建设工程扣分查询网站/青岛seo网站建设公司
【GiantPandaCV导读】训练大型的数据集的速度受很多因素影响,由于数据集比较大,每个优化带来的时间提升就不可小觑。硬件方面,CPU、内存大小、GPU、机械硬盘orSSD存储等都会有一定的影响。软件实现方面,PyTorch本身的DataLoader有时候会不够用,需要额外操作,比如使用混合精度、数据预读取、多线程读取数据、多卡并行优化等策略也会给整个模型优化带来非常巨大的作用。那什么时候需要采取这篇文章的策略呢?那就是明明GPU显存已经占满,但是显存的利用率很低。
本文将搜集到的资源进行汇总,由于目前笔者训练的GPU利用率已经很高,所以并没有实际实验,可以在参考文献中看一下其他作者做的实验。同时感谢作者群各位大佬的指点,yyds。
文章目录
- 1. 硬件层面
- 2. 如何测试训练过程的瓶颈
- 3. 图片解码
- 4. 数据增强加速
- 5. data Prefetch
- 6. 多GPU并行处理
- 7. 混合精度训练
- 8. 其他细节
- 参考文献
1. 硬件层面
CPU的话尽量看主频比较高的,缓存比较大的,核心数也是比较重要的参数。
显卡尽可能选现存比较大的,这样才能满足大batch训练,多卡当让更好。
内存要求64G,4根16G的内存条插满绝对够用了。
主板性能也要跟上,否则装再好的CPU也很难发挥出全部性能。
电源供电要充足,GPU运行的时候会对功率有一定要求,全力运行的时候如果电源供电不足对性能影响还是比较大的。
存储如果有条件,尽量使用SSD存放数据,SSD和机械硬盘的在训练的时候的读取速度不是一个量级。笔者试验过,相同的代码,将数据移动到SSD上要比在机械硬盘上快10倍。
操作系统尽量用Ubuntu就可以(实验室用)
如何实时查看Ubuntu下各个资源利用情况呢?
- GPU使用 watch -n 1 nvidia-smi 来动态监控
- IO情况,使用iostat命令来监控
- CPU情况,使用htop命令来监控
笔者对硬件了解很有限,欢迎补充,如有问题轻喷。
2. 如何测试训练过程的瓶颈
如果现在程序运行速度很慢,那应该如何判断瓶颈在哪里呢?PyTorch中提供了工具,非常方便的可以查看设计的代码在各个部分运行所消耗的时间。
瓶颈测试:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/bottleneck.html
可以使用PyTorch中bottleneck工具,具体使用方法如下:
python -m torch.utils.bottleneck /path/to/source/script.py [args]
详细内容可以看上面给出的链接。
当然,也可用cProfile这样的工具来测试瓶颈所在,先运行以下命令。
python -m cProfile -o 100_percent_gpu_utilization.prof train.py
这样就得到了文件100_percent_gpu_utilization.prof
对其进行可视化(用到了snakeviz包,pip install snakeviz即可)
snakeviz 100_percent_gpu_utilization.prof
可视化的结果如下图所示:
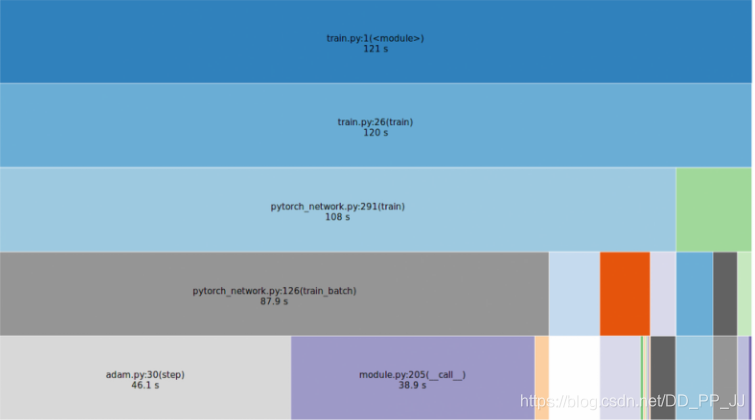
其他方法:
# Profile CPU bottlenecks
python -m cProfile training_script.py --profiling
# Profile GPU bottlenecks
nvprof --print-gpu-trace python train_mnist.py
# Profile system calls bottlenecks
strace -fcT python training_script.py -e trace=open,close,read
还可以用以下代码分析:
def test_loss_profiling():loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()with torch.autograd.profiler.profile(use_cuda=True) as prof:input = torch.randn((8, 1, 128, 128)).cuda()input.requires_grad = Truetarget = torch.randint(1, (8, 1, 128, 128)).cuda().float()for i in range(10):l = loss(input, target)l.backward()print(prof.key_averages().table(sort_by="self_cpu_time_total"))
3. 图片解码
PyTorch中默认使用的是Pillow进行图像的解码,但是其效率要比Opencv差一些,如果图片全部是JPEG格式,可以考虑使用TurboJpeg库解码。具体速度对比如下图所示:
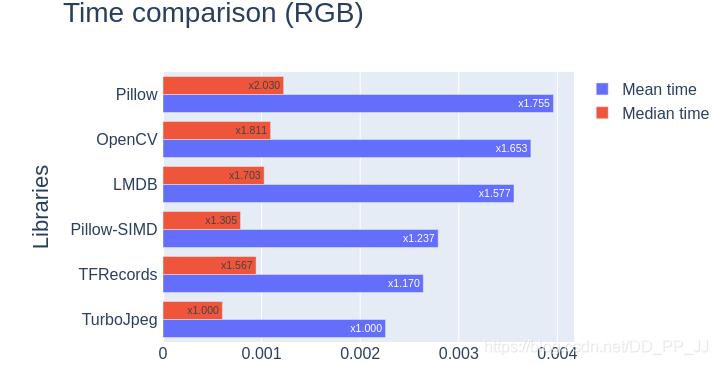
对于jpeg读取也可以考虑使用jpeg4py库(pip install jpeg4py),重写一个loader即可。
存bmp图也可以降低解码耗时,其他方案还有recordIO,hdf5,pth,n5,lmdb等格式
4. 数据增强加速
在PyTorch中,通常使用transformer做图片分类任务的数据增强,而其调用的是CPU做一些Crop、Flip、Jitter等操作。
如果你通过观察发现你的CPU利用率非常高,GPU利用率比较低,那说明瓶颈在于CPU预处理,可以使用Nvidia提供的DALI库在GPU端完成这部分数据增强操作。
Dali链接:https://github.com/NVIDIA/DALI
文档也非常详细:
Dali文档:https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/sdk/dali-developer-guide/index.html
当然,Dali提供的操作比较有限,仅仅实现了常用的方法,有些新的方法比如cutout需要自己搞。
具体实现可以参考这一篇:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77633542
5. data Prefetch
Nvidia Apex中提供的解决方案
参考来源:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66145913
Apex提供的策略就是预读取下一次迭代需要的数据。
class data_prefetcher():def __init__(self, loader):self.loader = iter(loader)self.stream = torch.cuda.Stream()self.mean = torch.tensor([0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255]).cuda().view(1,3,1,1)self.std = torch.tensor([0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255]).cuda().view(1,3,1,1)# With Amp, it isn't necessary to manually convert data to half.# if args.fp16:# self.mean = self.mean.half()# self.std = self.std.half()self.preload()def preload(self):try:self.next_input, self.next_target = next(self.loader)except StopIteration:self.next_input = Noneself.next_target = Nonereturnwith torch.cuda.stream(self.stream):self.next_input = self.next_input.cuda(non_blocking=True)self.next_target = self.next_target.cuda(non_blocking=True)# With Amp, it isn't necessary to manually convert data to half.# if args.fp16:# self.next_input = self.next_input.half()# else:self.next_input = self.next_input.float()self.next_input = self.next_input.sub_(self.mean).div_(self.std)
在训练函数中进行如下修改:
原先是:
training_data_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,num_workers=opts.threads,batch_size=opts.batchSize,pin_memory=True,shuffle=True,
)
for iteration, batch in enumerate(training_data_loader, 1):# 训练代码
修改以后:
data, label = prefetcher.next()
iteration = 0
while data is not None:iteration += 1# 训练代码data, label = prefetcher.next()
用prefetch库实现
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/97190313
安装:
pip install prefetch_generator
使用:
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from prefetch_generator import BackgroundGeneratorclass DataLoaderX(DataLoader):def __iter__(self):return BackgroundGenerator(super().__iter__())
然后用DataLoaderX替换原本的DataLoader
cuda.Steam加速拷贝过程
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/97190313
实现:
class DataPrefetcher():def __init__(self, loader, opt):self.loader = iter(loader)self.opt = optself.stream = torch.cuda.Stream()# With Amp, it isn't necessary to manually convert data to half.# if args.fp16:# self.mean = self.mean.half()# self.std = self.std.half()self.preload()def preload(self):try:self.batch = next(self.loader)except StopIteration:self.batch = Nonereturnwith torch.cuda.stream(self.stream):for k in self.batch:if k != 'meta':self.batch[k] = self.batch[k].to(device=self.opt.device, non_blocking=True)# With Amp, it isn't necessary to manually convert data to half.# if args.fp16:# self.next_input = self.next_input.half()# else:# self.next_input = self.next_input.float()def next(self):torch.cuda.current_stream().wait_stream(self.stream)batch = self.batchself.preload()return batch
调用:
# ----改造前----
for iter_id, batch in enumerate(data_loader):if iter_id >= num_iters:breakfor k in batch:if k != 'meta':batch[k] = batch[k].to(device=opt.device, non_blocking=True)run_step()# ----改造后----
prefetcher = DataPrefetcher(data_loader, opt)
batch = prefetcher.next()
iter_id = 0
while batch is not None:iter_id += 1if iter_id >= num_iters:breakrun_step()batch = prefetcher.next()
国外大佬实现
数据加载部分
import threading
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random class threadsafe_iter:"""Takes an iterator/generator and makes it thread-safe byserializing call to the `next` method of given iterator/generator."""def __init__(self, it):self.it = itself.lock = threading.Lock()def __iter__(self):return selfdef next(self):with self.lock:return self.it.next()def get_path_i(paths_count):"""Cyclic generator of paths indice"""current_path_id = 0while True:yield current_path_idcurrent_path_id = (current_path_id + 1) % paths_countclass InputGen:def __init__(self, paths, batch_size):self.paths = pathsself.index = 0self.batch_size = batch_sizeself.init_count = 0self.lock = threading.Lock() #mutex for input pathself.yield_lock = threading.Lock() #mutex for generator yielding of batchself.path_id_generator = threadsafe_iter(get_path_i(len(self.paths))) self.images = []self.labels = []def get_samples_count(self):""" Returns the total number of images needed to train an epoch """return len(self.paths)def get_batches_count(self):""" Returns the total number of batches needed to train an epoch """return int(self.get_samples_count() / self.batch_size)def pre_process_input(self, im,lb):""" Do your pre-processing hereNeed to be thread-safe function"""return im, lbdef next(self):return self.__iter__()def __iter__(self):while True:#In the start of each epoch we shuffle the data paths with self.lock: if (self.init_count == 0):random.shuffle(self.paths)self.images, self.labels, self.batch_paths = [], [], []self.init_count = 1#Iterates through the input paths in a thread-safe mannerfor path_id in self.path_id_generator: img, label = self.paths[path_id]img = cv2.imread(img, 1)label_img = cv2.imread(label,1)img, label = self.pre_process_input(img,label_img)#Concurrent access by multiple threads to the lists belowwith self.yield_lock: if (len(self.images)) < self.batch_size:self.images.append(img)self.labels.append(label)if len(self.images) % self.batch_size == 0: yield np.float32(self.images), np.float32(self.labels)self.images, self.labels = [], []#At the end of an epoch we re-init data-structureswith self.lock: self.init_count = 0def __call__(self):return self.__iter__()
使用方法:
class thread_killer(object):"""Boolean object for signaling a worker thread to terminate"""def __init__(self):self.to_kill = Falsedef __call__(self):return self.to_killdef set_tokill(self,tokill):self.to_kill = tokilldef threaded_batches_feeder(tokill, batches_queue, dataset_generator):"""Threaded worker for pre-processing input data.tokill is a thread_killer object that indicates whether a thread should be terminateddataset_generator is the training/validation dataset generatorbatches_queue is a limited size thread-safe Queue instance."""while tokill() == False:for batch, (batch_images, batch_labels) \in enumerate(dataset_generator):#We fill the queue with new fetched batch until we reach the max size.batches_queue.put((batch, (batch_images, batch_labels))\, block=True)if tokill() == True:returndef threaded_cuda_batches(tokill,cuda_batches_queue,batches_queue):"""Thread worker for transferring pytorch tensors intoGPU. batches_queue is the queue that fetches numpy cpu tensors.cuda_batches_queue receives numpy cpu tensors and transfers them to GPU space."""while tokill() == False:batch, (batch_images, batch_labels) = batches_queue.get(block=True)batch_images_np = np.transpose(batch_images, (0, 3, 1, 2))batch_images = torch.from_numpy(batch_images_np)batch_labels = torch.from_numpy(batch_labels)batch_images = Variable(batch_images).cuda()batch_labels = Variable(batch_labels).cuda()cuda_batches_queue.put((batch, (batch_images, batch_labels)), block=True)if tokill() == True:returnif __name__ =='__main__':import timeimport Threadimport sysfrom Queue import Empty,Full,Queuenum_epoches=1000#model is some Pytorch CNN modelmodel.cuda()model.train()batches_per_epoch = 64#Training set list suppose to be a list of full-paths for all#the training images.training_set_list = None#Our train batches queue can hold at max 12 batches at any given time.#Once the queue is filled the queue is locked.train_batches_queue = Queue(maxsize=12)#Our numpy batches cuda transferer queue.#Once the queue is filled the queue is locked#We set maxsize to 3 due to GPU memory size limitationscuda_batches_queue = Queue(maxsize=3)training_set_generator = InputGen(training_set_list,batches_per_epoch)train_thread_killer = thread_killer()train_thread_killer.set_tokill(False)preprocess_workers = 4#We launch 4 threads to do load && pre-process the input imagesfor _ in range(preprocess_workers):t = Thread(target=threaded_batches_feeder, \args=(train_thread_killer, train_batches_queue, training_set_generator))t.start()cuda_transfers_thread_killer = thread_killer()cuda_transfers_thread_killer.set_tokill(False)cudathread = Thread(target=threaded_cuda_batches, \args=(cuda_transfers_thread_killer, cuda_batches_queue, train_batches_queue))cudathread.start()#We let queue to get filled before we start the trainingtime.sleep(8)for epoch in range(num_epoches):for batch in range(batches_per_epoch):#We fetch a GPU batch in 0's due to the queue mechanism_, (batch_images, batch_labels) = cuda_batches_queue.get(block=True)#train batch is the method for your training step.#no need to pin_memory due to diminished cuda transfers using queues.loss, accuracy = train_batch(batch_images, batch_labels)train_thread_killer.set_tokill(True)cuda_transfers_thread_killer.set_tokill(True) for _ in range(preprocess_workers):try:#Enforcing thread shutdowntrain_batches_queue.get(block=True,timeout=1)cuda_batches_queue.get(block=True,timeout=1) except Empty:passprint "Training done"
6. 多GPU并行处理
PyTorch中提供了分布式训练API, nn.DistributedDataParallel, 推理的时候也可以使用nn.DataParallel或者nn.DistributedDataParallel。
推荐一个库,里面实现了多种分布式训练的demo: https://github.com/tczhangzhi/pytorch-distributed 其中包括:
- nn.DataParallel
- torch.distributed
- torch.multiprocessing
- apex再加速
- horovod实现
- slurm GPU集群分布式
7. 混合精度训练
mixed precision yyds,之前分享过mixed precision论文阅读,实现起来非常简单。在PyTorch中,可以使用Apex库。如果用的是最新版本的PyTorch,其自身已经支持了混合精度训练,非常nice。
简单来说,混合精度能够让你在精度不掉的情况下,batch提升一倍。其原理就是将原先float point32精度的数据变为float point16的数据,不管是数据传输还是训练过程,都极大提升了训练速度,炼丹必备。
8. 其他细节
batch_images = batch_images.pin_memory()
Batch_labels = Variable(batch_labels).cuda(non_blocking=True)
-
PyTorch的DataLoader有一个参数pin_memory,使用固定内存,并使用non_blocking=True来并行处理数据传输。
-
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark=True
-
及时释放掉不需要的显存、内存。
-
如果数据集比较小,直接将数据复制到内存中,从内存中读取可以极大加快数据读取的速度。
-
调整workers数量,过少的线程读取数据会导致速度非常慢,过多线程读取数据可能会由于阻塞也导致速度非常慢。所以需要根据自己机器的情况,尝试不同数量的workers,选择最合适的数量。一般设置为 cpu 核心数或gpu数量
-
编码的时候要注意尽可能减少CPU和GPU之间的数据传输,使用类似numpy的编码方式,通过并行的方式来处理,可以提高性能。
-
使用
TFRecord或者LMDB等,减少小文件的读写
参考文献
【1】https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66145913
【2】https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/bottleneck.html
【3】https://blog.csdn.net/dancer__sky/article/details/78631577
【4】https://sagivtech.com/2017/09/19/optimizing-pytorch-training-code/
【5】https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77633542
【6】https://github.com/NVIDIA/DALI
【7】https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/147723652
【8】https://www.zhihu.com/question/356829360/answer/907832358
