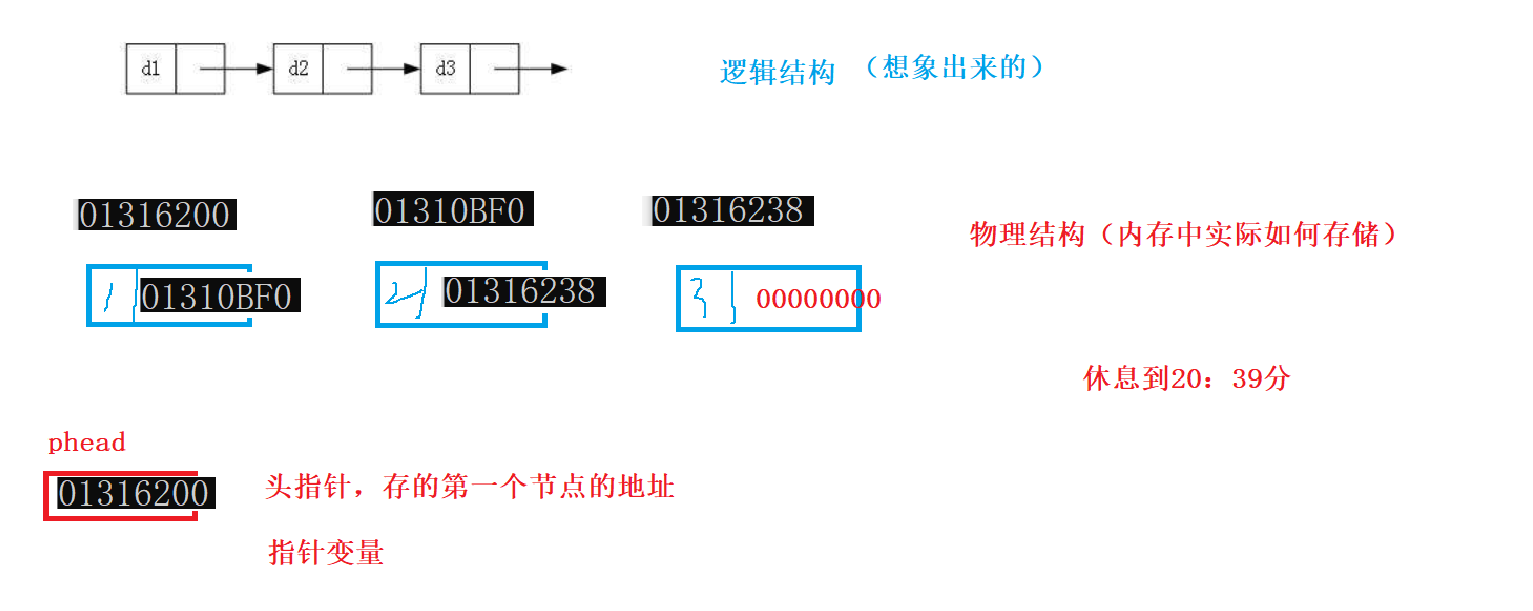
逻辑结构&物理结构
phead(头结点)是指针变量,存的是第一个节点的地址
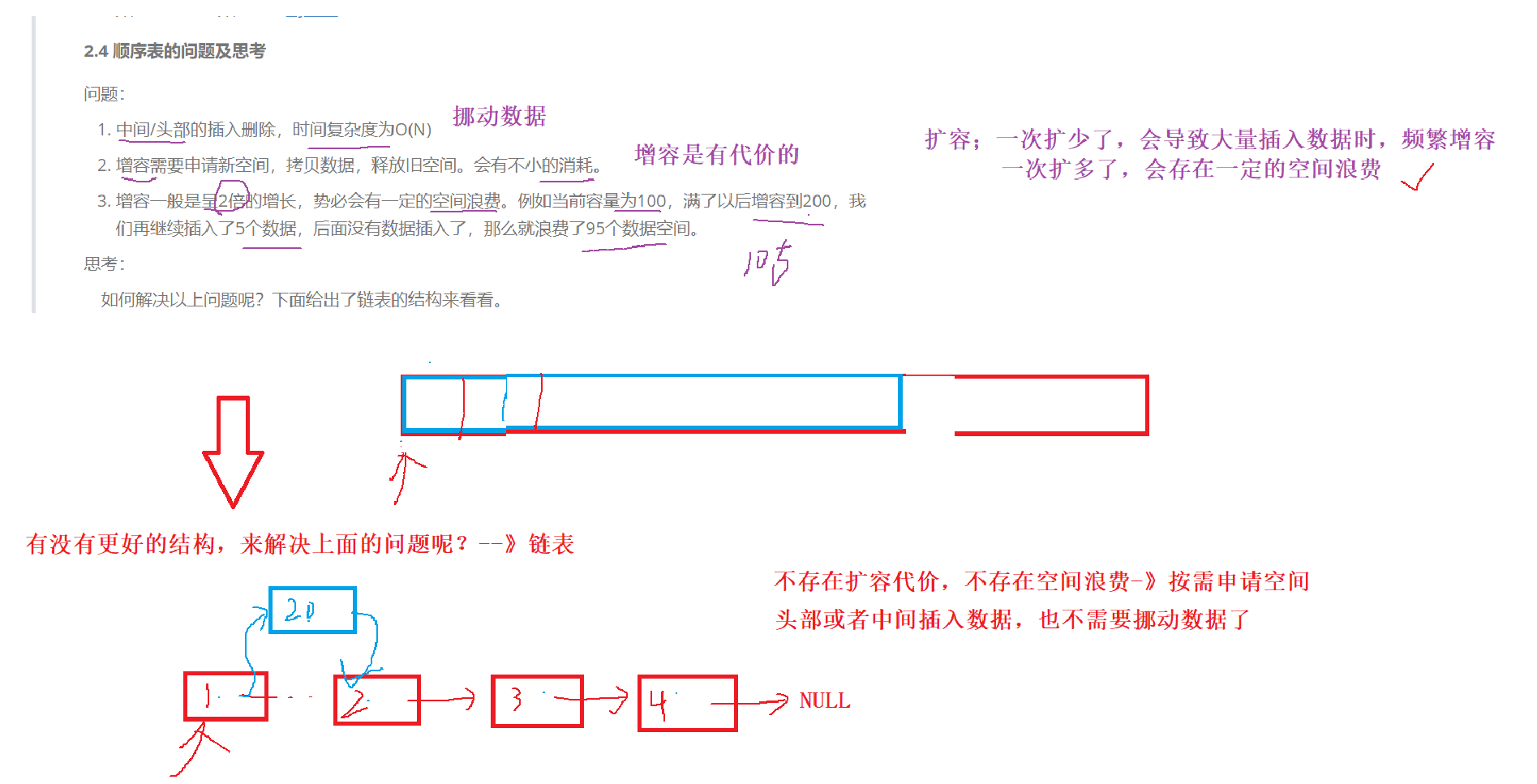
链表组合
- 单向双向
- 带头不带头
- 循环非循环
最多有8种
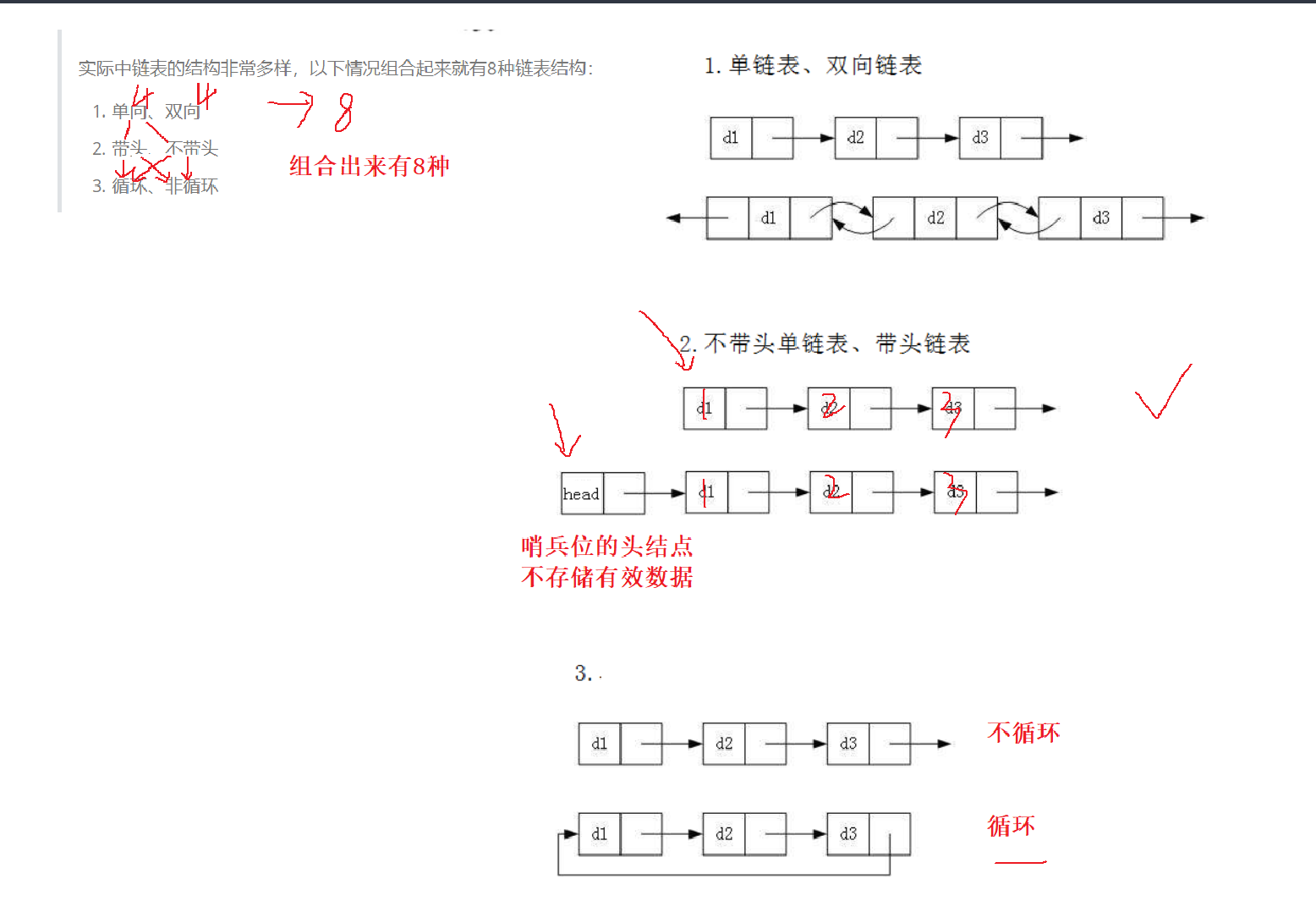
实现
定义
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDataType data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
创建节点
//创建结点
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x) {SLTNode* node = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//开辟失败的情况if (node == NULL) {printf("BuySLTNode Failed");return;}node->data = x;node->next = NULL;return node;
}
打印
void SListPrint(SLTNode* plist) {SLTNode* cur = plist;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data); cur = cur->next;//cur->next里面存的就是下一个结点的地址}printf("NULL\n");
}
查找
//单链表查找
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* plist, SLTDataType x) {SLTNode* cur = plist;//不要轻易zplist//while(cur != NULL)while (cur) {if (cur->data == x) {return cur;//查找兼具修改的作用}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
尾删
多个节点时,删除尾节点需要把prev->next置为NULL
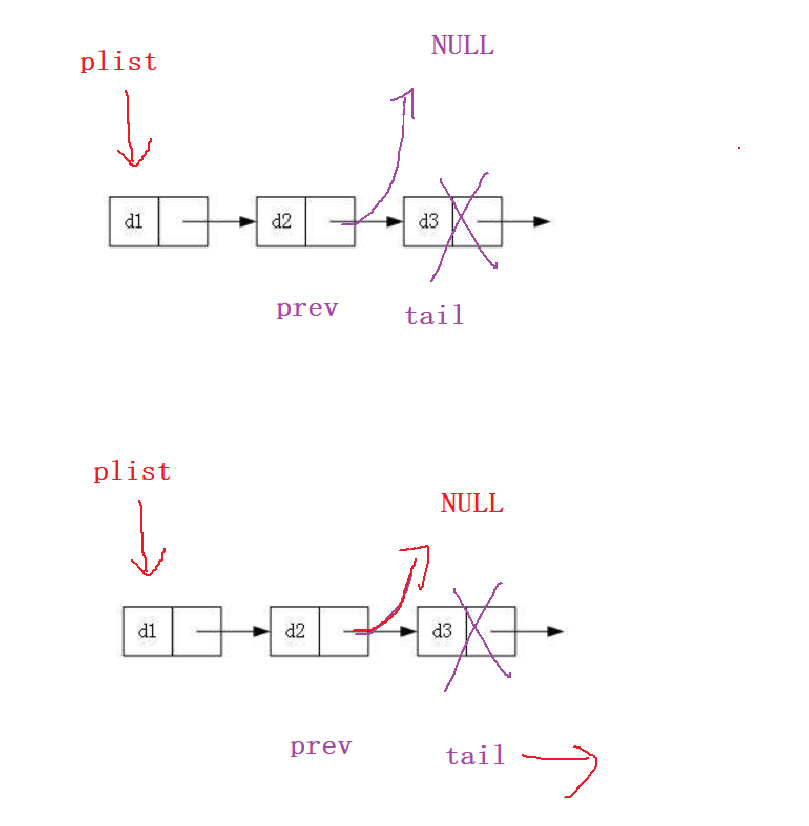
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pplist) {//1.没有节点//2.一个节点//3.多个节点if (*pplist == NULL) {return;}else if ((*pplist)->next == NULL) {free(*pplist);*pplist = NULL;//这样就达到了删除一个节点的目的}//多个节点else {SLTNode* prev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pplist;while (tail->next != NULL) {prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;//尾删时要将最后一个结点的上一个结点的next置为NULL才行}
}
单个节点或NULL时需单独考虑

头删
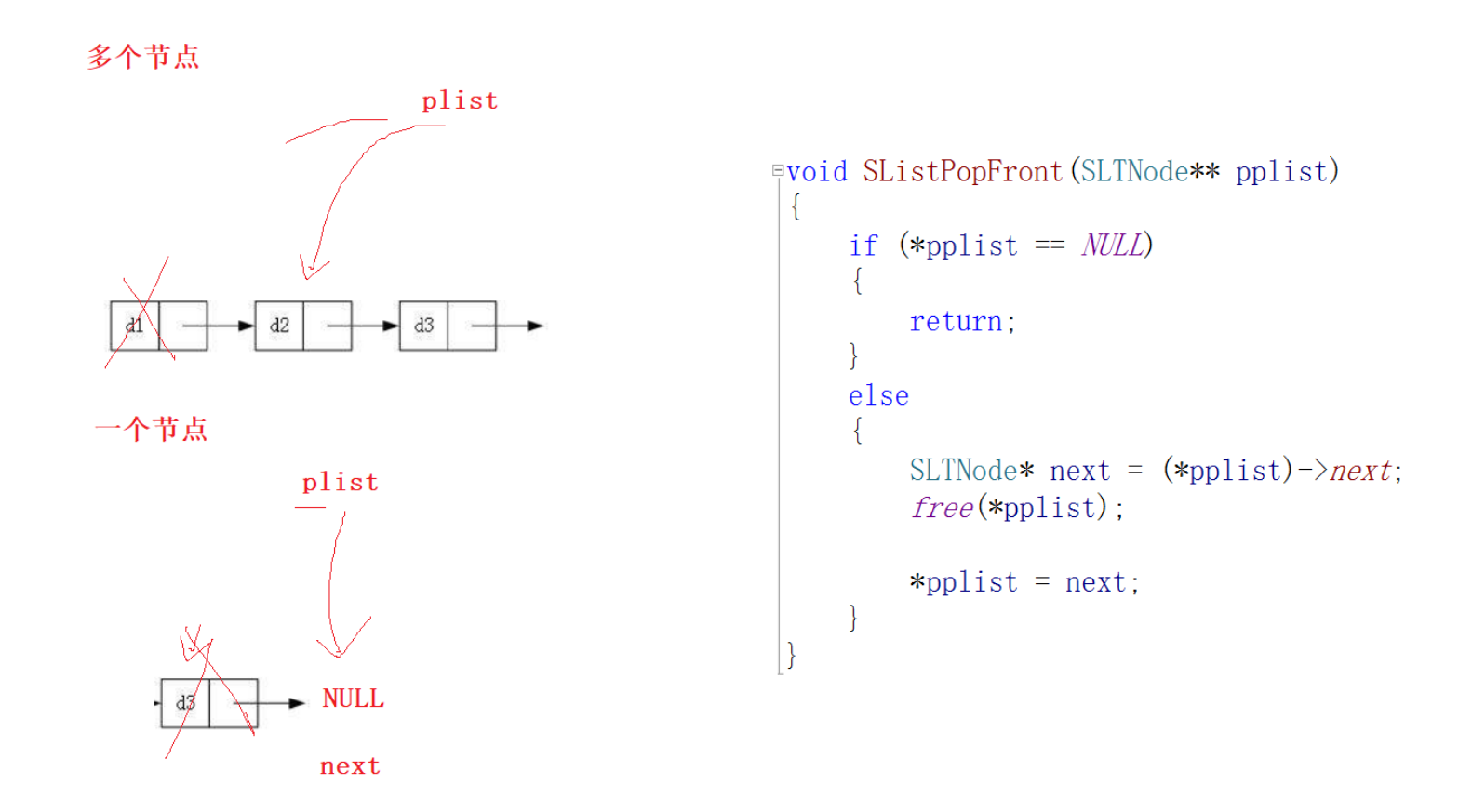
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pplist) {//1.没有节点//2.一个节点//3.多个节点if (*pplist == NULL) {return;}else {//恰好适用一个节点和多个节点的情况//保存plist->next,如果直接free plist就找不到后面的空间了SLTNode* next = (*pplist)->next;free(*pplist);*pplist = next;//因为要修改plist必须传址调用}
}
头插
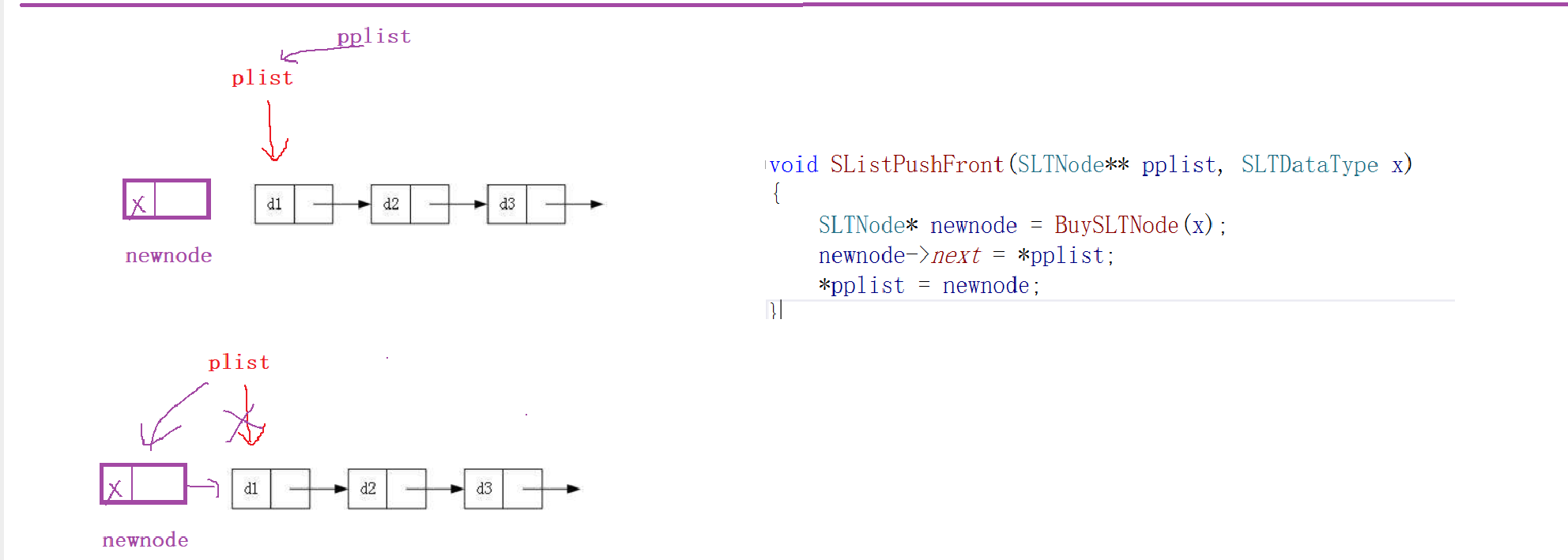
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pplist, SLTDataType x) {//即使传进来的是NULL也能解决SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);newnode->next = *pplist;//*pplist 其实就是plist*pplist = newnode;
}
尾插
//传址调用才行,二级指针
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pplist, SLTDataType x) {SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);//考虑空链表的情况if (*pplist == NULL) {*pplist = newnode;//传进来空链表,要修改plist必须传址调用}else {//找尾插地址SLTNode* tail = *pplist;//不能直接修改plist,plist一改就找不到链表了while (tail->next != NULL) {tail = tail->next;}//出来时tail->next 指向的是NULLtail->next = newnode;}
}
带上头节点可以不用传址调用,因为不需要修改plist
pos后插入
//在pos后面插入
void SListInserAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);//注意顺序不要反了newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}//反了需要将pos->nxet提前保存起来
//在pos后面插入
/* void SListInserAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);SLTNode* next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;newnode->next = next;
}
*/
pos前插入
//在pos之前插入
void SListInserBefore(SLTNode** pplist, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);//如果pos在第一个呢?if (pos == *pplist) {//相当于头插newnode->next = pos;*pplist = newnode;}else {SLTNode* prev = NULL;SLTNode* cur = *pplist;while (cur != pos) {prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}//避免prev为空if (prev == NULL) {return;}prev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}
在一个无头(不告诉头指针)单链表的某一个节点前面插入一个值x,怎么插?
后插,然后交换data

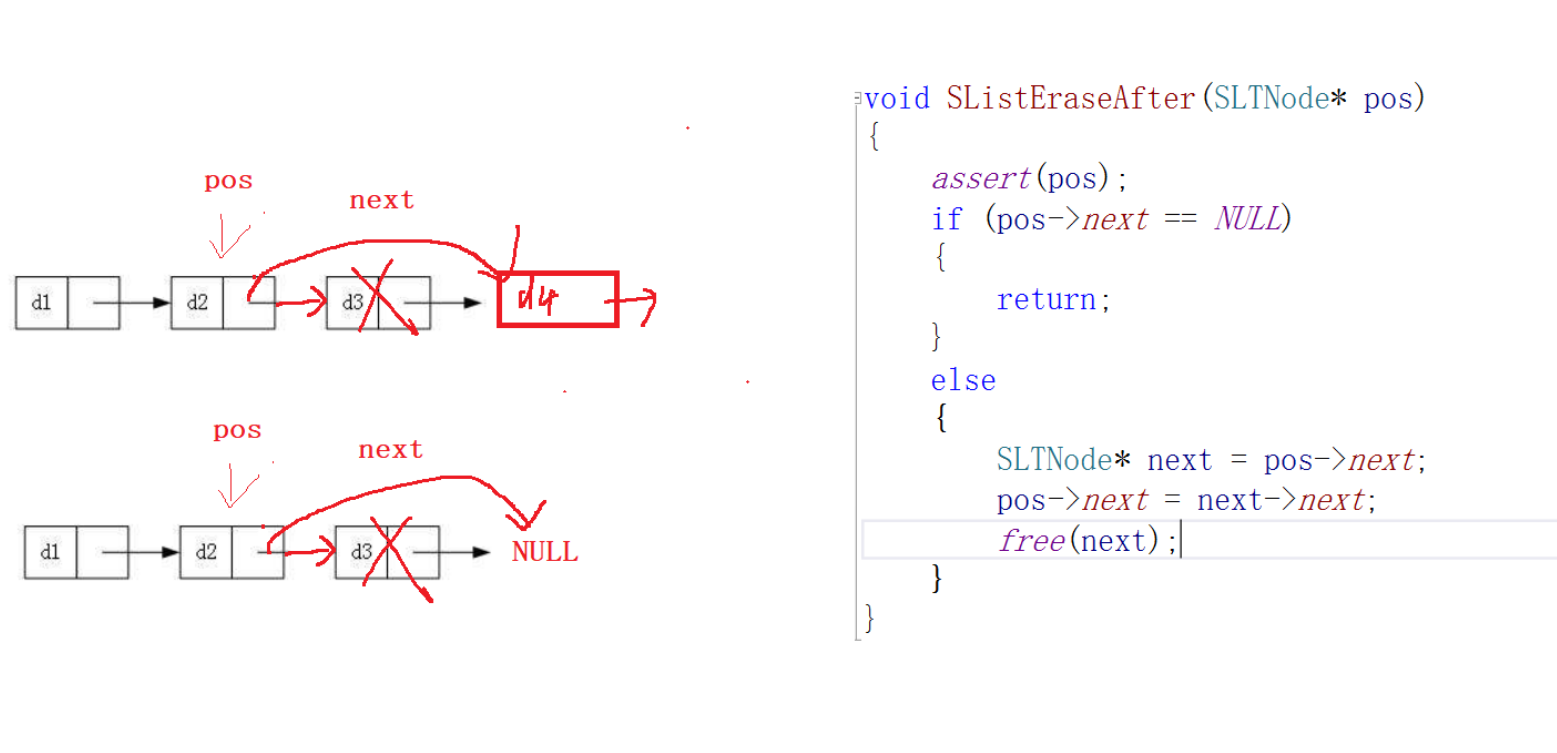
pos后擦除
//在pos之后擦除
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos) {assert(pos);//pos之后无节点if (pos->next == NULL) {return;}else {SLTNode* next = pos->next;pos->next = next->next;free(next);next = NULL;}
}
双向链表
结构虽然复杂,但是操作反而简单,这是其结构优势
头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;LTDataType data;
}ListNode;ListNode* ListInit();
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void LIstInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
int ListEmpty(ListNode* phead);//空返回1,非空返回0
int ListSize(ListNode* phead);
void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead);
初始化
ListNode* ListInit()
{ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);//指向自己,方便插入第一个节点phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}
创建节点
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{ListNode* node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (node == NULL){printf("BuyListNode Failed\n");exit(-1);}node->next = NULL;node->prev = NULL;node->data = x;return node;
}
尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);//phead->prev就是尾ListNode* tail = phead->prev;ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;
}
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{LIstInsert(phead, x);
}
//尾插相当于在phead前面插
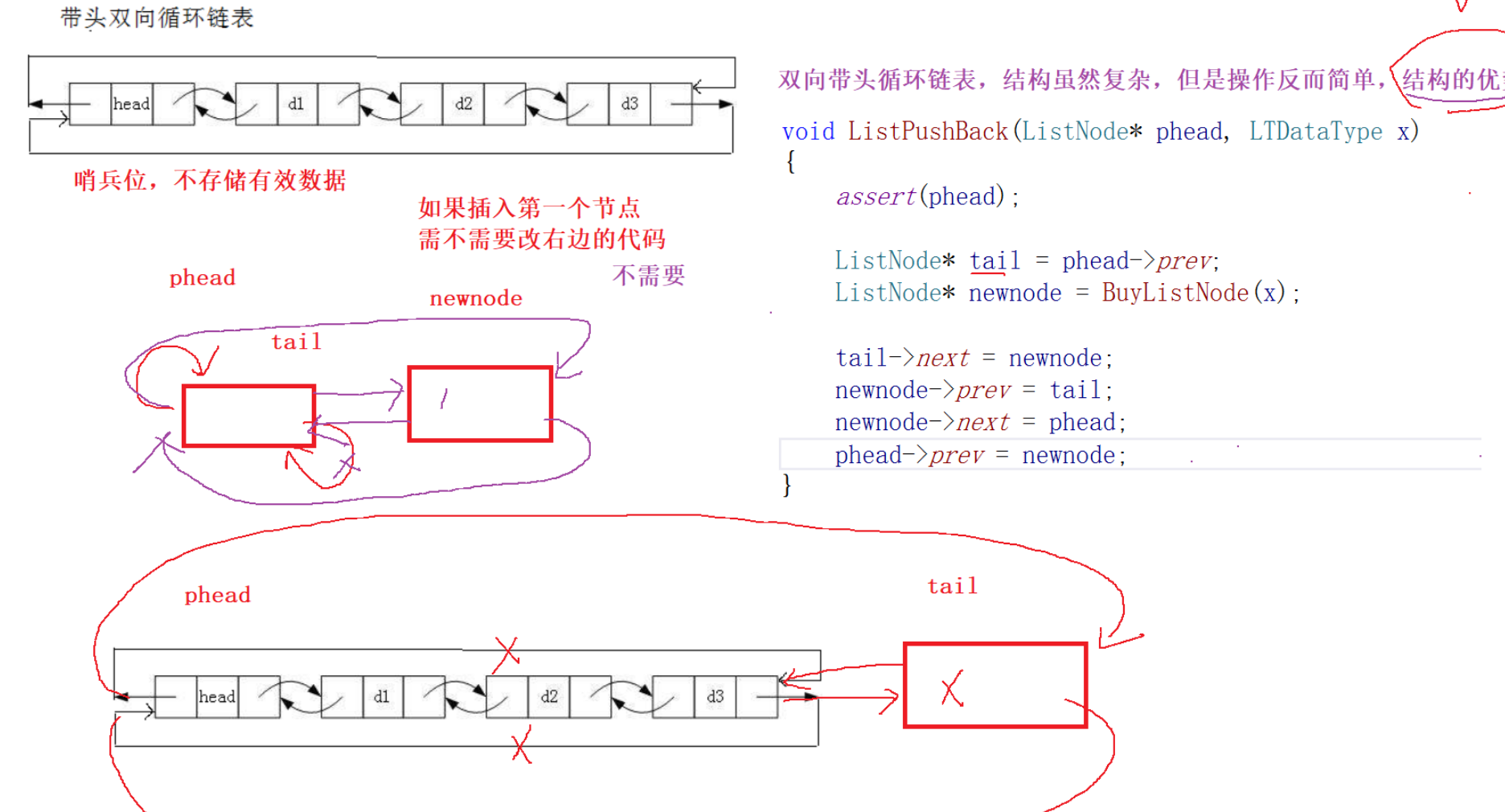
命名风格:驼峰法,PopBack
变量的第一个单词小写 toDelete
头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* first = phead->next;ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//phead newnode firstphead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode;
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{LIstInsert(phead->next, x);
}
//头插相当于在phead->next的前面去插入
尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead != phead->next);//只有一个头节点没法删ListNode* tail = phead->prev;ListNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;free(tail);tail = NULL;tailPrev->next = phead;phead->prev = tailPrev;
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{ListErase(phead->prev);
}
头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead != phead->next);//只有一个头节点没法删ListNode* toDelete = phead->next;ListNode* first = toDelete->next;free(toDelete);toDelete = NULL;//删到只剩头节点时,满足自己指向自己phead->next = first;first->prev = phead;
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{ListErase(phead->next);
}
查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
插入
void LIstInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//在pos前面插入//prev newnode posprev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;}
擦除
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;//prev pos nextprev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);
}
是否为空
int ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)//空返回1,非空返回0
{assert(phead);return phead->next == phead ? 1 : 0;
}
计算大小
int ListSize(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;int size = 0;while (cur != phead){++size;cur = cur->next;}return size;
}
摧毁
void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL;//这样不起作用的,除非传二级指针或者调用之后再手动置空//不用二级保持接口一致性
}
//s
ListDestroy(plist);
plist = NULL;
练习
OJ调试技巧
- 看描述是什么类型的错误,其次看测试用例,针对测试用例走读代码
- 如果还分析不出来,借助单个用例,进行打印相关值观察
- 拷贝到IDE上调试
27. 移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
//暴力双循环,只不过时间复杂度不符合
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){int size = numsSize;for(int i = 0; i<numsSize;i++){if(nums[i] == val){for(int j=i+1;j<size;j++){nums[j-1] = nums[j];}i--;size--;}}return size;
}
//快慢指针
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){int left = 0;for(int right = 0; right<numsSize;right++){if(nums[right] != val){nums[left] = nums[right];left++;}}return left;
}
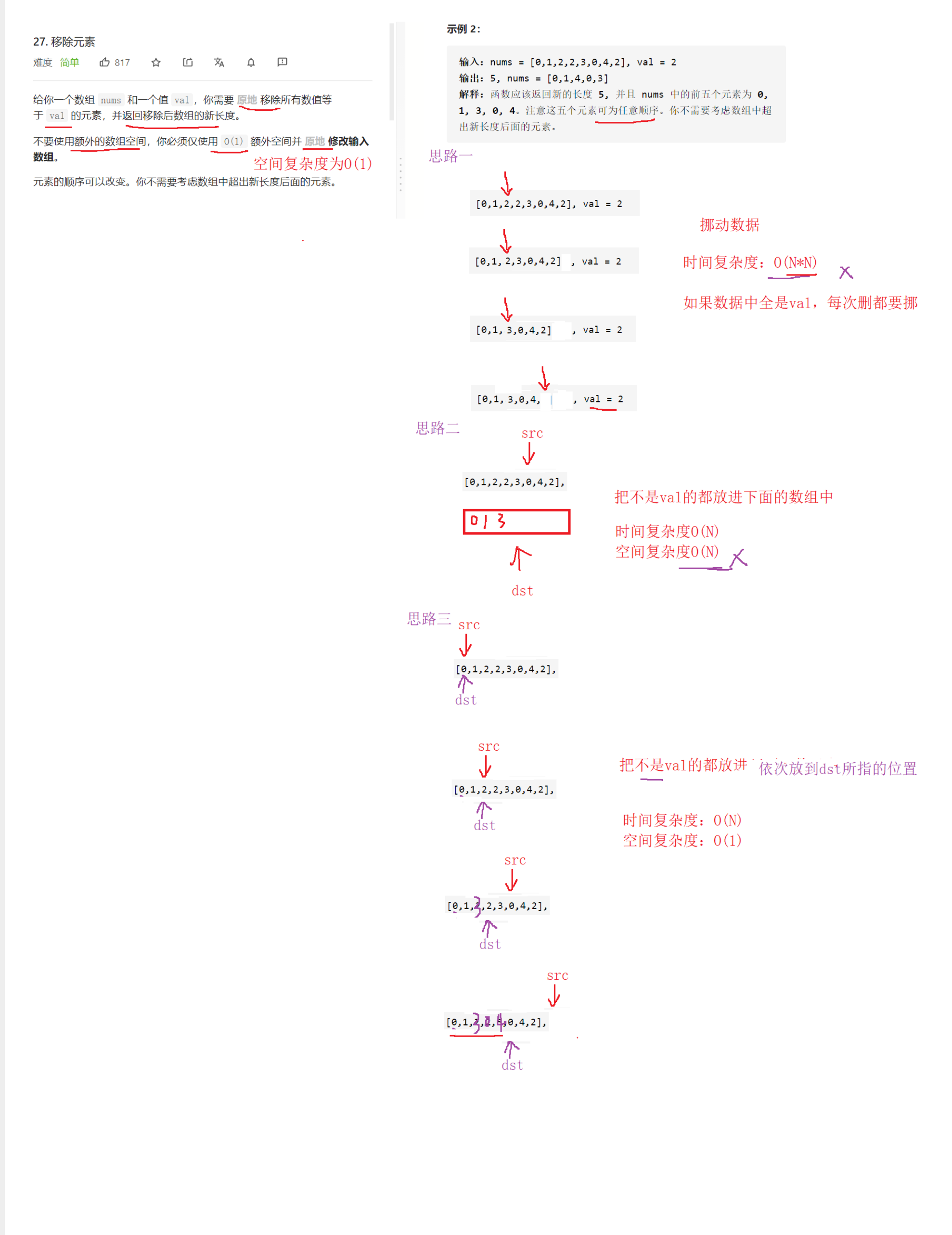
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val)
{int src = 0;int dst = 0;while(src < numsSize){if(nums[src] == val){++src;}else{nums[dst] = nums[src];++src;++dst;}}return dst;
}
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
//k
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){if(numsSize == 0){return 0;}int fast = 1;int slow = 1;while(fast<numsSize){if(nums[fast] != nums[fast-1]){nums[slow++] = nums[fast++];}else{++fast;}}return slow;}
989. 数组形式的整数加法
/*** Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().*/
int* addToArrayForm(int* num, int numSize, int k, int* returnSize){//不确定加完的数有多大//考虑到有进位,要多开1位,最多进1位int kSize = 0;int nums = k;while(nums){++kSize;nums /= 10;}int len = kSize > numSize ? kSize+1:numSize+1;int* retArr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*len);//倒着取数组的值并于k的每一位逐个相加int Ai = numSize-1;int ki = 0;int next = 0;//进位int reti = 0;while(Ai >= 0 || ki <kSize){int aVal = 0;if(Ai >= 0){//考虑到数组比K短aVal = num[Ai--];}int kVal = k%10;k /= 10;ki++; int ret = aVal + kVal +next;if(ret >= 10){next = 1;ret -= 10;}else{next = 0;}//正着放不确定从最后一位开始放还是倒数第二位开始放//倒着放到数组,再把数组倒置回来retArr[reti++] = ret;}if(next == 1){retArr[reti++] = 1;//还有一个进位没放要放进去}//逆置int begin = 0;int end = reti - 1;while(begin<end){int tmp = retArr[begin];retArr[begin] = retArr[end];retArr[end] = tmp;begin++;end--;}*returnSize = reti;return retArr;
}
88. 合并两个有序数组
思路一:
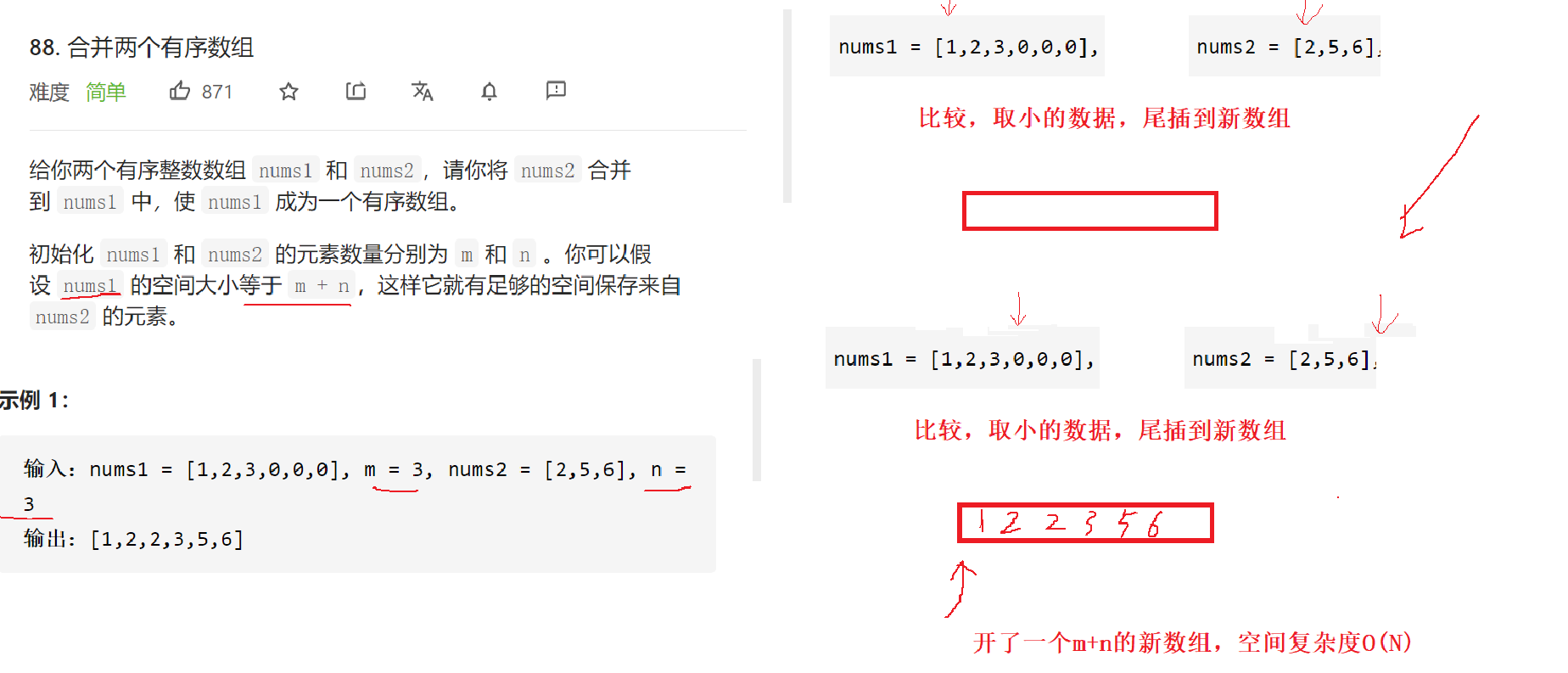
题目给的nums1空间大小是m+n,后面的n个位置是空的,就是为了放nums2的元素
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){int p1 = 0;int p2 = 0;int sorted[m+n];while(p1<m || p2<n){if(p1 == m){sorted[p1+p2-1] = nums2[p2++];}else if(p2 == n){sorted[p1+p2-1] = nums1[p1++];}else if(nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]){sorted[p1+p2-1] = nums1[p1++];}else{sorted[p1+p2-1] = nums2[p2++];}}for(int i = 0;i < m+n;i++){nums1[i] = sorted[i];}
}
//额外开辟数组,空间复杂度是O(N)
思路二:大的从后往前放,不需额外开辟数组
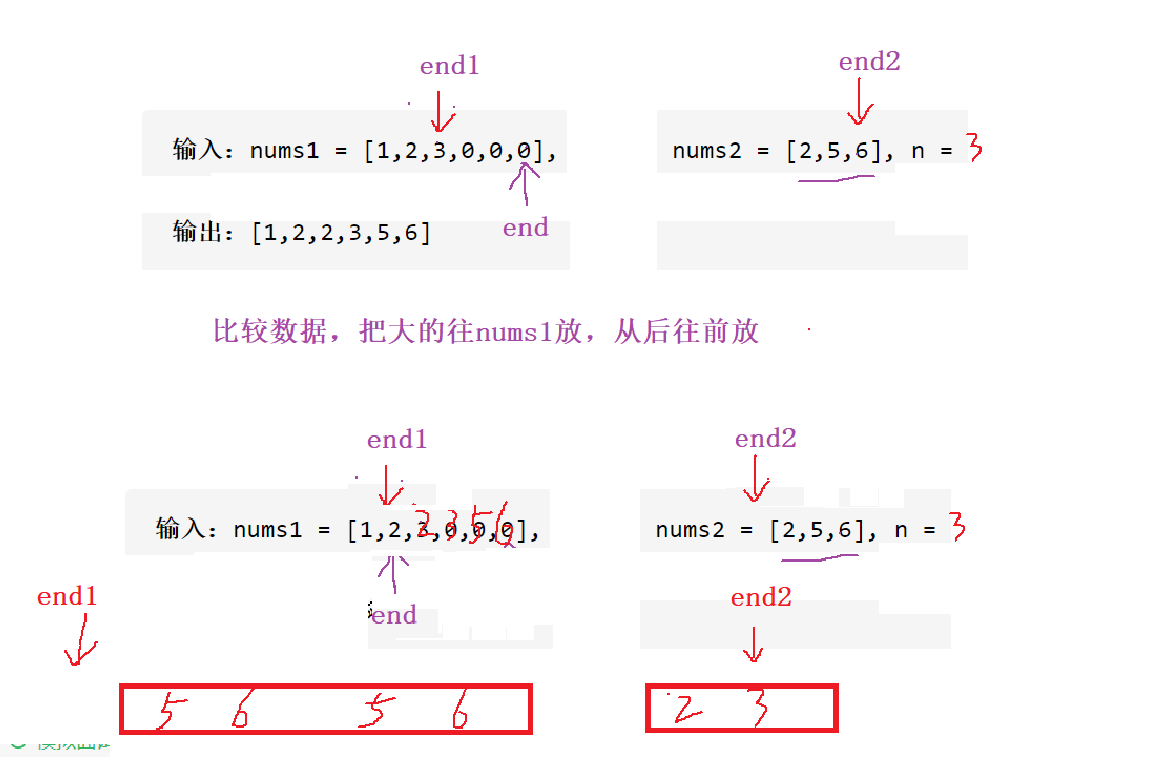
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){int end1 = m-1;int end2 = n-1;int end = m+n-1;while(end1>=0 && end2>=0){if(nums1[end1]>nums2[end2]){nums1[end--] = nums1[end1--];}else{nums1[end--] = nums2[end2--];}}//end2结束了,end1还有数据,无需挪动//end1先结束,需要把end2的数据放到nums1里面while(end2>=0){nums1[end--] = nums2[end2--];}
}
//时间复杂度O(m+n) 空间复杂度O(1)
另一种写法
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){int end1 = m-1;int end2 = n-1;int end = m+n-1;while(end1>=0 || end2>=0){if(-1 == end1){//end1为-1说明nums1里面没有元素nums1[end--] = nums2[end2--];}else if(-1 == end2){//nums2没有元素nums1[end--] = nums1[end1--];}else if(nums1[end1]>=nums2[end2]){//谁大谁就放进nums1[end--] = nums1[end1--];}else if(nums1[end1] <= nums2[end2]){nums1[end--] = nums2[end2--];}}
}
189. 轮转数组
给你一个数组,将数组中的元素向右轮转
k个位置,其中k是非负数。
思路一:两层循环
void rotate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){int end = numsSize-1;int temp = 0;for(int i=0; i<k; i++){temp = nums[end];for(int j=end; j>0; j--){nums[j] = nums[j-1];}nums[0] = temp;}
}
//时间复杂度O(N*K) 空间复杂度O(1)
思路二:以空间换时间
void rotate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){int newArr[numsSize];for(int i=0; i<numsSize; i++){newArr[(i+k)%numsSize] = nums[i];}for(int i=0; i<numsSize; i++){nums[i] = newArr[i];}
}
//时间复杂度O(N) 空间复杂度O(N)
思路三 3次逆置
//对原数组后k个数逆置
//对原数组前n-k个数逆置
//对原数组整体逆置
void Reverse(int* arr, int left, int right){while(left<right){int tmp = arr[right];arr[right] = arr[left];arr[left] = tmp;left++;right--;}
}void rotate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){if(k>numsSize){k %= numsSize;}Reverse(nums, 0, numsSize-k-1);Reverse(nums, numsSize-k, numsSize-1);Reverse(nums, 0, numsSize-1);
}
//空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(N)
203. 移除链表元素
考虑清楚多种情况再写代码,
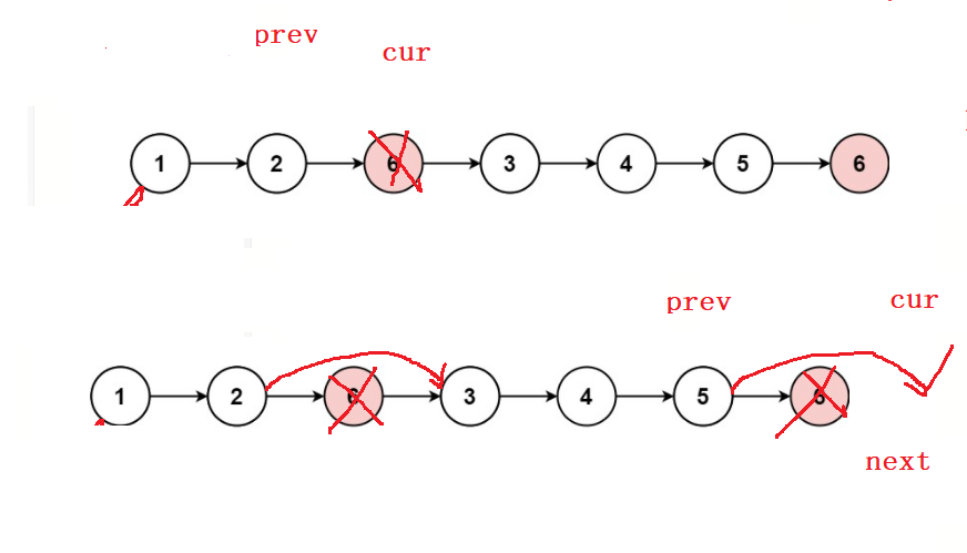
如果第一个值就是val需要单独考虑,prev为NULL的情况
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* prev = NULL;while(cur != NULL){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;if(cur->val == val){if(prev == NULL){//第一个值就是val的情况free(cur);head = next;cur = next;} else{prev->next = next;free(cur);cur = next;}}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}return head;//返回头指针,就不需要传二级指针修改头指针
}
带哨兵位的
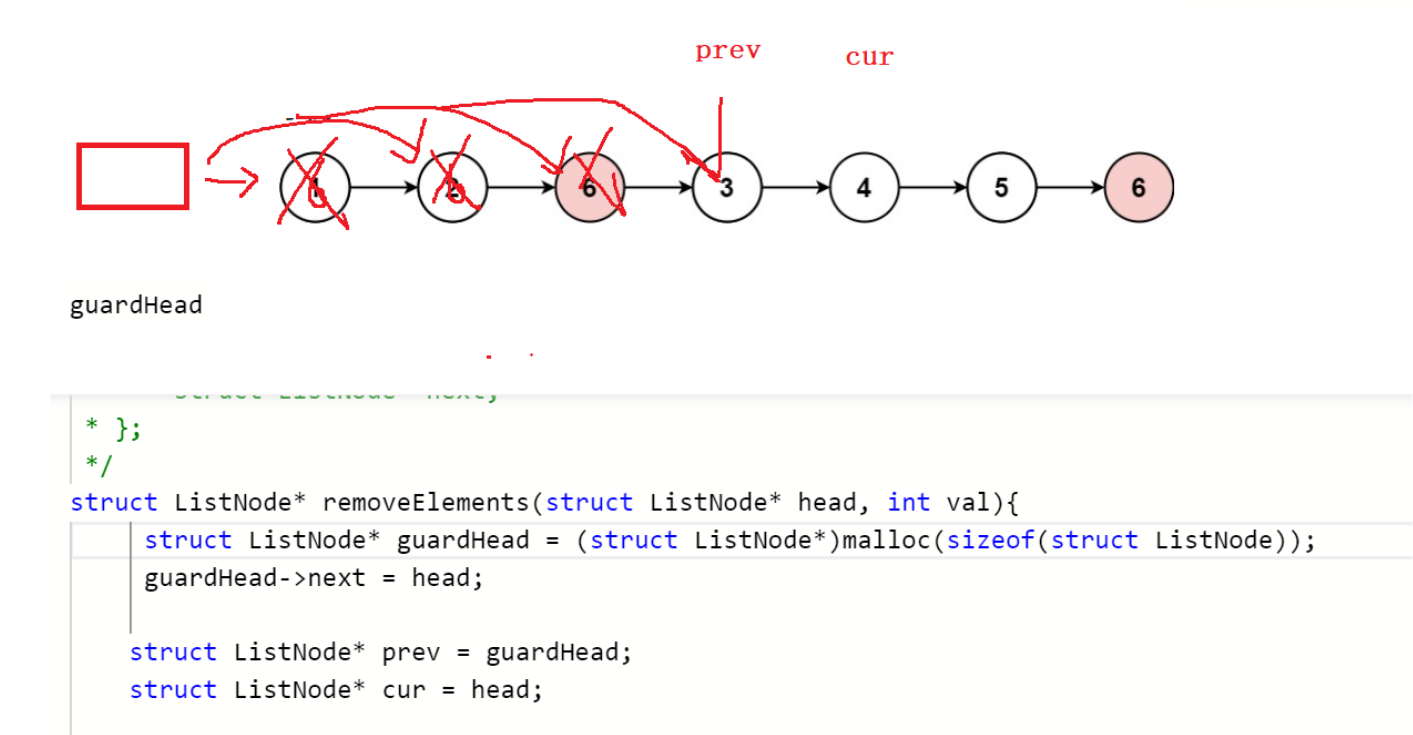
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){struct ListNode* guardHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));guardHead->next = head;struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* prev = guardHead;while(cur != NULL){if(cur->val == val){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;prev->next = next;free(cur);cur = next;}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}head = guardHead->next;free(guardHead);guardHead = NULL;return head;
}
206. 反转链表
思路一: 三指针翻转

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){//空链表和只有一个节点的情况return head;}struct ListNode* n1 = NULL;struct ListNode* n2 = head;struct ListNode* n3 = head->next;while(n2 != NULL){//翻转n2->next = n1;//迭代n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if(n3 != NULL){//n2指向最后一个元素时,n3指向的是NULL,不能解引用NULLn3 = n3->next;}}head = n1;return head;
}
思路二:头插法

struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){//包含了空链表和只有一个节点的情况//头插法struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;while(cur != NULL){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newHead;newHead = cur;cur = next;}head = newHead;return head;
}
思路三:递归
在稿纸上画图分析就行,递归核心就是假设后面n-1个已经翻转了
//1->2<-3<-4<-5
//而且第一个要指向NULL
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){//递归if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){return head;}struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* next = cur->next;struct ListNode* newHead = reverseList(next);next->next = cur;cur->next = NULL;return newHead;
}
876. 链表的中间结点
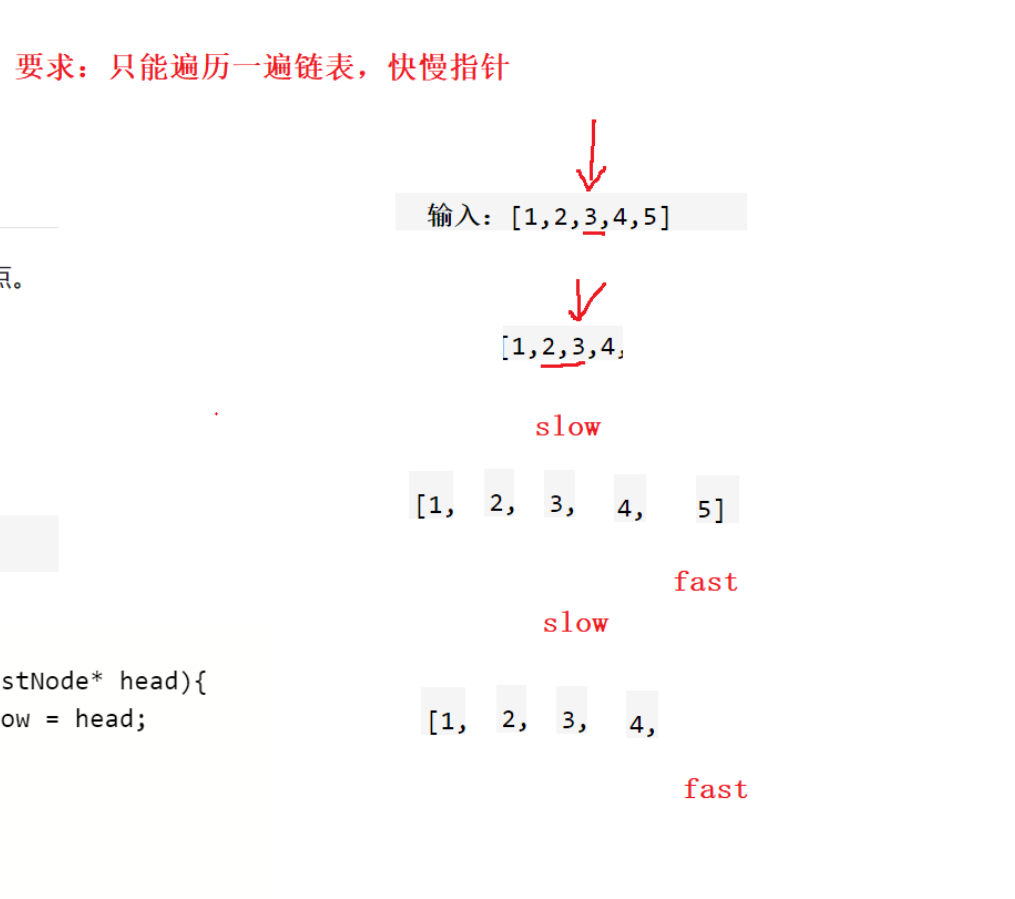
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;//快慢指针,快指针一次走2步while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
思路一:暴力循环
struct ListNode* getKthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int k){//求链表长度int len = 0;struct ListNode* cur = head;while(cur != NULL){cur = cur->next;len++;}//倒数第k个就是正数第len-k次访问for(int i=0; i<len-k; i++){head = head->next;}return head;
}
思路二:快慢指针
struct ListNode* getKthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int k){//快慢指针struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;//fast先走k步while(k--){//考虑空链表以及k>链表长度的问题if(fast == NULL){return NULL;}fast = fast->next;}//快慢同时走while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow;
}
牛客的OJ很恶心,很难调
1.自测常规情况,可以过
2.打印一些标记值,不显示输出标记值.比如:段错误
3.思考极端情况场景测试用例(链表为空,k大于链表长度,k为负数等等)力扣环境很舒服,错了会报测试用例,根据测试用例去改就行
21. 合并两个有序链表
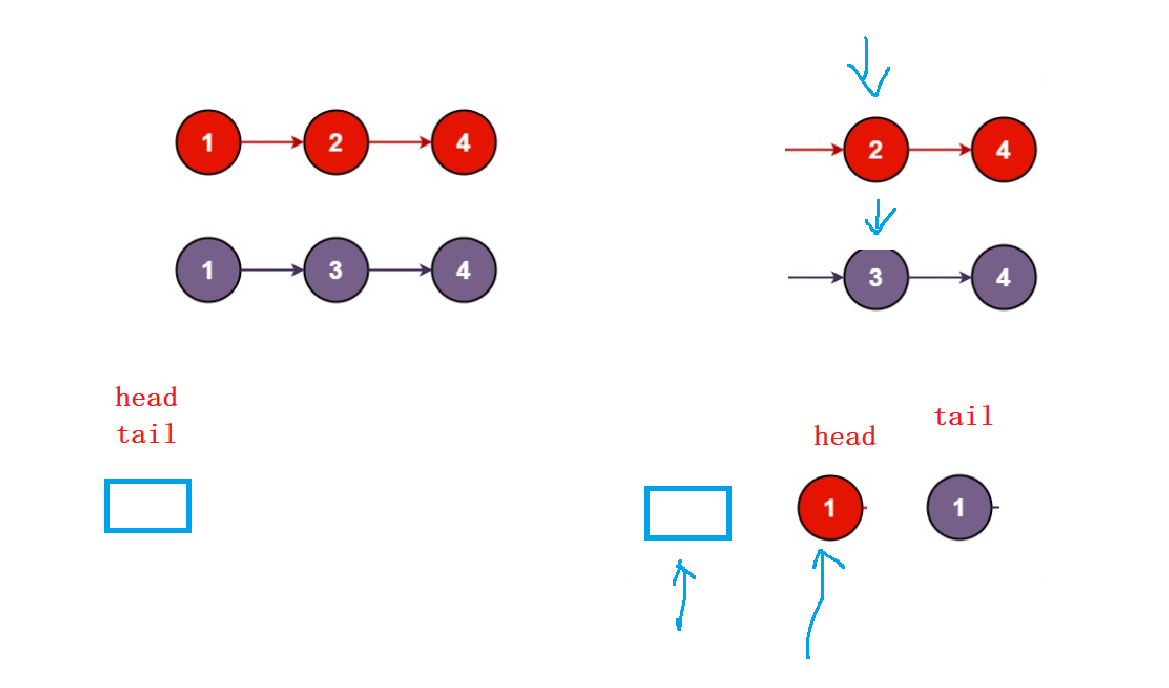
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){struct ListNode* head = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;if(list1 == NULL && list2 != NULL){return list2;}if(list2 == NULL && list1 != NULL){return list1;}if(list1 == NULL && list2 == NULL){return NULL;}//先取个小的去做头,方便后面尾插if(list1->val < list2->val){head = tail = list1;list1 = list1->next;}else{head = tail = list2;list2 = list2->next;}while(list1 && list2){if(list1->val < list2->val){tail->next = list1;list1 = list1->next;tail = tail->next;}else{tail->next = list2;list2 = list2->next;tail = tail->next;}}//l1或者l2为空就出来了if(list1 == NULL){tail->next = list2;}else if(list2 == NULL){tail->next = list1;}return head;
}
if(list1 == NULL && list2 != NULL){return list2;}if(list2 == NULL && list1 != NULL){return list1;}if(list1 == NULL && list2 == NULL){return NULL;}
//可以写得简洁一点
if(list1 == NULL){return list2;}if(list2 == NULL){return list1;}
思路二:哨兵位
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){struct ListNode* head = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;//带哨兵位的写法head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));tail->next = NULL;while(list1 && list2){if(list1->val < list2->val){tail->next = list1;list1 = list1->next;tail = tail->next;}else{tail->next = list2;list2 = list2->next;tail = tail->next;}}//l1或者l2为空就出来了if(list1){tail->next = list1;}else if(list2){tail->next = list2;}//开辟的哨兵位用完要释放struct ListNode* node = head;head = head->next;free(node);node = NULL;return head;
}
链表分割
现有一链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {//借助哨兵位struct ListNode* lessHead = NULL;struct ListNode* lessTail = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterHead = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterTail = NULL;//开辟哨兵位lessHead = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));lessTail->next = NULL;greaterTail->next = NULL;//把小于x的插到一个链表,大于x的插到一个链表while(pHead != NULL){if(pHead->val < x){lessTail->next = pHead;pHead = pHead->next;lessTail = lessTail->next;}else{greaterTail->next = pHead;pHead = pHead->next;greaterTail = greaterTail->next;}}//链接2个链表lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;//防止成环,要让最后的那个值指向NULLgreaterTail->next = NULL;pHead = lessHead->next;//释放空间free(lessHead);lessHead = NULL;free(greaterHead);greaterHead = NULL;return pHead;}
};
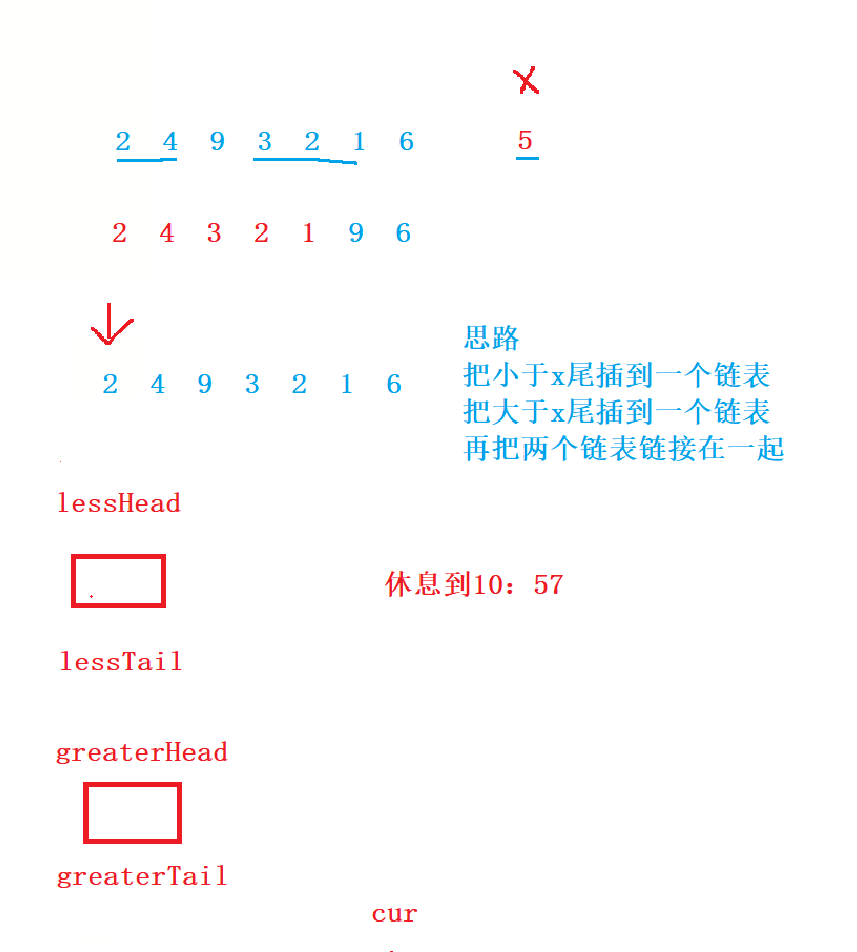
牛客的调试太难了,只能靠猜测极端情况
1.空链表过得去
2.全大于/全小于x也过得去
3.有可能成环成环了就陷入死循环,牛客就会报内存受限,其实不是真的内存不足,而是要考虑死循环的情况
VS下调试链表的题目
//在VS下调试链表的题目
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {//借助哨兵位struct ListNode* lessHead = NULL;struct ListNode* lessTail = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterHead = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterTail = NULL;//开辟哨兵位lessHead = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));if (lessTail == NULL){return 0;}if (lessHead == NULL){return 0;}if (greaterHead == NULL){return 0;}if (greaterTail == NULL){return 0;}lessTail->next = NULL;greaterTail->next = NULL;//把小于x的插到一个链表,大于x的插到一个链表while (pHead != NULL) {if (pHead->val < x) {lessTail->next = pHead;pHead = pHead->next;lessTail = lessTail->next;}else {greaterTail->next = pHead;pHead = pHead->next;greaterTail = greaterTail->next;}}//链接2个链表lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;//防止成环,要让最后的那个值指向NULLgreaterTail->next = NULL;pHead = lessHead->next;//释放空间free(lessHead);lessHead = NULL;free(greaterHead);greaterHead = NULL;return pHead;}
};void PrintList(struct ListNode* cur)
{while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}int main()
{struct ListNode* n1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n3 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n4 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n5 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n6 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n7 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* n8 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));if (n1 && n2 && n3 && n4 && n5 && n6 && n7 && n8)//防止开辟失败返回NULL程序崩溃{n1->val = 2;n2->val = 4;n3->val = 9;n4->val = 3;n5->val = 2;n6->val = 1;n7->val = 6;n8->val = 3;n1->next = n2;n2->next = n3;n3->next = n4;n4->next = n5;n5->next = n6;n6->next = n7;n7->next = n8;n8->next = NULL;}struct ListNode* head = Partition().partition(n1, 5);PrintList(head);return 0;
}
链表的回文结构
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。 给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
思路一:开一个int[900]的数组,用数组判断,虽然也能通过牛客的判断,但实际不符合空间复杂度O(1)的要求
思路二: 1.先找到中间节点 2.翻转后半部分链表 3.一一比较
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public://先找到中间节点struct ListNode* midNode(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}//翻转后半部分struct ListNode* ReverseList(struct ListNode* head){//头插法struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while(cur != NULL){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newHead;newHead = cur;cur = next;}head = newHead;return head;//再一一比较}bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {struct ListNode* mid = midNode(A);struct ListNode* rHead = ReverseList(A);while(A && rHead){if(A->val == rHead->val){A = A->next;rHead = rHead->next;}else{return false;}}return true;}
};

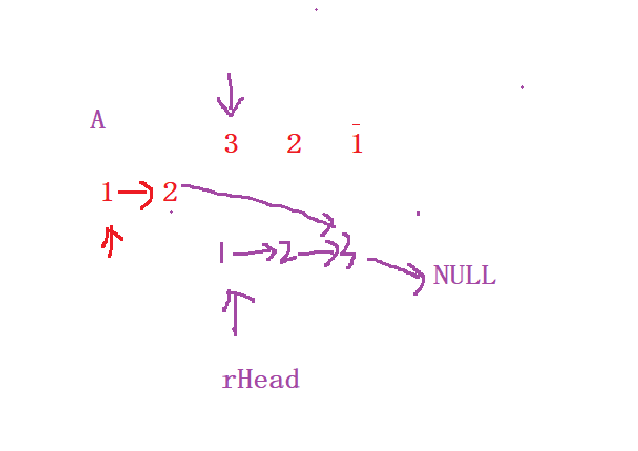
奇数个是怎么过的呢?奇数个理论上不是应该让中间的前一个指向NULL才行吗?
其实是虽然后半部分逆置了,但2还是指向3的,3的next为NULL
160. 相交链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{//考虑空链表if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}//先算2个链表长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;while(curA->next != NULL){curA = curA->next;lenA++;}//各自都少计算一步,相减没影响,这样方便后面判断是否相交while(curB->next != NULL){curB = curB->next;lenB++;}//不相交,此时curA->nxet == NULLif(curA != curB){return NULL;}//注意要把curA curB的位置调整回到一开始curA = headA;curB = headB;//让长的链表先把多出来的长度走了,再一起走if(lenA > lenB){int len = lenA - lenB;while(len--){curA = curA->next;}}if(lenA < lenB){int len = lenB - lenA;while(len--){curB = curB->next;}}//一起走,看谁的指针相同while(curA != curB){curA = curA->next;curB = curB->next;}return curA;
}
另一种写法,长度计算用abs
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{//考虑空链表if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}//先算2个链表长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;while(curA->next != NULL){curA = curA->next;lenA++;}//各自都少计算一步,相减没影响,这样方便后面判断是否相交while(curB->next != NULL){curB = curB->next;lenB++;}//不相交,此时curA->nxet == NULLif(curA != curB){return NULL;}//另一种写法struct ListNode* longList = headA;struct ListNode* shortList = headB;if(lenB > lenA){longList = headB;shortList = headA;}int gap = abs(lenB - lenA);while(gap--){longList = longList->next;}while(longList != shortList){longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}return longList;
}
不先判断是否相交也行,如果不相交最后返回的也是NULL
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{//考虑空链表if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}//先算2个链表长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;while(curA != NULL){curA = curA->next;lenA++;}//各自都少计算一步,相减没影响,这样方便后面判断是否相交while(curB != NULL){curB = curB->next;lenB++;}//另一种写法struct ListNode* longList = headA;struct ListNode* shortList = headB;if(lenB > lenA){longList = headB;shortList = headA;}int gap = abs(lenB - lenA);while(gap--){longList = longList->next;}while(longList != shortList){longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}return longList;
}
141. 环形链表
判断是否为环形链表
//快慢指针
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){return true;}}return false;
}
延申问题:
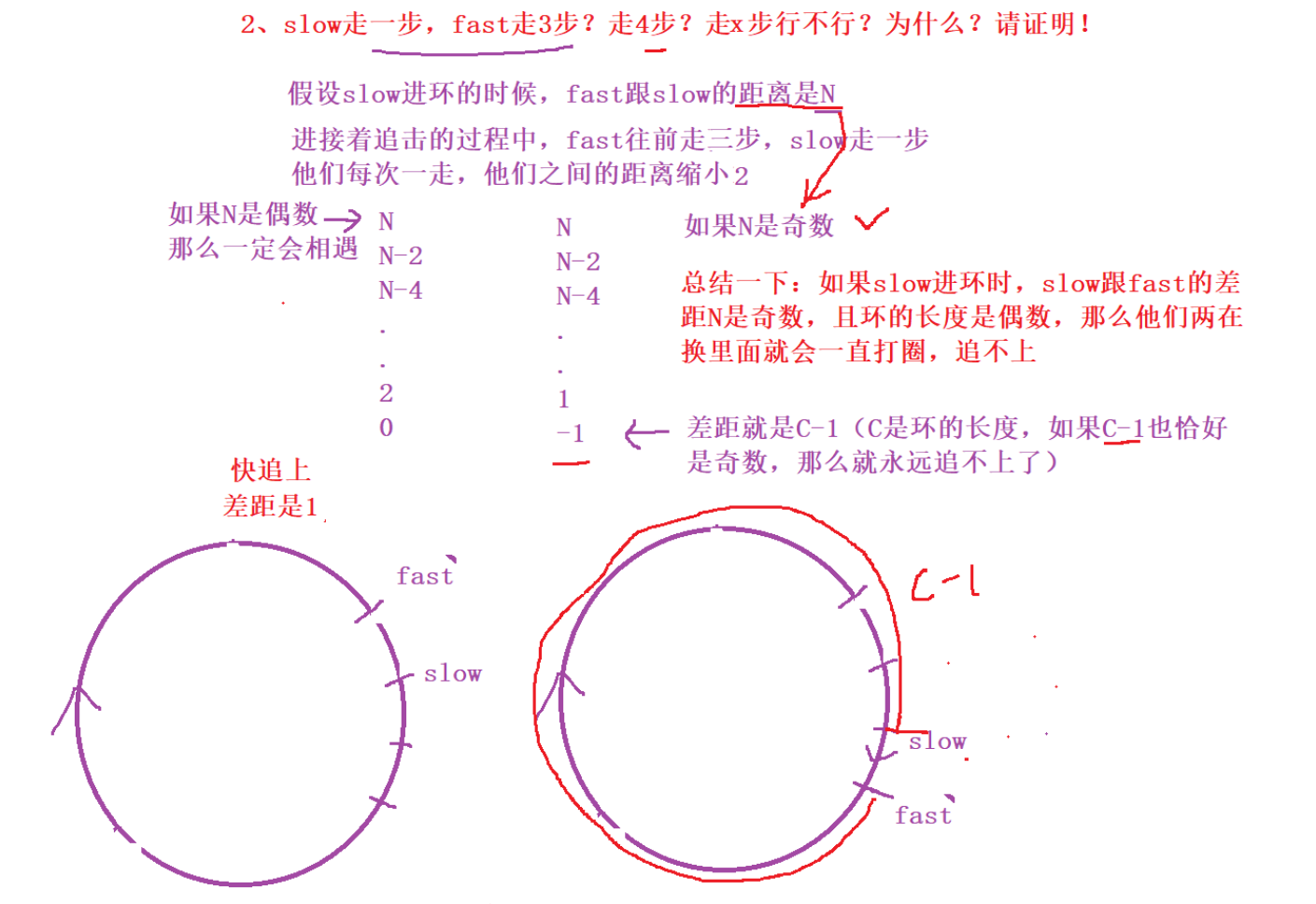
- 为什么slow走一步,fast走两步,他们一定会在环内相遇呢,会不会永远追不上?请证明
不会.假设slow进环的时候,fast跟slow的距离是N,紧接着追击的过程中,slow每走一步,fast走2步,也就是他们自己距离缩减1,迟早会追上- slow走一步,fast走3步,4步,x步呢?一定会相遇吗
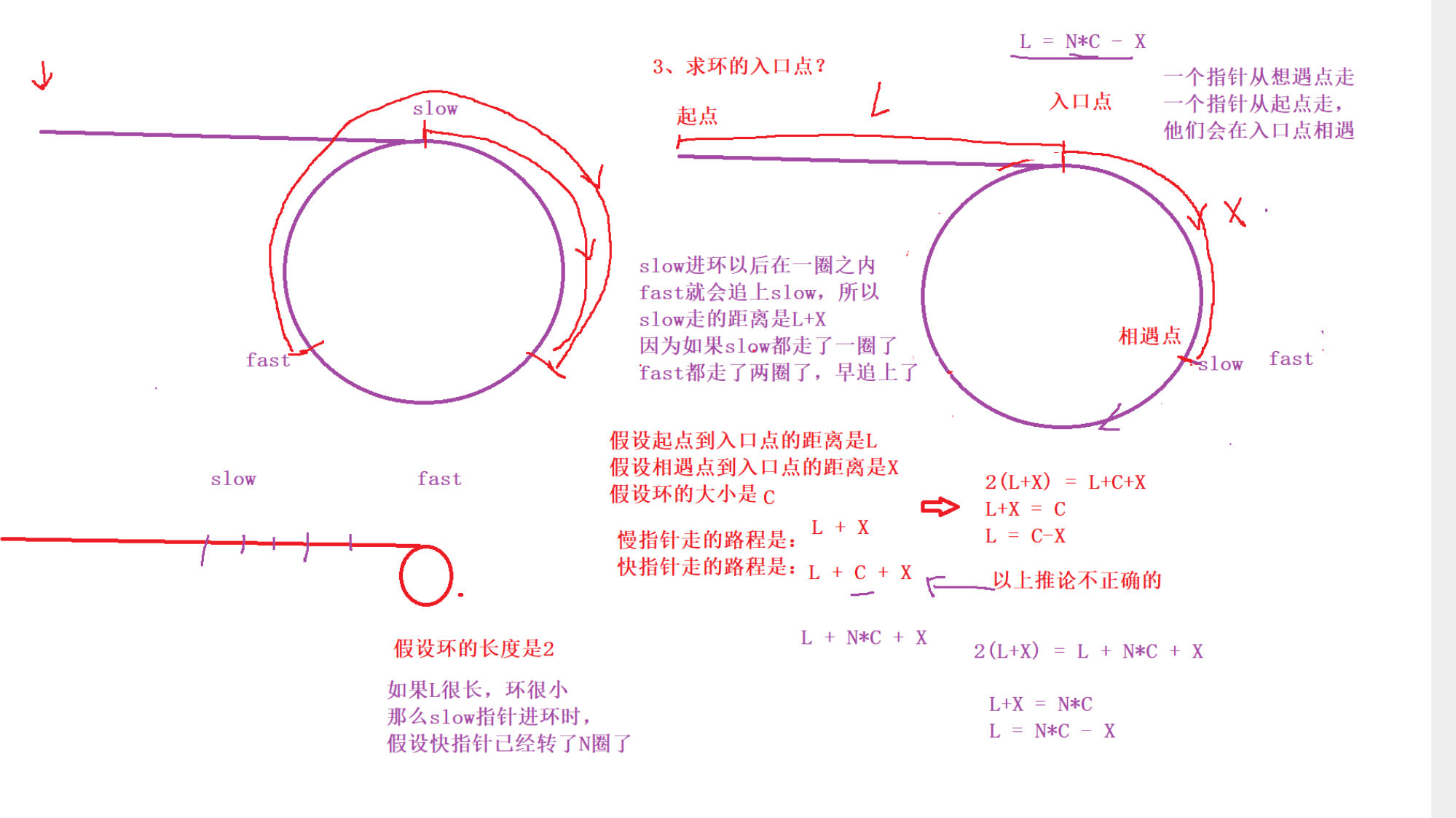
不一定.走3步时,他们每走一次,距离缩小2步,如果N是偶数就会相遇,奇数就不会相遇,变成-1时,实际相差C-1,如果C-1也是奇数,那么永远追不上- 求环的入口点
由图推出公式:2(L+X) = L+n * C+X
L是起点到入口点的距离,X是相遇点到入口点的距离,环的长度是C
L = n * C-x
也就是一个指针从head走,一个从meet走,他们会在入口相遇
142. 环形链表 II
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){//相遇//通过证明,一个指针从head走//一个从meet走,他们会在入口相遇struct ListNode* meet = fast;while(meet != head){meet = meet->next;head = head->next;}return head;}}return NULL;
}
思路二:转换成相交问题
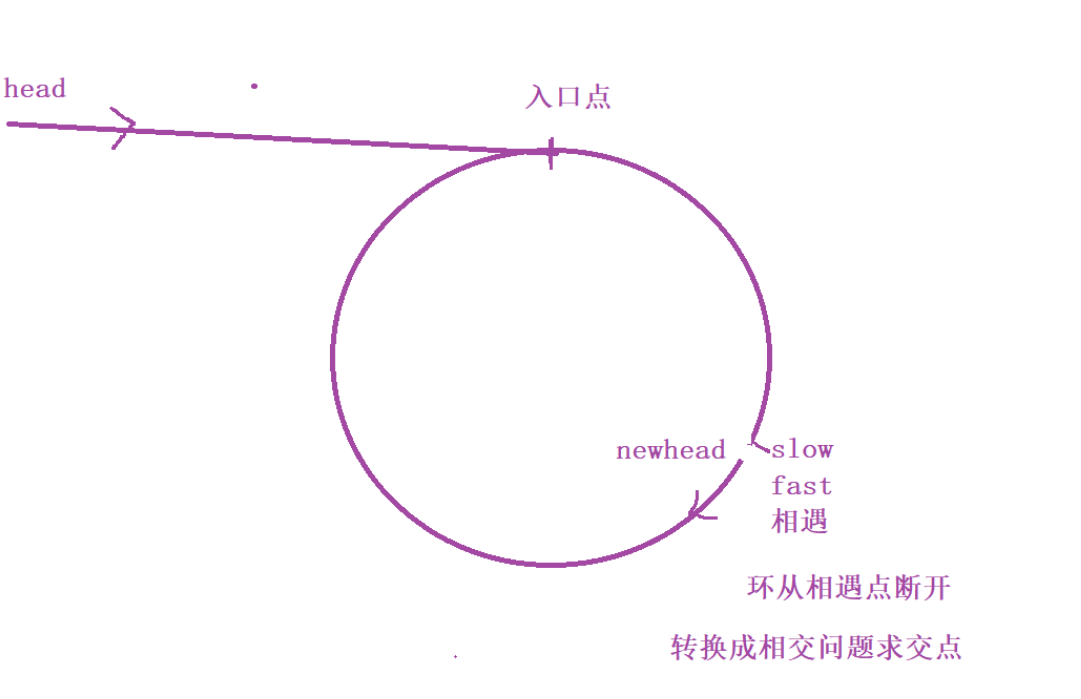
//把环折断,转化为相交问题 注意要翻转链表,且找到入口之后还有翻转回来
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){//包含了空链表和只有一个节点的情况//头插法struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;while(cur != NULL){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newHead;newHead = cur;cur = next;}head = newHead;return head;
}struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{//考虑空链表if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}//先算2个链表长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;while(curA->next != NULL){curA = curA->next;lenA++;}//各自都少计算一步,相减没影响,这样方便后面判断是否相交while(curB->next != NULL){curB = curB->next;lenB++;}//不相交,此时curA->nxet == NULLif(curA != curB){return NULL;}//另一种写法struct ListNode* longList = headA;struct ListNode* shortList = headB;if(lenB > lenA){longList = headB;shortList = headA;}int gap = abs(lenB - lenA);while(gap--){longList = longList->next;}while(longList != shortList){longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}return longList;
}struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){//相遇//转换成相交问题struct ListNode* meet = fast;struct ListNode* newHead = meet->next;//相交点断开环meet->next = NULL;//需要把head到meet的链表反转struct ListNode* rhead = reverseList(head);struct ListNode* node = getIntersectionNode(newHead,rhead);//再把环恢复原样head = reverseList(rhead);meet->next = newHead;return node;}}return NULL;
}
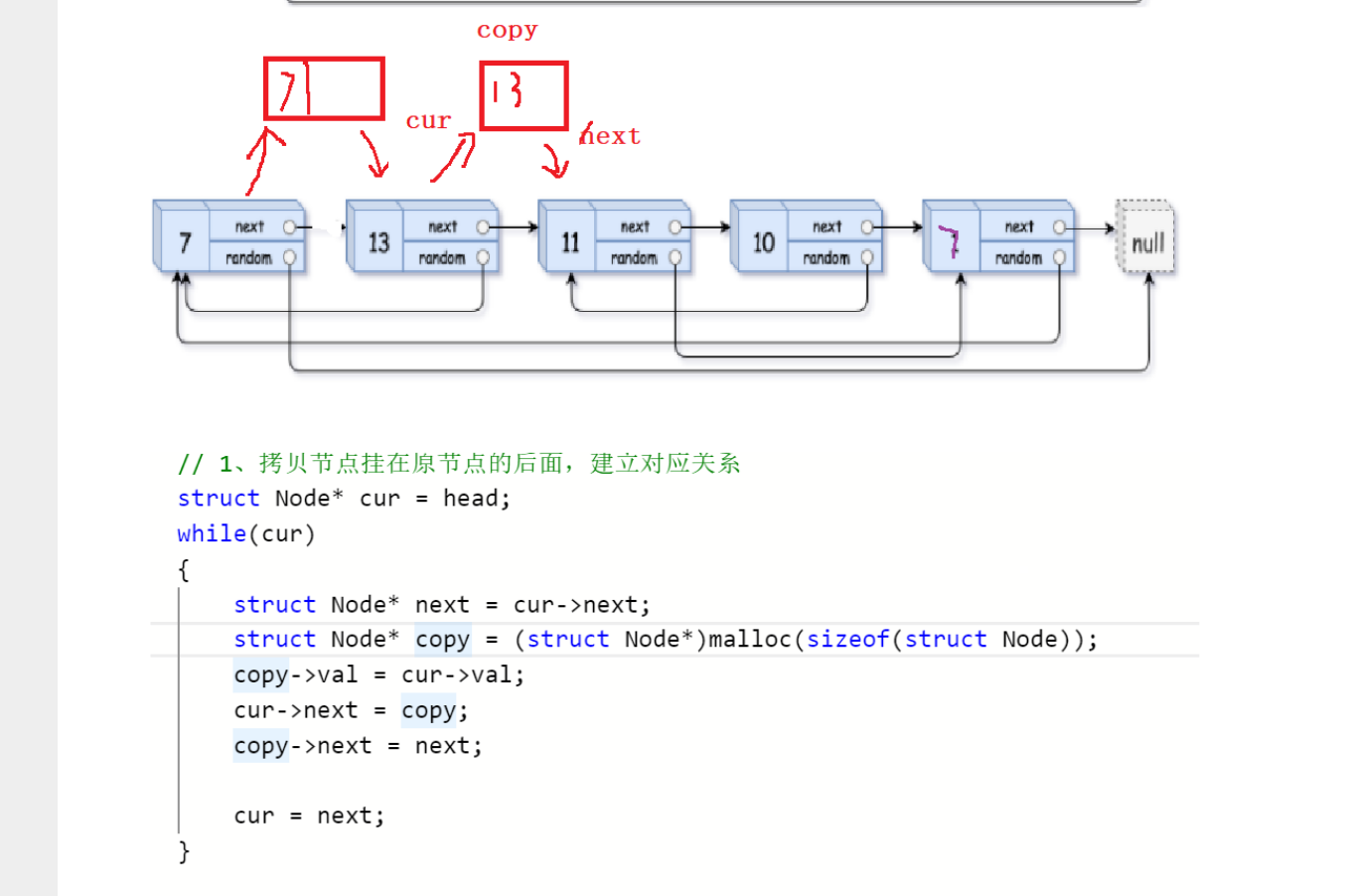
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
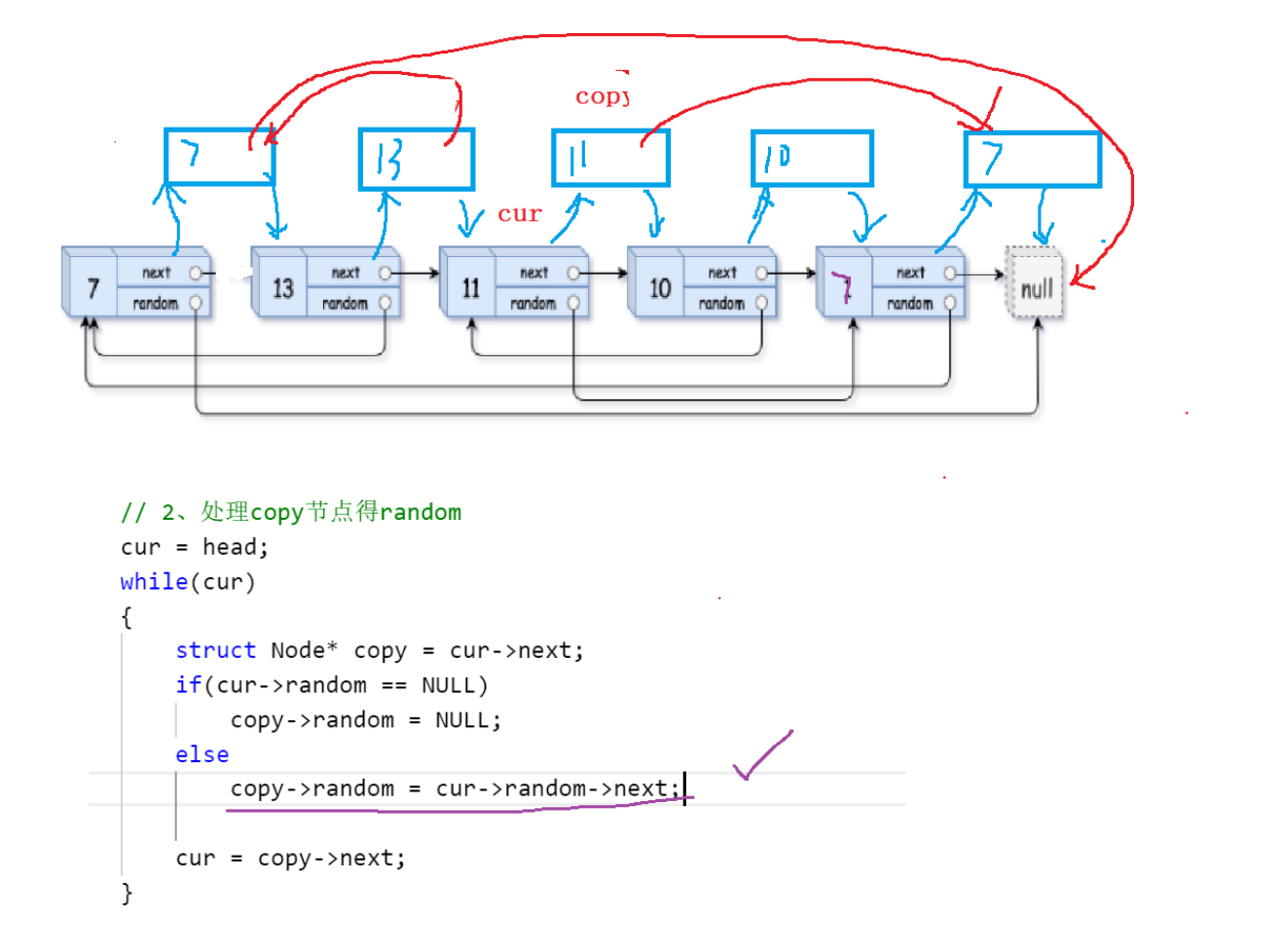
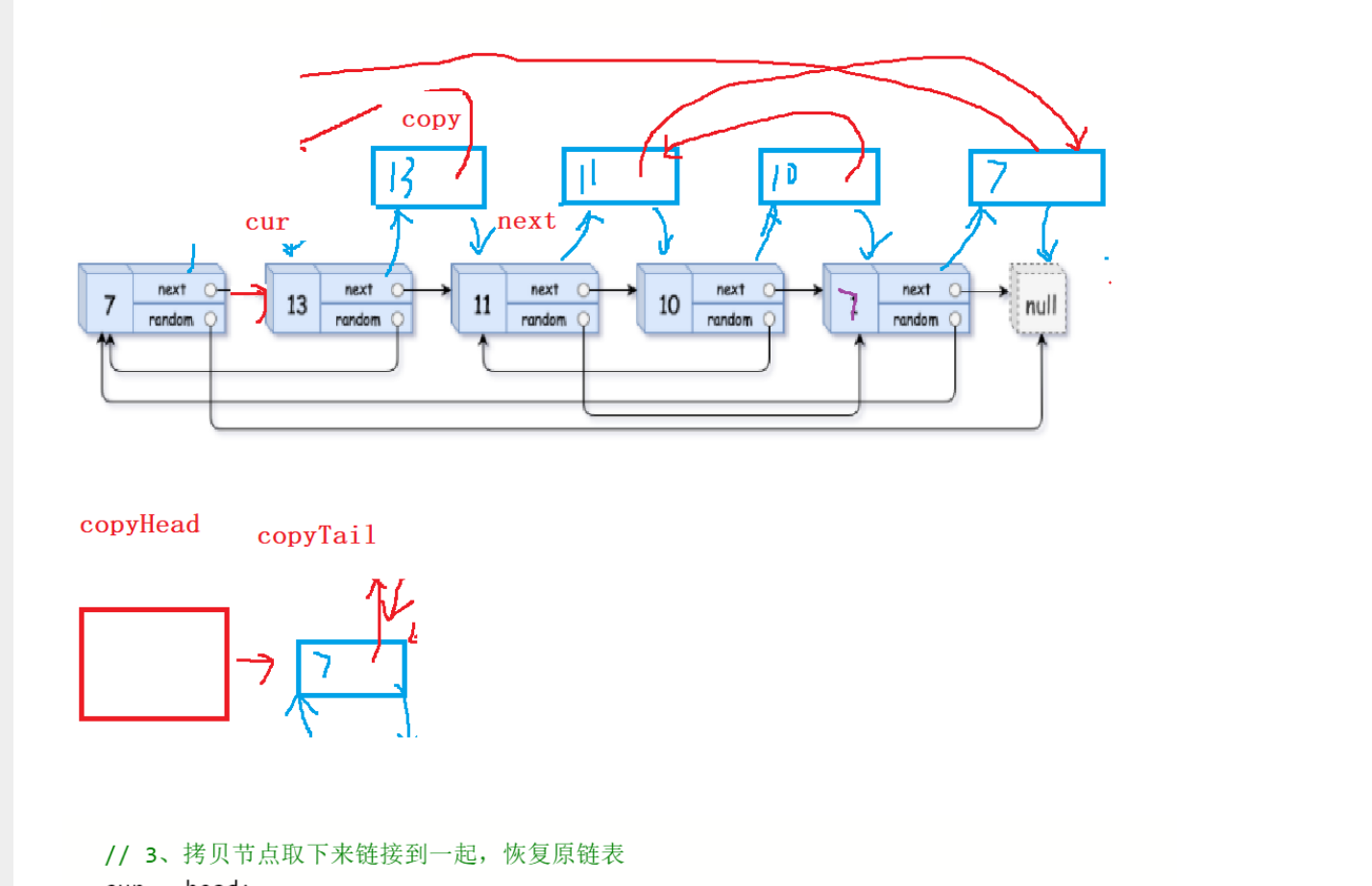
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {//考虑空链表if(head == NULL){return NULL;}//1.拷贝节点挂到原节点的后面,建立对应关系struct Node* cur = head;while(cur != NULL){struct Node* next = cur->next;struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val = cur->val;cur->next = copy;copy->next = next;cur = next;}//2.处理copy节点的randomcur = head;while(cur != NULL){struct Node* copy = cur->next;if(cur->random == NULL){copy->random = NULL;}else{copy->random = cur->random->next;}cur = copy->next;}//3.拷贝节点取下来链接到一起,恢复原链表cur = head;//借助哨兵位struct Node* copyHead = NULL;struct Node* copyTail = NULL;copyHead = copyTail = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));while(cur != NULL){struct Node* copy = cur->next;struct Node* next = copy->next;//尾插copyTail->next = copy;copyTail = copyTail->next;cur->next = next;cur = next;}struct Node* guard = copyHead;copyHead = copyHead->next;free(guard);guard = NULL;return copyHead;
}
147. 对链表进行插入排序

struct ListNode* insertionSortList(struct ListNode* head){//空链表或单个节点if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){return head;}//1.初始条件struct ListNode* sortHead = head;struct ListNode* cur = head->next;sortHead->next = NULL;while(cur)//2.终止条件{//3.迭代条件struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//将cur节点插入到前面有序区间struct ListNode* p = NULL;struct ListNode* c = sortHead;while(c){if(cur->val < c->val){break;}else{p = c;c = c->next;}}if(p == NULL)//头插{cur->next = c;sortHead = cur;}else//插中间和尾插{p->next = cur;cur->next = c;}cur = next;}return sortHead;
}
删除链表中重复的结点
自己考虑好极端情况,空链表,单节点,元素都相同
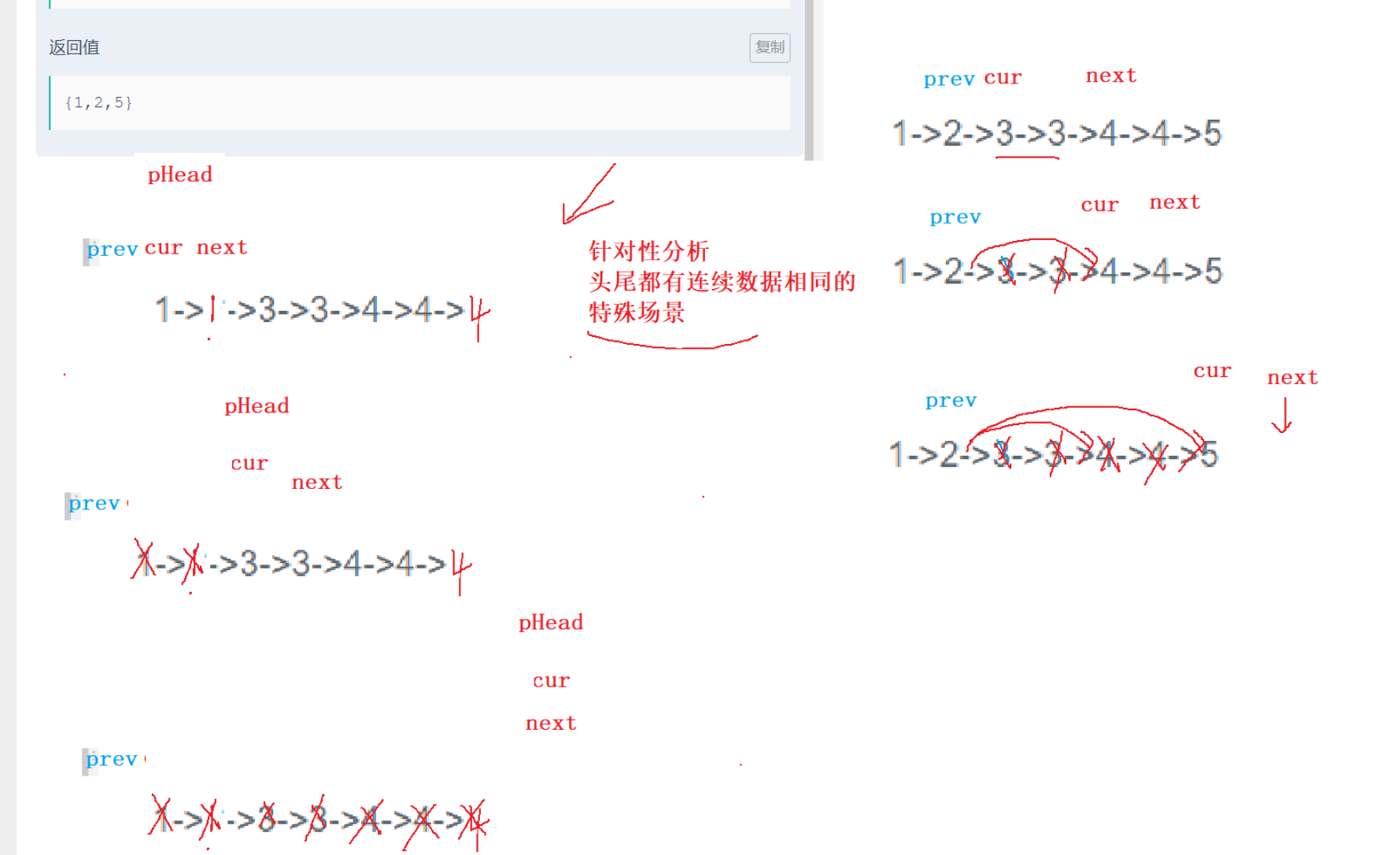
struct ListNode* deleteDuplication(struct ListNode* pHead ) {//空链表或一个节点if(pHead == NULL || pHead->next == NULL){return pHead;}//1.起始条件struct ListNode* prev = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = pHead;struct ListNode* next = pHead->next;while(next){if(cur->val == next->val){//删除重复的//让next往前走,直到碰到不相等的//如果最后几个元素都相等,那么next有可能走到空while(next && next->val == cur->val){next = next->next;}if(prev == NULL){pHead = next;cur = next;if(next != NULL){next = next->next;}}if(prev != NULL){cur = next;prev->next = next;if(next != NULL){next = next->next;}}}else{prev = cur;cur = next;if(next != NULL){next = next->next;}}}return pHead;
}
另一种写法:三指针
struct ListNode* deleteDuplication(struct ListNode* pHead ) {//空链表或一个节点if(pHead == NULL || pHead->next == NULL){return pHead;}//1.起始条件struct ListNode* prev = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = pHead;struct ListNode* next = pHead->next;while(next){if(cur->val == next->val){//删除重复的//让next往前走,直到碰到不相等的//如果最后几个元素都相等,那么next有可能走到空while(next && next->val == cur->val){next = next->next;}//删除cur到next之间的节点while(cur != next){struct ListNode* del = cur;cur = cur->next;free(del);del = NULL;}//考虑是否需要改变pHeadif(prev == NULL){pHead = cur;}else{prev->next = cur;}if(next != NULL){next = next->next;}}else{prev = cur;cur = next;next = next->next;}}return pHead;
}
