小说网站怎么做/网络推广方法有哪些
前提知识
基本的线段树写法:
洛谷线段树1
洛谷线段树2
以下是正文
一、区间最值操作
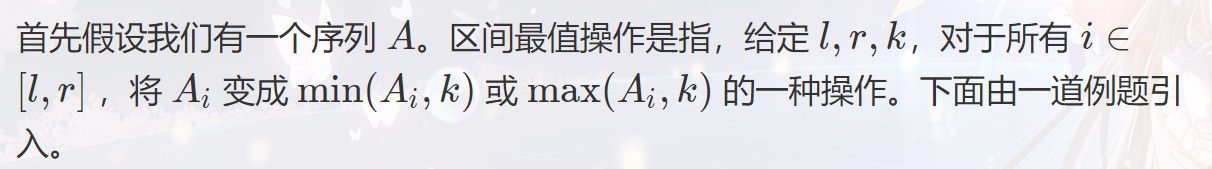
例题一、
Gorgeous Sequence
本题要求我们实现三个操作
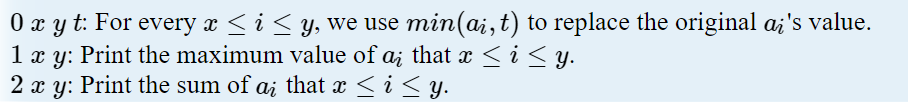
做法一、
对于第二种和第三种操作我们是已经知道如何写了。
问题就在于第一种操作。
考虑第一种操作是取min
因此当我们这个区间内的最大值
1.如果比给定的k来得小 那么我们不需要任何操作
2.如果这个k<最大值 但是k > 第二大的值(以下称为次大值)
那么我们只需要将最大值全部变成k,修改一下区间和即可.
3.如果这个k<最大值 && k < 次大值
那么我们当前这个结点是处理不了的,直接push_down交给儿子结点
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc (p<<1|1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1100000;
struct Node{int L,R,tag;//这个tag是维护区间最值操作的ll sum;int fir_big,sec_big;int fir_num;
}tree[N*4];
int a[N];
inline void push_up(int);
void build_tree(int l,int r,int p){//tag的取值是0~2^31-1 因此我们取-1tree[p].L=l,tree[p].R=r,tree[p].tag=-1;if(l==r){tree[p].sum=a[l];tree[p].fir_big=a[l];tree[p].sec_big=-1;tree[p].fir_num=1;return;}int mid = (l+r)>>1;build_tree(l,mid,lc);build_tree(mid+1,r,rc);push_up(p);
}
inline void push_up(int p){tree[p].sum=tree[lc].sum+tree[rc].sum;if(tree[lc].fir_big==tree[rc].fir_big){tree[p].fir_big=tree[lc].fir_big;tree[p].fir_num=tree[lc].fir_num+tree[rc].fir_num;tree[p].sec_big=max(tree[lc].sec_big,tree[rc].sec_big);}else if(tree[lc].fir_big>tree[rc].fir_big){tree[p].fir_big=tree[lc].fir_big;tree[p].fir_num=tree[lc].fir_num;tree[p].sec_big=max(tree[lc].sec_big,tree[rc].fir_big);}else{tree[p].fir_big=tree[rc].fir_big;tree[p].fir_num=tree[rc].fir_num;tree[p].sec_big=max(tree[rc].sec_big,tree[lc].fir_big);}
}
inline void update(int p,int cnt_val){if(cnt_val<tree[p].fir_big){//最大值全部变成cnt_valtree[p].sum+=(1ll*cnt_val-tree[p].fir_big)*tree[p].fir_num;tree[p].fir_big=tree[p].tag=cnt_val;}
}
inline void push_down(int p){if(~tree[p].tag){update(lc,tree[p].tag);update(rc,tree[p].tag);tree[p].tag=-1;}
}
void modify(int p,int l,int r,int cnt_val){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l||tree[p].fir_big<=cnt_val) return;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r&&tree[p].sec_big<cnt_val){update(p,cnt_val);return;}push_down(p);modify(lc,l,r,cnt_val);modify(rc,l,r,cnt_val);push_up(p);
}
int queryMax(int p,int l,int r){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return 0;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){return tree[p].fir_big;}push_down(p);return max(queryMax(lc,l,r),queryMax(rc,l,r));
}
ll querySum(int p,int l,int r){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return 0;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){return tree[p].sum;}push_down(p);return querySum(lc,l,r)+querySum(rc,l,r);
}
#undef lc
#undef rc
int read(){int x=0; char ch=0;while (!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();while (isdigit(ch)) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48), ch=getchar();return x;
}
#if 0
这份代码完成三个功能
1.区间最小值操作
2.求区间最大值
3.求区间和
#endif // 0
int main()
{int t,n,m;t=read();while(t--){n=read();m=read();for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){a[i]=read();}build_tree(1,n,1);for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){int op,x,y,t;op=read();if(op==0){x=read();y=read();t=read();modify(1,x,y,t);}else if(op==1){x=read();y=read();printf("%d\n",queryMax(1,x,y));}else{x=read();y=read();printf("%lld\n",querySum(1,x,y));}}}return 0;
}做法二、
2021.9.8复习更新另一个代码;
这份代码和上面那种做法不同点在于,他不是维护一个改变的tag,而是维护一个加法的tag;
按照例题二的思路,我们将值分为三种,最大值、次大值、其他值;
维护两个标记,最大值的加法标记,其他值的加法标记;
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc (p<<1|1)using namespace std;typedef long long ll;const int N = 1000010;struct Node{int l,r,mx,sec_mx,mx_num;int mx_tag,other_tag;ll sum;
}tr[N<<2];int a[N],t,n,m;
void push_down(int p);
int read()
{int x=0; char ch=0;while (!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();while (isdigit(ch)) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48), ch=getchar();return x;
}
void push_up(int p){tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;if(tr[lc].mx == tr[rc].mx){tr[p].mx = tr[lc].mx;tr[p].mx_num = tr[lc].mx_num + tr[rc].mx_num;tr[p].sec_mx = max(tr[lc].sec_mx,tr[rc].sec_mx);}else if(tr[lc].mx > tr[rc].mx){tr[p].mx = tr[lc].mx;tr[p].mx_num = tr[lc].mx_num;tr[p].sec_mx = max(tr[lc].sec_mx,tr[rc].mx);}else{tr[p].mx = tr[rc].mx;tr[p].mx_num = tr[rc].mx_num;tr[p].sec_mx = max(tr[rc].sec_mx,tr[lc].mx);}
}
void build(int p,int l,int r){tr[p].l = l,tr[p].r = r;tr[p].sec_mx = -1;//因为数据范围是从0开始的tr[p].mx_tag = tr[p].other_tag = 0;if(l == r){tr[p].sum = tr[p].mx = a[l];tr[p].mx_num = 1;return;}int mid = (l+r) >> 1;build(lc,l,mid);build(rc,mid+1,r);push_up(p);
}
//给这个节点的最大值、其他值加上某些数
void node_update_fun(int p,int mxk,int otherk){tr[p].sum += 1ll*mxk*tr[p].mx_num + 1ll*(tr[p].r-tr[p].l+1-tr[p].mx_num)*otherk;if(tr[p].sec_mx != -1) tr[p].sec_mx += otherk;tr[p].mx += mxk;tr[p].mx_tag += mxk;tr[p].other_tag += otherk;
}
void range_min_fun(int p,int l,int r,int k){if(k>=tr[p].mx) return;if(tr[p].l>=l&&tr[p].r<=r&&tr[p].sec_mx < k){node_update_fun(p,k-tr[p].mx,0);return;}push_down(p);int mid = (tr[p].l + tr[p].r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){range_min_fun(lc,l,r,k);}else if(l>mid){range_min_fun(rc,l,r,k);}else{range_min_fun(lc,l,mid,k);range_min_fun(rc,mid+1,r,k);}push_up(p);
}
void push_down(int p){int mxk = tr[p].mx_tag;int otherk = tr[p].other_tag;int mx = max(tr[lc].mx,tr[rc].mx);//分清楚左右儿子的值到底应该被哪个k所加node_update_fun(lc,tr[lc].mx==mx?mxk:otherk,otherk);node_update_fun(rc,tr[rc].mx==mx?mxk:otherk,otherk);tr[p].mx_tag = tr[p].other_tag = 0;
}
ll query_sum(int p,int l,int r){if(tr[p].l>=l&&tr[p].r<=r){return tr[p].sum;}push_down(p);int mid = (tr[p].l+tr[p].r)>>1;if(r<=mid){return query_sum(lc,l,r);}else if(l>mid){return query_sum(rc,l,r);}else{return query_sum(lc,l,mid) +query_sum(rc,mid+1,r);}
}
int query_max(int p,int l,int r){if(tr[p].l>=l&&tr[p].r<=r){return tr[p].mx;}push_down(p);int mid = (tr[p].l+tr[p].r)>>1;if(r<=mid){return query_max(lc,l,r);}else if(l>mid){return query_max(rc,l,r);}else{return max(query_max(lc,l,mid),query_max(rc,mid+1,r));}}
int main()
{t=read();while(t--){n=read();m=read();for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) a[i] =read();build(1,1,n);int op,l,r,k;while(m--){op=read();l=read();r=read();if(op == 0){k=read();range_min_fun(1,l,r,k);}else if(op == 1){printf("%d\n",query_max(1,l,r));}else{printf("%lld\n",query_sum(1,l,r));}}}return 0;
}例题二、
BZOJ4695
这题在上一题的基础之上
- 增加了区间加
- 区间最大值操作
- 求区间最小值
根据上一题区间最小值的操作 我们来仿造区间最大值操作
对于区间最小值操作
我们维护:区间最大值及个数、次大值
那么对于区间最大值操作
我们维护:区间最小值及个数、次小值
那么我们就将数分为了三类:最大值、最小值、其他值
对于题目要求的三种修改操作
- 对于区间加(减),我们直接对这三类数加(减) 即可
- 对于区间最小值操作以及最大值操作
思路与例题一处相同。
此处以区间最大值操作为例
1.如果最大值比给定的k来得小 那么我们不需要任何操作
2.如果这个k<最大值 但是k > 次大值
那么我们只需要将最大值全部变成k,修改一下区间和即可.
3.如果这个k<最大值 && k < 次大值
那么我们当前这个结点是处理不了的,直接push_down交给儿子结点
那么,我们需要维护三个tag
- 最大值tag
- 最小值tag
- 其他值tag
但是这里有个问题,如果一个区间内的数字很少。
比如只有1个或者2个当只有一个数字的时候 那么最大值是等于最小值的我们在push_down的时候不要搞错标记亦或者只有两个数字的时候 有可能发生次大值等于最小值也有可能发生次小值等于最大值 此时也要注意是哪个标记的作用
还有一个问题,当前节点的最大最小值是从儿子节点取过来的
此处以最大值为例
如果儿子节点不包含最大值
那么我们给它加的标记应该是其他值的标记(代码中的t3)
如果包含了 那么应该加最大值的标记(代码中的t2)
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc (p<<1|1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 550000;
const int INF = 1e9;
struct Node{int L,R;ll sum;//分别是最小值 最大值 其他值的tagint tag1,tag2,tag3;//最大值 最小值 次大值 次小值 最大值个数 最小值个数int fir_max,fir_min,sec_max,sec_min,mx_num,mn_num;
}tree[N<<2];
int a[N];
void push_up(int p){tree[p].sum=tree[lc].sum+tree[rc].sum;if(tree[lc].fir_min==tree[rc].fir_min){tree[p].fir_min=tree[lc].fir_min;tree[p].mn_num=tree[lc].mn_num+tree[rc].mn_num;tree[p].sec_min=min(tree[lc].sec_min,tree[rc].sec_min);}else if(tree[lc].fir_min<tree[rc].fir_min){tree[p].fir_min=tree[lc].fir_min;tree[p].mn_num=tree[lc].mn_num;tree[p].sec_min=min(tree[lc].sec_min,tree[rc].fir_min);}else{tree[p].fir_min=tree[rc].fir_min;tree[p].mn_num=tree[rc].mn_num;tree[p].sec_min=min(tree[rc].sec_min,tree[lc].fir_min);}if(tree[lc].fir_max==tree[rc].fir_max){tree[p].fir_max=tree[lc].fir_max;tree[p].mx_num=tree[lc].mx_num+tree[rc].mx_num;tree[p].sec_max=max(tree[lc].sec_max,tree[rc].sec_max);}else if(tree[lc].fir_max>tree[rc].fir_max){tree[p].fir_max=tree[lc].fir_max;tree[p].mx_num=tree[lc].mx_num;tree[p].sec_max=max(tree[lc].sec_max,tree[rc].fir_max);}else{tree[p].fir_max=tree[rc].fir_max;tree[p].mx_num=tree[rc].mx_num;tree[p].sec_max=max(tree[rc].sec_max,tree[lc].fir_max);}
}
void build(int p,int l,int r){tree[p].L=l,tree[p].R=r;tree[p].tag1=tree[p].tag2=tree[p].tag3=0;if(l==r){tree[p].fir_max=tree[p].fir_min=tree[p].sum=a[l];tree[p].sec_max=-INF;tree[p].sec_min=INF;tree[p].mx_num=tree[p].mn_num=1;return;}int mid = (l+r)>>1;build(lc,l,mid);build(rc,mid+1,r);push_up(p);
}
//t1,t2,t3分别是最小值 最大值 其他值的tag标记
void update(int p,int t1,int t2,int t3){//处理sumif(tree[p].fir_max==tree[p].fir_min){//如果只有一个值(最大值等于最小值)//那么将其他值的tag丢掉if(t1==t3) t1=t2;else if(t2==t3) t2=t1;tree[p].sum+=1ll*tree[p].mx_num*t2;//else t2=t1;//tree[p].sum+=1ll*t1*tree[p].mn_num;}else{tree[p].sum+=1ll*tree[p].mx_num*t2+1ll*tree[p].mn_num*t1+(tree[p].R-tree[p].L+1-tree[p].mx_num-tree[p].mn_num)*t3*1ll;}//处理次大值//如果次大值和最小值相等 那么给它加tag1的值//否则加tag3的值//处理次小值同理if(tree[p].sec_max==tree[p].fir_min){tree[p].sec_max+=t1;}else if(tree[p].sec_max!=-INF){tree[p].sec_max+=t3;}//处理次小值if(tree[p].sec_min==tree[p].fir_max){tree[p].sec_min+=t2;}else if(tree[p].sec_min!=INF){tree[p].sec_min+=t3;}//处理最大值、最小值、以及tagtree[p].fir_max+=t2;tree[p].fir_min+=t1;tree[p].tag1+=t1;tree[p].tag2+=t2;tree[p].tag3+=t3;
}
void push_down(int p){int mx = max(tree[lc].fir_max,tree[rc].fir_max);int mn = min(tree[lc].fir_min,tree[rc].fir_min);int l1,l2,r1,r2;l1=tree[lc].fir_min==mn?tree[p].tag1:tree[p].tag3;l2=tree[lc].fir_max==mx?tree[p].tag2:tree[p].tag3;update(lc,l1,l2,tree[p].tag3);r1=tree[rc].fir_min==mn?tree[p].tag1:tree[p].tag3;r2=tree[rc].fir_max==mx?tree[p].tag2:tree[p].tag3;update(rc,r1,r2,tree[p].tag3);tree[p].tag1=tree[p].tag2=tree[p].tag3=0;
}//给一个区间[L,R] 加上一个数x
void fun1(int p,int l,int r,int k){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){update(p,k,k,k);return;}push_down(p);fun1(lc,l,r,k);fun1(rc,l,r,k);push_up(p);
}
//把一个区间[L,R] 里小于x 的数变成x
void fun2(int p,int l,int r,int k){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l||tree[p].fir_min>=k) return;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r&&tree[p].sec_min>k){update(p,k-tree[p].fir_min,0,0);return;}push_down(p);fun2(lc,l,r,k);fun2(rc,l,r,k);push_up(p);
}
//把一个区间[L,R] 里大于x 的数变成x
void fun3(int p,int l,int r,int k){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l||tree[p].fir_max<=k) return;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r&&tree[p].sec_max<k){update(p,0,k-tree[p].fir_max,0);return;}push_down(p);fun3(lc,l,r,k);fun3(rc,l,r,k);push_up(p);
}
//求区间[L,R] 的和
ll fun4(int p,int l,int r){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return 0;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){return tree[p].sum;}push_down(p);return fun4(lc,l,r)+fun4(rc,l,r);
}
//求区间[L,R] 的最大值
int fun5(int p,int l,int r){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return -INF;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){return tree[p].fir_max;}push_down(p);return max(fun5(lc,l,r),fun5(rc,l,r));
}
//求区间[L,R] 的最小值
int fun6(int p,int l,int r){if(tree[p].L>r||tree[p].R<l) return INF;if(tree[p].L>=l&&tree[p].R<=r){return tree[p].fir_min;}push_down(p);return min(fun6(lc,l,r),fun6(rc,l,r));
}
#undef lc
#undef rc
int read()
{int x=0, w=0; char ch=0;while (!isdigit(ch)) w|=ch=='-', ch=getchar();while (isdigit(ch)) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48), ch=getchar();return w?-x:x;
}
template<class T>
inline void write(T x)
{if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;if(x>9) write(x/10);putchar(x%10+'0');//取出个位
}int main()
{int n;n=read();for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){a[i]=read();}build(1,1,n);int m;m=read();while(m--){int op,l,r,k;op=read();switch(op){case 1:l=read();r=read();k=read();fun1(1,l,r,k);break;case 2:l=read();r=read();k=read();fun2(1,l,r,k);break;case 3:l=read();r=read();k=read();fun3(1,l,r,k);break;case 4:l=read();r=read();write(fun4(1,l,r));putchar('\n');break;case 5:l=read();r=read();write(fun5(1,l,r));putchar('\n');break;case 6:l=read();r=read();write(fun6(1,l,r));putchar('\n');break;}}return 0;
}
代码二
2021.9.7复习,写了一份新的,我觉得更加适合理解,思路和上面是一致的;
#include <iostream>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;const int N = 5e5+10;const int INF = 1e9;#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc (p<<1|1)struct Node{int l,r,mx,mn,mx_num,mn_num,sec_mx,sec_mn;ll sum;int mx_tag,mn_tag,other_tag;
}tr[N<<2];
int n,m,a[N];
void push_down(int p);void push_up(int p){Node &left = tr[lc],&right = tr[rc],&root = tr[p];root.sum = left.sum + right.sum;//操作最大值、次大值if(left.mx == right.mx){root.mx = left.mx;root.mx_num = left.mx_num + right.mx_num;root.sec_mx = max(left.sec_mx,right.sec_mx);}else if(left.mx > right.mx){root.mx = left.mx;root.mx_num = left.mx_num;root.sec_mx = max(left.sec_mx,right.mx);}else{root.mx = right.mx;root.mx_num = right.mx_num;root.sec_mx = max(right.sec_mx,left.mx);}//最小值、次小值if(left.mn == right.mn){root.mn = left.mn;root.mn_num = left.mn_num + right.mn_num;root.sec_mn = min(left.sec_mn,right.sec_mn);}else if(left.mn < right.mn){root.mn = left.mn;root.mn_num = left.mn_num;root.sec_mn = min(left.sec_mn,right.mn);}else{root.mn = right.mn;root.mn_num = right.mn_num;root.sec_mn = min(right.sec_mn,left.mn);}
}
//这个方法对某个节点的最大值、最小值、其他值加上某些数
void node_update_fun(int p,int mnk,int mxk,int otherk){Node & root = tr[p];if(root.mx == root.mn){//不应该被其他值的标签所影响,因为这里只有一个值if(mnk == otherk) mnk = mxk;else mxk = mnk;root.sum += 1ll*root.mn_num * mnk;}else{root.sum += 1ll*root.mn_num * mnk + 1ll*root.mx_num * mxk+ 1ll*(root.r-root.l+1-root.mn_num-root.mx_num)*otherk;}//操作次值if(root.mx == root.sec_mn){root.sec_mn += mxk;}else if(root.sec_mn != INF){root.sec_mn += otherk;}if(root.mn == root.sec_mx){root.sec_mx += mnk;}else if(root.sec_mx != -INF){root.sec_mx +=otherk;}root.mx += mxk;root.mn += mnk;root.mx_tag += mxk;root.mn_tag += mnk;root.other_tag += otherk;
}
void range_max_fun(int p,int l,int r,int k){Node &root = tr[p];if(root.mn >= k) return;if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r&&root.sec_mn > k){node_update_fun(p,k-root.mn,0,0);return;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){range_max_fun(lc,l,r,k);}else if(l>mid){range_max_fun(rc,l,r,k);}else{range_max_fun(lc,l,mid,k);range_max_fun(rc,mid+1,r,k);}push_up(p);
}
void range_min_fun(int p,int l,int r,int k){Node &root = tr[p];if(root.mx <= k) return;if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r&&root.sec_mx<k){node_update_fun(p,0,k-root.mx,0);return;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){range_min_fun(lc,l,r,k);}else if(l>mid){range_min_fun(rc,l,r,k);}else{range_min_fun(lc,l,mid,k);range_min_fun(rc,mid+1,r,k);}push_up(p);
}
void range_add_fun(int p,int l,int r,int k){Node & root = tr[p];if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r){node_update_fun(p,k,k,k);return;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){range_add_fun(lc,l,r,k);}else if(l>mid){range_add_fun(rc,l,r,k);}else{range_add_fun(lc,l,mid,k);range_add_fun(rc,mid+1,r,k);}push_up(p);
}
ll query_sum(int p,int l,int r){Node & root = tr[p];if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r){return root.sum;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){return query_sum(lc,l,r);}else if(l>mid){return query_sum(rc,l,r);}else{return query_sum(lc,l,mid)+query_sum(rc,mid+1,r);}
}
int query_max(int p,int l,int r){Node & root = tr[p];if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r){return root.mx;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){return query_max(lc,l,r);}else if(l>mid){return query_max(rc,l,r);}else{return max(query_max(lc,l,mid),query_max(rc,mid+1,r));}
}
int query_min(int p,int l,int r){Node & root = tr[p];if(root.l>=l&&root.r<=r){return root.mn;}push_down(p);int mid = (root.l + root.r) >> 1;if(r<=mid){return query_min(lc,l,r);}else if(l>mid){return query_min(rc,l,r);}else{return min(query_min(lc,l,mid),query_min(rc,mid+1,r));}
}
void push_down(int p){int mx = max(tr[lc].mx,tr[rc].mx);int mn = min(tr[lc].mn,tr[rc].mn);int mxk = tr[p].mx_tag,mnk = tr[p].mn_tag,otherk=tr[p].other_tag;node_update_fun(lc,tr[lc].mn==mn?mnk:otherk,tr[lc].mx==mx?mxk:otherk,otherk);node_update_fun(rc,tr[rc].mn==mn?mnk:otherk,tr[rc].mx==mx?mxk:otherk,otherk);tr[p].mx_tag = tr[p].mn_tag = tr[p].other_tag = 0;
}void build(int p,int l,int r){tr[p].l = l,tr[p].r = r;tr[p].mn_tag = tr[p].mx_tag = tr[p].other_tag = 0;tr[p].mx = tr[p].sec_mx = -INF;tr[p].mn = tr[p].sec_mn = INF;if(l==r){tr[p].sum = tr[p].mn = tr[p].mx = a[l];tr[p].mx_num = tr[p].mn_num = 1;return;}int mid = (l+r) >> 1;build(lc,l,mid);build(rc,mid+1,r);push_up(p);
}int main()
{std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);cin >> n;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin >> a[i];build(1,1,n);cin >> m;int op,l,r,k;while(m--){cin >> op >> l >> r;switch(op){case 1:cin >> k;range_add_fun(1,l,r,k);break;case 2:cin >> k;range_max_fun(1,l,r,k);break;case 3:cin >> k;range_min_fun(1,l,r,k);break;case 4:cout << query_sum(1,l,r) <<'\n';break;case 5:cout << query_max(1,l,r) << '\n';break;case 6:cout << query_min(1,l,r) << '\n';break;}}return 0;
}例题三、
待完成…
