网站备案失败/网络热词大全
关注微信号:javalearns 随时随地学Java
或扫一扫

随时随地学Java
1. 一些常用的公共属性介绍
1) layout_width - 宽
fill_parent: 宽度和父元素相同,wrap_content: 宽度随本身的内容所调整,或者指定 px 值来设置宽
2) layout_height - 高
fill_parent: 高度和父元素相同,wrap_content: 高度随本身的内容所调整,或者指定 px 值来设置高
3) background - 设置背景图
4) padding - 设置边距
可以具体设置paddingBottom,paddingLeft,paddingRight,paddingTop来设定不同的px值
5) id - 该object的id号
@+id/id1 代表添加新的id名为id1, @id/id1 代表引用id1的控件
6) layout_weight - 重要度
个人理解为显示的优先级。默认为0(最高),数值越大,优先级越低!参考下面的Linear Layout例子。要让layout_weight生效,需要父层或父父层的相应layout_width/layout_height = "fill_parent",否则wrap_content会压缩到最小足够空间!
7) layout_gravity - Container组件的对齐方式
组件在layout里面的对齐方式。
8) gravity - 文字在组件里的对齐方式
例如设置button里面的文字在button中居中显示。
* 大多数属性是可以调用对应的函数来动态改变状态的,请查看SDK Doc。
2. Linear Layout 线形布局
orientation - 容器内元素的排列方式。vertical: 子元素们垂直排列,horizontal: 子元素们水平排列。在代码里可通过setOrientation()进行动态改变,值分别为HORIZONTAL或者VERTICAL。
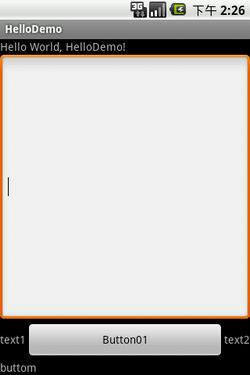
* 在Linear Layout, 宽度/高度都是按着组件的次序逐个占用的!所以当某个组件设置"fill_parent",在没有设置Layout_weight的情况下,该组件会占用了余下的空间,那么在它后面的组件就会显示不出来。如下图的EditText如果没有设置android:layout_weight="1", 它下面的其他组件就看不见了!
baselineAligned 一般情况下,这个属性默认为true,代表在同一方向的组件都基于第一个组件对齐。所以可以看到下图的text1, button1, text2是在同一水平线的。当不需要这效果时,可以设置为false。
可以参考官方网页http://androidappdocs.appspot.com/resources/tutorials/views/hello-linearlayout.html。
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
- <TextView
- android:text="@string/hello"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- <EditText
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_weight="1"
- android:id="@+id/edittext"
- />
- <LinearLayout
- android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal">
- <TextView
- android:text="text1"
- android:id="@+id/TextView01"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- <Button android:text="Button01"
- android:id="@+id/Button01"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_weight="1"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="text2"
- android:id="@+id/TextView02"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="buttom"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
3. RelativeLayout 相对定位布局
这个布局比较易懂,但组件间容易存在依赖关系,“牵一发而动全身“,所以在确定组件间布局关系不会再变动时,可以考虑采用!先看看xml代码:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <RelativeLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/relativelayout">
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/image"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/icon"
- />
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/text1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/hello"
- android:layout_toRightOf="@id/image"
- />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/button1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="button1"
- android:layout_toRightOf="@id/image"
- android:layout_below="@id/text1"
- />
- </RelativeLayout>
Java代码(动态添加组件):
- public class RelativeDemo extends Activity {
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.relative);
- RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, //width
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT //height
- );
- //设置editText layout_below="@id/button1"
- lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, R.id.button1);
- //设置editText layout_alignLeft="@id/image"
- lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_LEFT, R.id.image);
- ((RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.relativelayout)).addView(
- new EditText(this), lp);
- }
- }
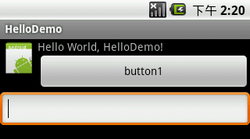
效果图:
先添加参照物(ImageView),然后就可以依次添加其他组件,定义位置规则rule!位置规则是不分先后的!另外ADT插件提供的预览图,有时候是不准的,未能及时更新,所以最好还是要到模拟器上测试!
RelativeLayout的xml属性很多,总的来说分为2类:
1) 要指定参照物的,layout_alignBottom,layout_toLeftOf,layout_above,layout_alignBaseline系列的;
layout_above = ”@id/text1“
2) 以parent为参照物,设置true/false,layout_centerVertical,layout_alignParentLeft系列的。
layout_alignParentLeft = ”true“
其中layout_alignWithParentIfMissing是比较有用且要注意的属性,当设置为true,在指定的参照物找不到的情况下,会使用parent作为新的参照物!
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams是用于设置位置规则的。上述的xml属性均来自此静态类。但它的AddRule(int verb, int anchor),参数的verb动作却是引用RelativeLayout的常量,而这些常量和部分xml属性相对应。参数anchor的值可能是参照物的id,RelativeLayout.TRUE,-1(当不需要指定anchor的verb)。可以这样理解verb和anchor:
xml属性 (verb) = "value" (anchor)
其中它的构造函数之一: RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h),参数指定所要设置子View的宽度和高度。
关注微信号:javalearns 随时随地学Java
或扫一扫

随时随地学Java