怎样对一个网站做性能测试/优化网站怎么做
Association Rules关联规则
- Apriori property (downward closure property)
- Evaluation of Candidate Rules
•一种无监督学习方法
•描述性的,而不是预测性的
•发现有趣的、隐藏的关系 -表示为规则或频繁项目集
•通常用于挖掘数据库中的 transactions
Each transaction consists of one or more items
Itemset
– A collection of items or individual entities that contain some kind of relationship
k-itemset
– An itemset containing k items– {item1, item2, …, item k}
Apriori algorithm
– One of the earliest and the most fundamental algorithms for generating association rules.
Support
– Given an item X, the support of X is the percentage of transactions that contain X
– Denoted by support(X)
Frequent itemset
– Contains items that appear together often enough
– Formally, its support >= a minimum support
当最小支持度设置为 0.5时 ,如果至少 50%交易包含某个项集,那么该项集可以被认为是一个频繁项集。
Apriori property (downward closure property)
– If an itemset is frequent, then any subset of this itemset must also be frequent
– It provides the basis for the Apriori algorithm
如果一个项目集是频繁的,那么这个项目集的任何子集也必须是频繁的
举个例子方便理解:
如果 60%的交易包含{bread,jam},那么至少 60%的交易将包含{bread}或{jam}。换句话说,当{bread,jam}的支持度为 0.6 时,{bread}或{jam}的支持度至少为 0.6.

It takes a bottom-up iterative approach to uncovering frequent itemsets
– First, identify all frequent items (or 1-itemsets).
– The identified frequent 1-itemsets are paired into 2-itemsets to identify frequent 2-itemsets.
– Grow the size of identified frequent itemsets and identify again.
– Repeat this process until 1) it runs out of support or 2) the itemsets reach a predefined length.
Apriori 算法的下一次迭代中,所识别的频繁 1 项集被配对成 2 项集(例如,{面包,鸡蛋}, {面包,牛奶}, {鸡蛋,牛奶}, …),并再次进行评价以确定当中的频繁 2 项集。在每次迭代中,算法检查支持度准则是否被满足;如果满足,算法将增大项集并重复这个过程,直到支持度过低,或者项集达到了预定长度。
So, the input is:

Output of the Apriori algorithm– The collection of all the frequent k-itemsets
接下来,将以前面讲解的迭代过程中发现的频繁项集为基础,形成一个候选规则candidate rules的集合。
例如,一个频繁项集{milk,eggs}可以表示出候选规则{mils}→{eggs}和{eggs}→{milk}。
Evaluation of Candidate Rules
频繁项集可以形成候选规则,比如 X 意味着 Y(X → Y)。我们讨论如果使用诸如置信度、
提升度和杠杆率这样的度量来评估这些候选规则是否合适。
Confidence
– The measure of certainty or trustworthiness associated with each rule
置信度是同时包含 X 和 Y 的交易与所有包含 X 的交易的百分比
例如,如果{bread,eggs,milk}的支持度为 0.15,{bread,eggs}的支持度也为 0.15,规则{bread,eggs}→{milk}的置信度为 1,这意味着客户在购买面包和鸡蛋时,肯定也会购买牛奶。
我们需要设置Minimum Confidence来判定在什么置信度以上我们认为两者关系是有趣的。
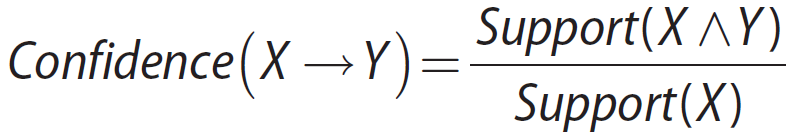
Lift
– Measures how many times more often X and Y occur together than expected if they are
statistically independent of each other.
– Measures how X and Y are really related rather than coincidentally happening together
– Lift is 1 if X and Y are statistically independent of each other.
– A lift of X → Y greater than 1 indicates some usefulness of the rule.
– A larger lift suggests a greater strength of the association between X and Y.
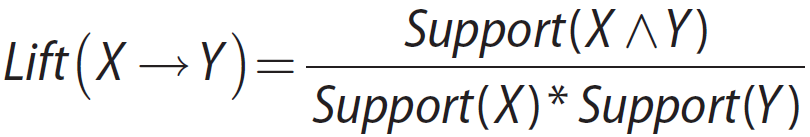
提升度(lift)测量当 X 和 Y 相互统计独立时,X 和 Y 一起出现的次数比预期多多少。提升度是 X 和 Y 真正相关性(而非巧合地共同出现)的一种度量
如果 X 和 Y 相互统计独立的,那么提升度为是 1。相比之下,规则 X→Y 的提升度大于 1则表示规则是有用的。提升度的值越大,表明 X 和 Y 之间的关联性更强。
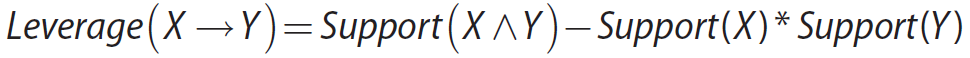
Leverage (Pitetsky-Shapiro’s)
– Measures the difference in the probability of X and Y appearing together compared to what would be expected if X and Y were statistically independent of each other
– Its value will be zero when X and Y are statistically independent of each other.
– If X and Y have some kind of relationship, the leverage would be greater than zero.
X 和 Y 相互统计独立时,杠杆率为 0。如果 X 和 Y 具有某种关系,杠杆率
将大于 0。较大的杠杆率表示 X 和 Y 之间有更强的联系。
置信度能够识别信的规则,但是它不能确定这个规则是否是巧合。高置信度的规则有时会
产生误导,因为置信度没有考虑规则右边(RHS)项集的支持度。提升度和杠杆率等度量不但
能确保识别出有趣的规则,还能过滤出巧合的规则。
Combination of Measures
– Measures are often used in combination.
– Example: Find all rules with a minimum level of confidence then, of those rules, sort rules in descending order by lift or leverage.
参考书目
-
Data Science and Big Data Analytics: Discovering, Analyzing, Visualizing and Presenting Data, EMC Education Services, John Wiley & Sons, 27 Jan. 2015
-
Data Mining: The Textbook by Charu C. Aggarwal, Springer 2015
-
C.M. Christopher, P. Raghavan and H. Schutze. Introduction to Information Retrieval, Cambridge University Press. 20084.
-
Computer Vision: A Modern Approach (2nd Edition), by David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce, Pearson, 2011.
图片来自课件和个人的整理。
中文图片来自网络。
