风水网站建设的策划书/黑帽seo联系方式
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (21) — 之如何恢复训练
文章目录
- [源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (21) --- 之如何恢复训练
- 0x00 摘要
- 0x01 总论
- 0x02 Sampler
- 2.1 PyTorch Distributed Optimizer
- 2.1.1 定义
- 2.1.2 问题点
- 2.2 ElasticSampler
- 2.2.1 定义
- 2.2.2 弹性方案
- 2.2.2.1 常规流程
- 2.2.2.2 异常处理
- 2.2.1 如何使用
- 2.2.1.1 主体代码
- 2.2.1.2 训练代码
- 0x03 保存和定期检查
- 3.1 定期保存
- 3.2 异常处理
- 3.3 Commit
- 0x04 State
- 4.1 恢复训练
- 4.2 TorchState
- 4.3 设置 handler
- 4.4 SamplerStateHandler
- 4.5 保存
- 4.6 HostsUpdatedInterrupt
- 4.7 HorovodInternalError
- 4.8 `ElasticSampler.__iter__`
- 0xEE 个人信息
- 0xFF 参考
0x00 摘要
本文以 PyTorch on Horovod 为切入点,分析一下 Horovod 弹性训练的恢复流程,具体涉及知识点有:
ElasticSampler与PyTorch 原生DistributedSampler 的区别,Horovod 弹性训练如何恢复等。
本系列其他文章链接如下:
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 Horovod — (1) 基础知识
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (2) — 从使用者角度切入
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (3) — Horovodrun背后做了什么
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (4) — 网络基础 & Driver
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (5) — 融合框架
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (6) — 后台线程架构
[\源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (7) — DistributedOptimizer
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (8) — on spark
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (9) — 启动 on spark
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (10) — run on spark
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (11) — on spark — GLOO 方案
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (12) — 弹性训练总体架构
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (13) — 弹性训练之 Driver
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (14) — 如何发现节点挂了?
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (15) — 广播 & 通知
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (16) — 弹性训练之Worker生命周期
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (17) — 弹性训练之容错
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (18) — kubeflow tf-operator
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (19) — kubeflow MPI-operator
[源码解析] 深度学习分布式训练框架 horovod (20) — Elastic Training Operator
0x01 总论
本文缘起于一个兄弟的留言:
请问在弹性训练中,如果节点数目发生变化,数据怎么重新划分呢?比如一个epoch还没有进行完,这时添加了新节点,新数据重新划分的话,当前内存中用旧数据训练的模型还有效吗?
我恰好在分析PyTorch分布式的时候也有类似疑问,所以就回头再看看Horovod是如何实现的。
我们之前对于 Horovod 的分析和示例大多以 TensorFlow 为例。大家对各种框架如何在Horovod之中适配的总体逻辑和思路应该有了一个大致的认识,所以我们本部分主要看看一些PyTorch 相关的特殊之处。
使用PyTorch做切入的另外一个原因是:在恢复训练这个流程上,PyTorch相关部分确实相对清晰明确。
在 horovod/torch/elastic/ 目录下,有两个文件 :state.py 和 sampler.py。既然是弹性相关,所以我们先来看看其特殊之处。
0x02 Sampler
在 horovod/torch/elastic/sampler.py 之中,有一个 ElasticSampler 类,我们看看具体针对弹性做了哪些处理。
因为 ElasticSampler 类之中注明,它的实现非常类似DistributedSampler,也就是 PyTorch 原生的实现,所以我们要先看看 DistributedSampler。
2.1 PyTorch Distributed Optimizer
2.1.1 定义
DistributedSampler代码位于:torch/distributed/optim/optimizer.py。
总结一下DistributedSampler的分配方法是:每段连续的 num_replicas 个数据被拆成一个一个,分给 num_replicas 个进程,这样就达到了不重叠不交叉的目的,但也要注意的是:这样每个进程拿到的数据是不连续的。
__iter__ 代码的一个技术细节是 本worker如何遍历?
indices = indices[self.rank:self.total_size:self.num_replicas]
这里,num_replicas 实际就是rank的总数,起始位置是self.rank,结束位置是总数据长度,按照num_replicas(就是world size)作为步长来递增,所以这里每个worker就会严格返回自己rank对应的那部分数据序号。
我们用一个例子来看看,比如:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]
print(a[0:15:3])
print(a[1:15:3])
print(a[2:15:3])
得到:
[1, 4, 7, 10, 13]
[2, 5, 8, 11, 14]
[3, 6, 9, 12, 15]
具体代码如下:
class DistributedSampler(Sampler[T_co]):def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[T_co]:if self.shuffle: # 如果需要shuffle,则会基于epoch和seed进行处理# deterministically shuffle based on epoch and seedg = torch.Generator()g.manual_seed(self.seed + self.epoch)indices = torch.randperm(len(self.dataset), generator=g).tolist() # type: ignore[arg-type]else: # 否则直接返回数据集长度序列indices = list(range(len(self.dataset))) # type: ignore[arg-type]# 是否需要补齐数据if not self.drop_last:# add extra samples to make it evenly divisiblepadding_size = self.total_size - len(indices)if padding_size <= len(indices):indices += indices[:padding_size]else:indices += (indices * math.ceil(padding_size / len(indices)))[:padding_size]else:# remove tail of data to make it evenly divisible.indices = indices[:self.total_size]assert len(indices) == self.total_size# subsample# 依据自己的rank,依次返回自己的数据序号indices = indices[self.rank:self.total_size:self.num_replicas]assert len(indices) == self.num_samplesreturn iter(indices) # 后续就使用这些indices来对数据进行提取def __len__(self) -> int:return self.num_samplesdef set_epoch(self, epoch: int) -> None:r"""Sets the epoch for this sampler. When :attr:`shuffle=True`, this ensures all replicasuse a different random ordering for each epoch. Otherwise, the next iteration of thissampler will yield the same ordering.Args:epoch (int): Epoch number."""self.epoch = epoch
2.1.2 问题点
DistributedSampler 如果直接用到 弹性训练,是有一定问题的,让我们分析一下,有几个问题:
- 如果用户已经训练了5轮,那么就意味着已经使用了前面5个批次的数据。假设此时加入了新的worker节点,那么就应该恢复训练。那么对于已经使用过的前面 5 个批次的数据,按说就不应该再次被用来训练了。
- 问题1: 恢复训练之后,应该怎么去除已经处理的数据index?
- 如果加入或者减少节点,如果告诉 Sampler,我们需要更改提取规则,最起码,num_replicas 需要被更新,以后按照新的 num_replicas 进行提取,比如原来5个节点,num_replicas = 5,现在6个节点,num_replicas 应该为 6。
- 问题2: 恢复训练之后,何时调用
__iter__以进行新的训练? - 问题3: 恢复训练之后,何时修改 num_replicas?
- 问题2: 恢复训练之后,何时调用
我们看看 DistributedSampler 就会发现,其__iter__之中,没有任何保存状态的相关信息。即如果重新开始训练,依然会从全体数据中提取,而非从剩余数据中提取。也没有发现对后面两个问题的解决办法。
因此,很难利用 DistributedSampler进行弹性训练,所以 Horovod 就使用 ElasticSampler 来解决这个问题。
2.2 ElasticSampler
2.2.1 定义
从注释中我们可以看到,ElasticSampler 自称与 DistributedSampler 非常类似。我们随后针对两个类代码比较可以看到,功能基本一致。
但是有两个新加入的变量值得注意,即:
self.processed_indices = set()self.remaining_indices = []
定义如下:
import math
import random
import torch.utils.data.distributed
from horovod.torch.mpi_ops import rank, sizeclass ElasticSampler(torch.utils.data.Sampler):"""Sampler that partitions dataset across ranks and repartitions after reset events.Works similar to `DistributedSampler`, but with an optional capability to recordwhich dataset indices have been processed each batch. When tracked by a `TorchState`object, the sampler will automatically repartition the unprocessed indices among thenew set of workers.In order to use this object successfully it is recommended that the user:1. Include this object in the `TorchState`.2. Call `record_batch` or `record_indices` after processing a set of samples.3. Call `set_epoch` at the end of each epoch to clear the processed indices.Args:dataset: Dataset used for sampling (assumed to be of constant size).shuffle: If `True` (default), shuffle the indices.seed: Random seed used to shuffle the sampler when `shuffle=True`.This number should be identical across all ranks (default: 0)."""def __init__(self, dataset, shuffle=True, seed=0):self.dataset = datasetself.shuffle = shuffleself.seed = seedself.epoch = 0self.processed_indices = set() # 新加入的特色成员变量self.num_replicas = 0self.rank = 0self.remaining_indices = [] # 新加入的特色成员变量self.num_samples = 0self.total_size = 0self.reset()2.2.2 弹性方案
具体弹性方案就围绕之前提到的两个变量来进行。
2.2.2.1 常规流程
我们回忆其注释中提到的如何使用:
1. Include this object in the `TorchState`.
2. Call `record_batch` or `record_indices` after processing a set of samples.
3. Call `set_epoch` at the end of each epoch to clear the processed indices.
我们可以推导出来其内在逻辑:
- 进行本 epoch 训练。
- 当使用
__iter__获取下一批次数据时候,self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:]就会 只从未训练的数据里面提取。 - 每处理一个批次数据 之后,用户使用
record_batch或者record_indices来把已经训练完的数据批次信息保存在processed_indices。这样就记录了已经训练完的数据。 - 如果产生了问题,或者有节点变更,则:
- 会调用 reset 函数,reset 会把已经训练完的数据
processed_indices从总数据中移除,剩下的self.remaining_indice就是没有训练的数据。 - 恢复训练, 只从未训练的数据里面提取。
- 会调用 reset 函数,reset 会把已经训练完的数据
- 当使用
- 当完成这个epoch 之后,会调用
set_epoch来重置processed_indices,也会调用 reset 方法进行清零。
具体功能代码是:
def set_epoch(self, epoch):"""Sets the epoch for this sampler.When `shuffle=True`, this ensures all replicas use a different random orderingfor each epoch.Will clear and reset the `processed_indices` for the next epoch. It is importantthat this is called at the end of the epoch (not the beginning) to ensure thatpartially completed epochs do not reprocess samples.Args:epoch: Epoch number."""self.epoch = epoch# 这里也许有网友会有疑问,就是下面两行代码应该交换一下次序。# 但是实际上是没有问题的,因为 reset 其实在异常处理时候的作用更大,在这里其实就是个清零作用。self.processed_indices = set()self.reset()def record_batch(self, batch_idx, batch_size):"""Record indices at batch `batch_idx` with length `batch_size` as processed."""indices = set(self.get_indices(batch_idx, batch_size))self.record_indices(indices)def record_indices(self, indices):"""Record set `indices` as processed."""self.processed_indices.update(indices) # 记录已经训练完的数据def get_indices(self, batch_idx, batch_size):"""Return list of indices at batch `batch_idx` with length `batch_size`."""start_idx = batch_idx * batch_size end_idx = min(start_idx + batch_size, len(self.indices))return self.indices[start_idx:end_idx]def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):self.epoch = state_dict['epoch']self.processed_indices = state_dict['processed_indices'] # 从保存的数据中提取self.reset()def state_dict(self):return dict( # 这里是为了State.save 时候调用,就是模型保存时候,需要保存这两个变量epoch=self.epoch,processed_indices=self.processed_indices)def reset(self):# size 代码位于horovod/torch/mpi_ops.py,是 size = _basics.size,可以认为就是 hvd.size()self.num_replicas = size() # 重新配置有几个workerself.rank = rank()# Exclude any samples we have already processed this epoch# 把已经训练完的数据移除,得到的数据 remaining_indices 都是没有经过训练的self.remaining_indices = [idx for idx in range(len(self.dataset))if idx not in self.processed_indices]self.num_samples = int(math.ceil(len(self.remaining_indices) * 1.0 / self.num_replicas))self.total_size = self.num_samples * self.num_replicasdef __iter__(self): self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:] # 从剩余数据中提取if self.shuffle:# Shuffle indices across workers deterministically in placeseed = self.seed + self.epochrandom.Random(seed).shuffle(self.indices)# add extra samples to make it evenly divisibleself.indices += self.indices[:(self.total_size - len(self.indices))]assert len(self.indices) == self.total_size# subsample# 本worker如何遍历?起始index是self.rank,终止index是总数据长度,按照num_replicas来递增self.indices = self.indices[self.rank:self.total_size:self.num_replicas]assert len(self.indices) == self.num_samples# 后续就按照上面的遍历逻辑来遍历return iter(self.indices) def __len__(self):return self.num_samples
2.2.2.2 异常处理
在 horovod/torch/elastic/state.py 之中,当重新训练时候,会调用到 ElasticSampler 的 load_state_dict 方法。
而 load_state_dict 之中,会调用 reset,这样就把已经训练完的数据移除,得到的数据都是没有经过训练的。
所以重新训练时候,本epoch之内,不会用已经训练的数据再次重复训练。
我们后续会详细分析这个流程。
2.2.1 如何使用
ElasticSampler 的使用如下,代码位于:examples/elastic/pytorch/pytorch_imagenet_resnet50_elastic.py。
本节我们主要介绍如何使用,就是正常使用/处理流程,后续会介绍异常处理,这里省略部分次要代码。
2.2.1.1 主体代码
主体代码主要注意就是使用ElasticSampler分别配置了两个弹性采样器。
if __name__ == '__main__':allreduce_batch_size = args.batch_size * args.batches_per_allreduce# Elastic Horovod: use ElasticSampler to partition data among workers.train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder()train_sampler = hvd.elastic.ElasticSampler(train_dataset) # 配置了弹性采样train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,batch_size=allreduce_batch_size,sampler=train_sampler,**kwargs)val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder()val_sampler = hvd.elastic.ElasticSampler(val_dataset) # 配置了弹性采样val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,batch_size=args.val_batch_size,sampler=val_sampler,**kwargs)# Set up standard ResNet-50 model.model = models.resnet50()# Horovod: scale learning rate by the number of GPUs.optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=(args.base_lr *lr_scaler),momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.wd)# Horovod: wrap optimizer with DistributedOptimizer.optimizer = hvd.DistributedOptimizer(optimizer, named_parameters=model.named_parameters(),compression=compression,backward_passes_per_step=args.batches_per_allreduce,op=hvd.Adasum if args.use_adasum else hvd.Average,gradient_predivide_factor=args.gradient_predivide_factor)# Restore from a previous checkpoint, if initial_epoch is specified.# Horovod: restore on the first worker which will broadcast weights to other workers.state = hvd.elastic.TorchState(model=model,optimizer=optimizer,train_sampler=train_sampler,val_sampler=val_sampler,epoch=resume_from_epoch,batch=0)full_train(state)
2.2.1.2 训练代码
以下代码是具体训练代码。
def train(state):model.train()epoch = state.epochbatch_offset = state.batchwith tqdm(total=len(train_loader),desc='Train Epoch #{}'.format(epoch + 1),disable=not verbose) as t:# 循环获取数据,会间接调用到 ElasticSampler 的 __iter__ 方法来获取数据 indexfor idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):# Elastic Horovod: update the current batch index this epoch# and commit / check for host updates. Do not check hosts when# we commit as it would be redundant.state.batch = batch_idx = batch_offset + idxif args.batches_per_commit > 0 and \state.batch % args.batches_per_commit == 0:state.commit()elif args.batches_per_host_check > 0 and \state.batch % args.batches_per_host_check == 0:state.check_host_updates()adjust_learning_rate(epoch, batch_idx)optimizer.zero_grad()# Split data into sub-batches of size batch_sizefor i in range(0, len(data), args.batch_size):data_batch = data[i:i + args.batch_size]target_batch = target[i:i + args.batch_size]output = model(data_batch)train_accuracy.update(accuracy(output, target_batch))loss = F.cross_entropy(output, target_batch)train_loss.update(loss)# Average gradients among sub-batchesloss.div_(math.ceil(float(len(data)) / args.batch_size))loss.backward()# Elastic Horovod: record which samples were processed this batch# so we do not reprocess them if a reset event occurs# 这里会记录已经完成的数据state.train_sampler.record_batch(idx, allreduce_batch_size)# Gradient is applied across all ranksoptimizer.step()state.commit()def end_epoch(state):state.epoch += 1state.batch = 0state.train_sampler.set_epoch(state.epoch) # 这里会对剩余数据信息清零state.commit()@hvd.elastic.run
def full_train(state):while state.epoch < args.epochs:train(state)validate(state.epoch)save_checkpoint(state.epoch)end_epoch(state) # 这里会对剩余数据信息清零
某一个epoch具体逻辑(正常处理)如下:
- 如果是最初运行,则调用reset进行初始化,其中会依据 dataset 长度构建一个 index list。用这个index list 减去 processed_indices ,就得到了本次epoch应该处理的数据 index,赋值给 remaining_indices,就是剩下来应该处理的数据index;
- 在
__iter__函数中,调用self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:],这样 indices 就可以用来做迭代提取; - 训练函数中,调用 iter(indices) 进行迭代提取,然后调用 record_indices 把本次使用过的index 更新到 processed_indices 之中。processed_indices 就记录了目前使用的所有index;
- epoch 结束之后,调用 set_epoch 进行重置,即给 processed_indices 清零,调用 reset 重置 remaining_indices;
+---------------------------------------------------------------+| ElasticSampler || |+--------------------------------------------> + |
4 | set_epoch | | || | | || | 1 | reset || | | || | | || | v || | || | remaining_indices = dataset - processed_indices || | || | + || | | || | | || | 2 | __iter_ || | | || | | || | v || | indices = remaining_indices[:] || | + || | | || +---------------------------------------------------------------+| || 3 || || v| +--------------------------------------+------------------------------------+| | train() train loop || | || | ----------------------------> iter(indices)+--------------------> || | ^ | || | | | || | step() backward() || | | +----------------------------------------+ | || | | |record_indices | | || | | | | | || | <-------------+ processed_indices.update(indices) +------+ v || | | | || | +----------------------------------------+ || | || +---------------------------------------+-----------------------------------+| || |+-----------------------------------------------+
0x03 保存和定期检查
3.1 定期保存
Hovorod 建议用户定周期性调用 state.commit() 来把状态(state)备份到内存。
- 定期备份非常有用。在某些worker发生意外错误时,定期备份可以避免因为状态被损坏而在重新训练时候无法恢复现场。比如,如果一个worker刚好在更新参数过程中突然出错,此时部分梯度更新完毕,部分梯度可能只更新到一半,这个状态是不可逆转而又无法继续。因此,当此状态发生时,会抛出一个 HorovodInternalError 异常,当 hvd.elastic.run 捕获到这个异常后,会利用最新一次commit中恢复所有状态。
- 因为commit状态代价高昂(比如如参数量太大会导致耗时过长),所以需要在"每个batch的处理时间"与"如果出错,训练需要从多久前的状态恢复"之间选取一个平衡点。比如,如果你每训练10个batches就commit一次,你就把复制时间降低了10倍。但是当发生错误时,你需要回滚到10个batches前的状态。
- Elastic Horowod可以通过执行我们称之为“优雅地移除worker”操作来避免这些回滚。如果driver进程发现主机已可用或标记为删除,它将向所有workers推送一个通知。于是在下次调用state.commit()或更轻量级的state.check_host_updates()时,一个HostsUpdatedInterrupt异常将被抛出。此异常的处理方式与“HorovodInternalError”类似,只是参数状态不会还原到上次commit,而是从当前实时参数中恢复。
- 一般来说,如果你的硬件设施是可靠与稳定的,并且你的编排系统会在任务节点移除时提供足够的告警,你就可低频次调用 state.commit() 函数,同时只在每个batch结束时调用相对不耗时的 state.check_host_updates() 来检查节点变更情况。
具体示例代码如下:
@hvd.elastic.run
def train(state):for state.epoch in range(state.epoch, epochs):for state.batch in range(state.batch, batches_per_epoch):data, target = get_random_batch()train_one_batch(data, target)if state.batch % batches_per_commit == 0:state.commit() # 定期保存state.batch = 0
3.2 异常处理
我们可以看到,HorovodInternalError 和 HostsUpdatedInterrupt 这两个异常最大的区别:
- HorovodInternalError 异常:当 hvd.elastic.run 捕获到这个异常后,会利用最新一次commit中恢复所有状态。
- HostsUpdatedInterrupt 异常:处理方式与“HorovodInternalError”类似,只是参数状态不会还原到上次commit,而是从当前实时参数中恢复。
之所以要强调这个,因为后面就要介绍如何做到不同恢复。
3.3 Commit
在用户调用 State.commit 的时候,有两个动作:一个是保存状态。一个是调用 check_host_updates 检查更新。
class State(object):"""State representation used for tracking in memory state across workers."""def commit(self):self.save()self.check_host_updates()
这里 save 就会调用到 State 的 save 操作,结合本文,就是下面要介绍的 TorchState 的 save 操作。
另外,check_host_updates 会抛出HostsUpdatedInterrupt异常。HostsUpdatedInterrupt 异常里面,是否需要 sync,从下面 check_host_updates 代码可以看出来,就是如果节点数目有变化了,就需要sync。HostUpdateResult.removed 数值为1,这里其实可以改进,HostUpdateResult.removed 在目前这个情况之下,设定过细了。
class HostUpdateResult(IntFlag):no_update = 0removed = 1added = 2mixed = removed | addeddef check_host_updates(self):"""Checks that a notification has been sent indicating that hosts can be added or will be removed.Raises a `HostsUpdatedInterrupt` if such a notification has been received."""# Iterate through the update messages sent from the server. If the update timestamp# is greater than the last update timestamp, then trigger a HostsUpdatedException.last_updated_timestamp = prev_timestamp = self._last_updated_timestampall_update = HostUpdateResult.no_updatewhile not self._host_messages.empty():timestamp, update = self._host_messages.get()if timestamp > last_updated_timestamp:last_updated_timestamp = timestampall_update |= update# In order to ensure all workers raise the exception at the same time, we need to sync# the updated state across all the workers.# TODO(travis): this should be a max allreduce to account for changes in rank 0prev_timestamp, self._last_updated_timestamp, all_update = \self._bcast_object((prev_timestamp, last_updated_timestamp, all_update))# At this point, updated state is globally consistent across all ranks.if self._last_updated_timestamp > prev_timestamp:# 在这里设定,其实含义就是:如果节点有变化,就设置为True,需要同步raise HostsUpdatedInterrupt(all_update == HostUpdateResult.removed) # 抛出异常
0x04 State
我们接下来介绍异常处理逻辑,具体围绕着 State 来介绍。对于State,我们先回忆一下其在恢复训练时候的逻辑。
4.1 恢复训练
重新训练时候,会抛出两种异常:
- 如果是 ring allreduce 相关,就转为抛出异常 HorovodInternalError(e)。
- 如果当驱动进程通过节点发现脚本发现一个节点被标记为新增或者移除时,会抛出异常 HostsUpdatedInterrupt。
然后会进行如下处理:
def run_fn(func, reset):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(state, *args, **kwargs):notification_manager.init()notification_manager.register_listener(state)skip_sync = Falsetry:while True:if not skip_sync:state.sync() # 进行同步try:return func(state, *args, **kwargs)except HorovodInternalError:state.restore() # 进行恢复训练skip_sync = False # 需要同步except HostsUpdatedInterrupt as e:skip_sync = e.skip_sync # 记录是否需要同步reset()state.on_reset() # 进行重启finally:notification_manager.remove_listener(state)return wrapper
逻辑如下:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Worker |
| |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | run_fn | |
| | +----------------------------------+ | |
| | | while True: | | |
| | | | | |
| | v | | |
| | | | |
| | state.sync() | | |
| | + | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | v | | |
| | +------------------+---------------+ | | |
| | | train | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | optimizer.apply_gradients +---------+ | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | +-------+ state.commit() | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | +----------------------------------+ | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | v v | | |
| | HostsUpdatedInterrupt HorovodInternalError | | |
| | + | | |
| | + | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | v | | |
| | | state.restore() | | |
| | | + | | |
| | | | | | |
| | +------------------+ <------------------+ | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | v v | | |
| | reset() | | |
| | | | |
| | state.on_reset() | | |
| | | | |
| | + | | |
| | | | | |
| | +-----------------------------------> | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
因为这里涉及了大量的state操作,所以我们接下来要看看 TorchState:
4.2 TorchState
首先,我们要看看 TorchState 如何使用。当调用时候,使用如下方法来生成一个TorchState:
state = hvd.elastic.TorchState(model, optimizer, batch=0, epoch=0)state.register_reset_callbacks([on_state_reset]) # 注册用户定义的方法 on_state_resettrain(state)
其次,我们看看 TorchState 的定义,这里的 sync,restore,reset方法就在恢复训练中被调用。
在初始化函数 __init__ 之中,会设置 handler,以我们的调用为例,就是 train_sampler,val_sampler这两个对应的sampler会配置对应的handler,即SamplerStateHandler。
TorchState 继承了 ObjectState,ObjectState 继承了 State,所以前面提到的 commit 代码中的 self.save(),就会调用到TorchState.save,而这里又会调用到 SamplerStateHandler.save。
class TorchState(ObjectState):"""State representation of a PyTorch training process.Multiple models and optimizers are supported by providing them askwargs. During initialization, `TorchState` will assign attributesfor every keyword argument, and handle its state synchronization.Args:model: Optional PyTorch model.optimizer: Optional PyTorch optimizer.kwargs: Attributes sync, will be exposed as attributes of the object. If a handler existsfor the attribute type, it will be used to sync the object, otherwise it will behandled an ordinary Python object."""def __init__(self, model=None, optimizer=None, **kwargs):kwargs.update(dict(model=model, optimizer=optimizer))# 这里会设置 handler,以我们的调用为例,就是train_sampler,val_sampler这两个对应的sampler会配置对应的handlerself._handlers, kwargs = _get_handlers(kwargs) for name, handler in self._handlers.items():setattr(self, name, handler.value)super(TorchState, self).__init__(bcast_object=broadcast_object,get_rank=rank,**kwargs)def save(self):for handler in self._handlers.values():handler.save() # 调用到save,针对我们,就是调用到了SamplerStateHandler的savesuper(TorchState, self).save()def restore(self):# 会进行恢复状态for handler in self._handlers.values():handler.restore() # 这里会调用到sampler的restore方法。super(TorchState, self).restore()def sync(self):# 会进行同步状态for handler in self._handlers.values():handler.sync() # 这里会调用到sampler的sync方法。super(TorchState, self).sync()def __setattr__(self, name, value):if hasattr(self, name) and name in self._handlers:self._handlers[name].set_value(value)super().__setattr__(name, value)
基类代码中有:
class State(object):def on_reset(self):self._host_messages = queue.Queue()self.reset() # 调用到resetfor callback in self._reset_callbacks:callback()
4.3 设置 handler
上节中,我们可以看到,无论是reset,还是restore,都会调用到 _handlers 来进行处理,所以我们需要进一步分析。
首先就是如何设置handler。具体参见如下代码,主要是通过一个全局配置 _handler_registry 来指定哪个 handler 处理哪种类型实例,比如这里有 (ElasticSampler, SamplerStateHandler),就代表着 SamplerStateHandler 是用来处理 ElasticSampler的 handler。
_handler_registry = [(torch.nn.Module, ModelStateHandler),(torch.optim.Optimizer, OptimizerStateHandler),(ElasticSampler, SamplerStateHandler), # SamplerStateHandler 是用来处理 ElasticSampler的
]def get_handler_registry():return _handler_registrydef set_handler_registry(registry):global _handler_registry_handler_registry = registrydef _get_handler(v): # 依据我们的样例代码,v是 train_sampler,而 train_sampler,val_sampler就是 ElasticSampler 的实例,所以得到 handler_type是 ElasticSampler,则会构建一个 SamplerStateHandler 并且返回for handler_type, handler_cls in _handler_registry:if isinstance(v, handler_type):return handler_cls(v) # 调用 SamplerStateHandler(train_sampler) 生成实例return Nonedef _get_handlers(kwargs):handlers = {}remainder = {}# 这里k,v就是 train_sampler=train_sampler,所以 k 是 "train_sampler", v是实例 train_samplerfor k, v in kwargs.items():handler = _get_handler(v)if handler:handlers[k] = handlerelse:remainder[k] = vreturn handlers, remainder
4.4 SamplerStateHandler
既然知道了 ElasticSampler 由 SamplerStaeHandler 处理,就来分析一下 SamplerStateHandler。
初始化之后,self.value 就是 sampler,针对我们之前的分析,就是ElasticSampler。
SamplerStateHandler 具体代码是,这里需要注意的是:初始化时候,会把ElasticSampler的状态保存起来,以后如果出错,会用此来恢复。
同时,save 也会被调用,用来恢复,我们马上就会分析。
class SamplerStateHandler(StateHandler):def __init__(self, sampler):super().__init__(sampler)# 这里会保存 ElasticSampler 的属性和数据self._saved_sampler_state = copy.deepcopy(self.value.state_dict())def save(self):# 保存 ElasticSampler 的属性和数据self._saved_sampler_state = copy.deepcopy(self.value.state_dict())def restore(self):# load_state_dict 会用__init__ 之中保存的原始数据来恢复,最终会调用到 ElasticSampler.reset 方法self.value.load_state_dict(self._saved_sampler_state)def sync(self):# 1)Get the set of processed indices from all workersworld_processed_indices = _union(allgather_object(self.value.processed_indices))# 2) Replace local processed indices with global indicesstate_dict = self.value.state_dict() # 这里会调用到 ElasticSampler 的 state_dict 方法state_dict['processed_indices'] = world_processed_indices# 3) Broadcast and load the state to make sure we're all in sync# 注意,这里的 load_state_dict 最终也会调用一次 resetself.value.load_state_dict(broadcast_object(state_dict))
SamplerStateHandler 的 基类是:
class StateHandler(object):def __init__(self, value):self.value = valuedef save(self):raise NotImplementedError()def restore(self):raise NotImplementedError()def sync(self):raise NotImplementedError()def set_value(self, value):self.value = valueself.save()
4.5 保存
我们拓展一下save相关操作序列。
TorchState 继承了 ObjectState,ObjectState 继承了 State,所以:
- 前面提到的 commit 代码中的 self.save(),就会调用到TorchState.save。
- 而TorchState.save又会调用到 SamplerStateHandler.save。
- SamplerStateHandler.save 会保存 ElasticSampler 的属性和数据,就是保存了 ElasticSampler 的 epoch 和 processed_indices。
这样,在定期 commit 的时候,就定期保存了模型的状态和 ElasticSampler 的状态,这些会在恢复训练中用到。具体下图所示:
+---------------------------+| TorchState || || commit || + || | || | 1 || | || v || save || | || | |+---------------------------+|| 2||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
|SamplerStateHandler | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| def save(self): v |
| |
| _saved_sampler_state = copy.deepcopy( value.state_dict() ) |
| + |
| | |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------+||| 3||+------------------------------------------+| ElasticSampler | || | || | || | || def state_dict(self): | || return dict( v || self.epoch, || self.processed_indices || ) || |+------------------------------------------+
只看静态定义,还是很难理解,需要分析动态流程。因为有两种异常,所以我们分开剖析。
回忆一下两个异常最大的区别:
- HorovodInternalError 异常:当 hvd.elastic.run 捕获到这个异常后,会利用最新一次commit中恢复所有状态。
- HostsUpdatedInterrupt 异常:处理方式与“HorovodInternalError”类似,只是参数状态不会还原到上次commit,而是从当前实时参数中恢复。
4.6 HostsUpdatedInterrupt
如果当驱动进程通过节点发现脚本发现一个节点被标记为新增或者移除时,会抛出异常 HostsUpdatedInterrupt。此时不是关键异常,因此可以继续训练本epoch,只是从后续训练数据中,移除本epoch已经处理的数据。因此可以做到 参数状态不会还原到上次commit,而是从当前实时参数中恢复。
下面代码之中,我们只保留 HostsUpdatedInterrupt 相关代码。
def run_fn(func, reset):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(state, *args, **kwargs):notification_manager.init()notification_manager.register_listener(state)skip_sync = Falsetry:while True:if not skip_sync:state.sync() # 3) 进行同步try:return func(state, *args, **kwargs) # 这里会出错,而且重新训练也是来到这里except HostsUpdatedInterrupt as e:# 1) 进行异常处理skip_sync = e.skip_sync # 2.1) 记录是否需要同步 reset() # 2)这里会调用_basics.init 重新初始化 horovod,间接设定了ElasticSampler之中的 num_replicasstate.on_reset() # 进行重启finally:notification_manager.remove_listener(state)return wrapper
发生异常之后,
- 1)HostsUpdatedInterrupt 表示本 epoch 需要继续训练,所以进行异常处理,其中只是会:
- 1.1) 记录本异常处理是否需要同步 :skip_sync = e.skip_sync。
- 2)这个步骤主要是重启 hvd,对worker数目进行更改。具体是调用 State 自身的 reset() 方法(代码位于
horovod/torch/elastic/__init__.py),其中会:- 2.1) 调用 shutdown() 来结束本次任务。
- 2.2) 调用 init(),从而调用_basics.init,最终重新建立 MPI 相关 context,所以 hvd.size() 就根据最新的worker数目进行了更改。后续
ElasticSampler.__iter__之中会相应修改num_replicas。
- 3)这个步骤是把已经训练完的数据移除,得到的数据都是没有经过训练的。如果需要同步,则会调用 state.sync() ,其会调用 SamplerStateHandler.sync 方法,其内部会:
- 3.1) SamplerStateHandler会利用集合通信从所有worker中收集processed_indices,赋予给 world_processed_indices,这就是所有workers 已经处理过的数据 index。
- 3.2) 调用 ElasticSampler.state_dict方法,得到本地 ElasticSampler.epoch 和 ElasticSampler.processed_indices 的引用。然后将 world_processed_indices 赋值给 state_dict[‘processed_indices’],这样,本地 ElasticSampler.processed_indices 就是所有workers 已经处理过的数据 index。
- 3.3)
self.value.load_state_dict(broadcast_object(state_dict))有两步操作:- 广播,这样在同步之后,所有worker都有同样的 state_dict[‘processed_indices’] 数据了。
- load_state_dict 会再调用一次 ElasticSampler.reset,此次 reset 会更改
num_replicas,也会从总数据中去除processed_indices,得到新的remaining_indices, 从而 后续__iter__之中,就会相应对提取index 的策略进行相应更改。
- 4)所以这样就把已经训练完的数据移除,所以得到的 remaining_indices 数据都是没有经过训练的。所以重新训练时候,本epoch之内,不会用已经训练的数据再次重复训练,而是从当前实时参数中恢复。
- 重新训练会调用 return func(state, *args, **kwargs) 进行训练,这里会处理
ElasticSampler.__iter__。 - 当使用
__iter__获取下一批次数据时候,self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:]就会 只从未训练的数据里面提取。
- 重新训练会调用 return func(state, *args, **kwargs) 进行训练,这里会处理
具体逻辑如下:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Worker |
| |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | run_fn | |
| | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | while True: | | |
| | | | | |
| | v 3) | | |
| | state.sync() +------------------------------------------+----------------------+ | | |
| | | | | | |
| | + | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | v | | | | |
| | +------------------+---------------+ 3.1) | 3.2) | | | |
| | | train | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | optimizer.apply_gradients +---------+ | | | | |
| | | + | v | | | |
| | +-------+ state.commit() | | | | |
| | | | + | ElasticSampler.load_state_dict | | | |
| | | +----------------------------------+ | + | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | v v | | | | |
| | HostsUpdatedInterrupt HorovodInternalError v | | | |
| | + ElasticSampler.reset | | | |
| | + | + | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 1) v | | | | |
| | | state.restore() v | | | |
| | | + +-----------+-----------------+ | | | |
| | | | | ElasticSampler | | | | |
| | +------------------+ <------------------+ | | | | | |
| | | | | remaining_indices | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | v v | num_samples | | | | |
| | reset() | | | | | |
| | 2) | total_size | | | | |
| | state.on_reset() | | | | | |
| | | epoch | | | | |
| | + | | | | | |
| | | | processed_indices | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | state_dict <-------------+ | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | +-----------------------------+ | | |
| | | | | |
| | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------^ | |
| | | |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
手机如下:
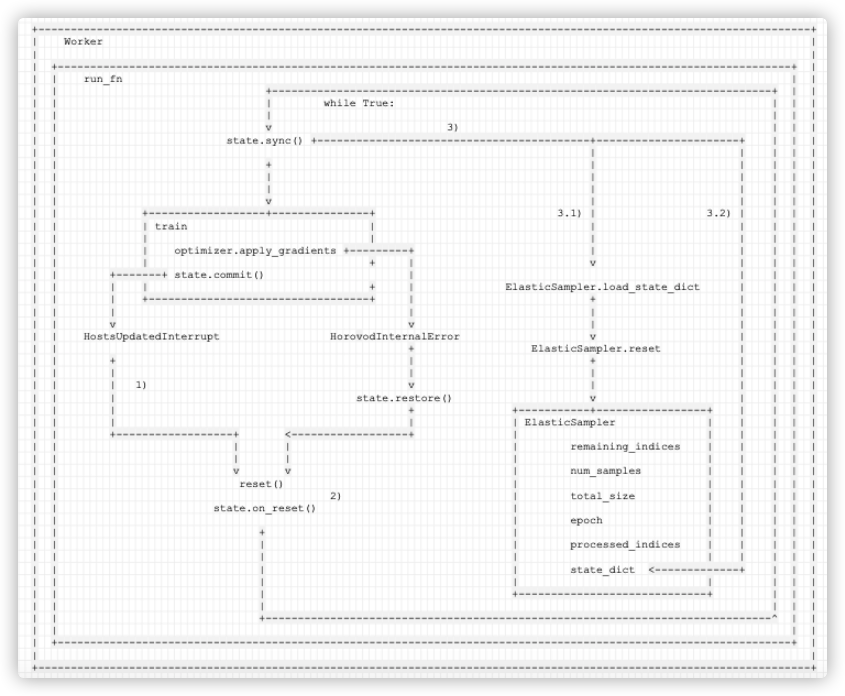
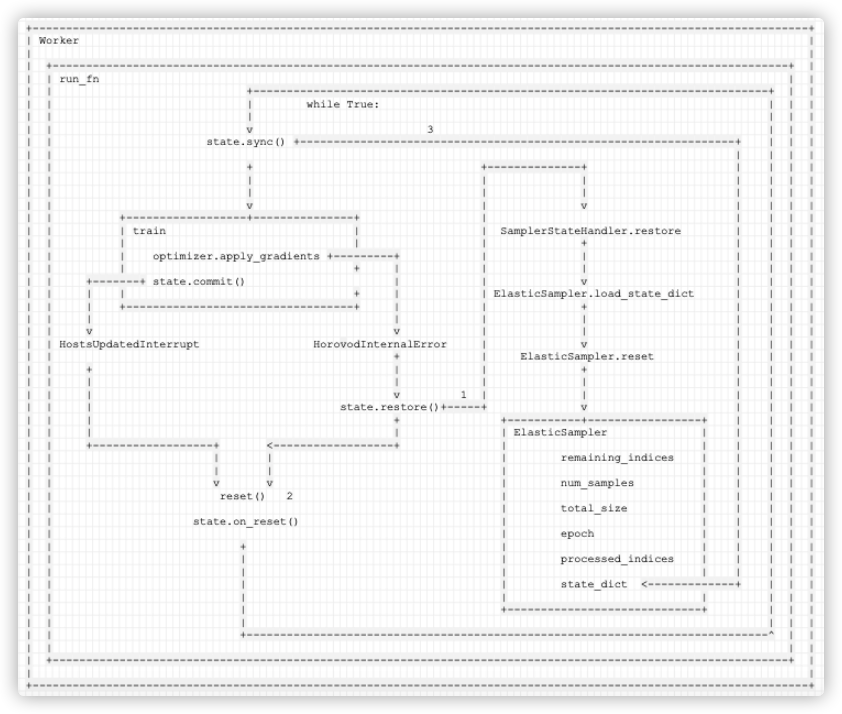
4.7 HorovodInternalError
如果是 ring allreduce 相关,就转为抛出异常 HorovodInternalError(e)。HorovodInternalError 是关键异常,此时本 epoch 现有状态其实意义不大,应该利用最新一次commit中恢复所有状态。
下面代码之中,我们只保留 HorovodInternalError 相关代码。
def run_fn(func, reset):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(state, *args, **kwargs):notification_manager.init()notification_manager.register_listener(state)skip_sync = Falsetry:while True:if not skip_sync:state.sync() # 3) 进行同步try:return func(state, *args, **kwargs) # 这里会出错,而且重新训练也是来到这里except HorovodInternalError:# 1) 进行异常处理state.restore() #1.1) 进行恢复训练,这里是和 HostsUpdatedInterrupt 的不同之处skip_sync = False # 1.2) 记录需要同步reset() # 2)这里会调用_basics.init 重新初始化 horovod,间接设定了ElasticSampler之中的 num_replicasstate.on_reset() # 进行重启finally:notification_manager.remove_listener(state)return wrapper
HorovodInternalError 和 HostsUpdatedInterrupt 的代码路径几乎一样,只是多了一步 state.restore() 。
这里为啥也要查看节点变化呢?因为Horovod是定期检查节点变化,所以可能产生HorovodInternalError时候,也有节点变化了,只是还没有发现而已,所以可以一并处理了。
具体逻辑为:
- 1)HorovodInternalError 表示本 epoch 需要恢复训练,所以先进行异常处理:
- 1.1)state.restore() 会调用 SamplerStateHandler.restore(这里是与HostsUpdatedInterrupt处理差异之处)。
- 进而调用 ElasticSampler.load_state_dict方法,会用在
SamplerStateHandler.__init__或者SamplerStateHandler.save之中原始保存的数据来恢复 ElasticSampler。保存的数据就是 processed_indices 和 epoch。 - ElasticSampler.load_state_dict方法 进而会调用 ElasticSampler.reset方法,使用 processed_indices 把已经训练完的数据移除,最新得到的 remaining_indices 数据都是没有经过训练的(针对上次保存的 processed_indices 来说)。
- 进而调用 ElasticSampler.load_state_dict方法,会用在
- 1.2) 记录本异常处理需要同步 : skip_sync = False。
- 1.1)state.restore() 会调用 SamplerStateHandler.restore(这里是与HostsUpdatedInterrupt处理差异之处)。
- 2)这个步骤主要是重启 hvd。调用 State 自身的 reset() 方法(代码位于
horovod/torch/elastic/__init__.py),其中会:- 2.1) 调用 shutdown() 来结束本次任务。
- 2.2) 调用 init(),从而调用_basics.init,最终重新建立 MPI 相关 context。
- 3)这个步骤是把已经训练完的数据移除,得到的数据都是没有经过训练的。因为这里需要同步,所以会调用 state.sync() ,其会调用 SamplerStateHandler.sync 方法,其内部会:
- 3.1) SamplerStateHandler会利用集合通信从所有worker中收集processed_indices,赋予给 world_processed_indices,这就是所有workers 已经处理过的数据 index。需要注意的是:因为是使用在
__init__或者save之中原始保存的数据来恢复,所以其实这一步是恢复到上次commit状态。 - 3.2) 调用 ElasticSampler.state_dict方法,得到本地 ElasticSampler.epoch 和 ElasticSampler.processed_indices 的引用。然后将 world_processed_indices 赋值给 state_dict[‘processed_indices’],这样,本地 ElasticSampler.processed_indices 就是所有workers 已经处理过的数据 index。
- 3.3) 这里
self.value.load_state_dict(broadcast_object(state_dict))有两步操作:- 广播,这样在同步之后,所有worker都有同样的 state_dict[‘processed_indices’] 数据了。
- load_state_dict 会再调用一次 ElasticSampler.reset,此次 reset 会更改
num_replicas,也会从总数据中去除processed_indices,得到新的remaining_indices, 从而 后续__iter__之中,就会相应对提取index 的策略进行相应更改。
- 3.1) SamplerStateHandler会利用集合通信从所有worker中收集processed_indices,赋予给 world_processed_indices,这就是所有workers 已经处理过的数据 index。需要注意的是:因为是使用在
- 4)这样就是恢复到epoch 上次 commit 的状态进行训练。
- 重新训练会调用 return func(state, *args, **kwargs) 进行训练,这里会处理
ElasticSampler.__iter__。 - 当使用
__iter__获取下一批次数据时候,self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:]就会 只从未训练的数据里面提取。
- 重新训练会调用 return func(state, *args, **kwargs) 进行训练,这里会处理
具体逻辑如下图:
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Worker |
| |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | run_fn | |
| | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | while True: | | |
| | | | | |
| | v 3 | | |
| | state.sync() +-----------------------------------------------------------------+ | | |
| | | | | |
| | + +--------------+ | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | v | v | | | |
| | +------------------+---------------+ | | | | |
| | | train | | SamplerStateHandler.restore | | | |
| | | | | + | | | |
| | | optimizer.apply_gradients +---------+ | | | | | |
| | | + | | | | | | |
| | +-------+ state.commit() | | v | | | |
| | | | + | | ElasticSampler.load_state_dict | | | |
| | | +----------------------------------+ | | + | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | v v | | | | | |
| | HostsUpdatedInterrupt HorovodInternalError | v | | | |
| | + | ElasticSampler.reset | | | |
| | + | | + | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | v 1 | | | | | |
| | | state.restore()+-----+ v | | | |
| | | + +-----------+-----------------+ | | | |
| | | | | ElasticSampler | | | | |
| | +------------------+ <------------------+ | | | | | |
| | | | | remaining_indices | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | v v | num_samples | | | | |
| | reset() 2 | | | | | |
| | | total_size | | | | |
| | state.on_reset() | | | | | |
| | | epoch | | | | |
| | + | | | | | |
| | | | processed_indices | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | state_dict <-------------+ | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | +-----------------------------+ | | |
| | | | | |
| | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------^ | |
| | | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+手机如下:
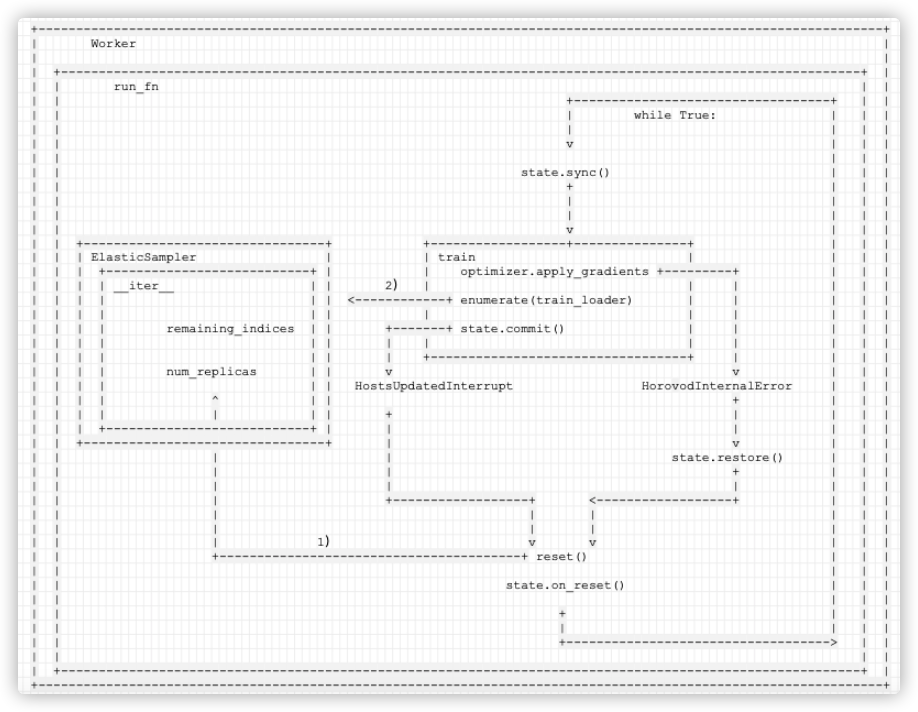
4.8 ElasticSampler.__iter__
到目前为止,我们还有一个问题没有仔细分析,就是何时调用 ElasticSampler.__iter__
我们仔细梳理一下,以下是弹性训练总体逻辑:
def run_fn(func, reset):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(state, *args, **kwargs):notification_manager.init()notification_manager.register_listener(state)skip_sync = Falsetry:while True:if not skip_sync:state.sync()try:# 如果出错恢复,这里会继续调用 func 进行训练return func(state, *args, **kwargs)except HorovodInternalError:state.restore()skip_sync = Falseexcept HostsUpdatedInterrupt as e:skip_sync = e.skip_syncreset()state.on_reset()finally:notification_manager.remove_listener(state)return wrapper
弹性逻辑使用注解来封装了full_train,所以 func 就是 full_train。
@hvd.elastic.run
def full_train(state):while state.epoch < args.epochs:train(state)validate(state.epoch)save_checkpoint(state.epoch)end_epoch(state)
我们看看 train 的主要代码:
def train(state):model.train()epoch = state.epochwith tqdm(...) as t:# 这里 enumerate 之中会调用到 ElasticSampler.__iter__for idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):# Split data into sub-batches of size batch_sizefor i in range(0, len(data), args.batch_size):data_batch = data[i:i + args.batch_size]target_batch = target[i:i + args.batch_size]output = model(data_batch)train_accuracy.update(accuracy(output, target_batch))loss = F.cross_entropy(output, target_batch)train_loss.update(loss)# Average gradients among sub-batchesloss.div_(math.ceil(float(len(data)) / args.batch_size))loss.backward()# Elastic Horovod: record which samples were processed this batch# so we do not reprocess them if a reset event occursstate.train_sampler.record_batch(idx, allreduce_batch_size)# Gradient is applied across all ranksoptimizer.step()state.commit()
所以我们可以理出来总体逻辑:
- 当出错恢复时候,train 会再次被调用,调用时候就会使用 enumerate(train_loader)调用到
ElasticSampler.__iter__。 - num_replicas 在之前 reset 时候已经被设置,所以此时就是根据新的 world size 和 remaining_indices 重新确定提取数据的策略。
def __iter__(self): self.indices = self.remaining_indices[:] # 从剩余数据中提取if self.shuffle:# Shuffle indices across workers deterministically in placeseed = self.seed + self.epochrandom.Random(seed).shuffle(self.indices)# add extra samples to make it evenly divisibleself.indices += self.indices[:(self.total_size - len(self.indices))]assert len(self.indices) == self.total_size# subsample# 本worker如何遍历?起始index是self.rank,终止index是总数据长度,按照 num_replicas 来递增self.indices = self.indices[self.rank:self.total_size:self.num_replicas]assert len(self.indices) == self.num_samples# 后续就按照上面的遍历逻辑来遍历return iter(self.indices)
具体逻辑如下,其中
1)在 reset 之中设置了num_replicas。
2)在 ElasticSampler.__iter__ 之中根据新的 world size 和 remaining_indices 重新确定提取数据的策略。
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Worker |
| |
| +----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | run_fn | |
| | +----------------------------------+ | |
| | | while True: | | |
| | | | | |
| | v | | |
| | | | |
| | state.sync() | | |
| | + | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | v | | |
| | +--------------------------------+ +------------------+---------------+ | | |
| | | ElasticSampler | | train | | | |
| | | +---------------------------+ | | optimizer.apply_gradients +---------+ | | |
| | | | __iter__ | | 2) | | | | | |
| | | | | | <------------+ enumerate(train_loader) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | remaining_indices | | +-------+ state.commit() | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | +----------------------------------+ | | | |
| | | | num_replicas | | v v | | |
| | | | | | HostsUpdatedInterrupt HorovodInternalError | | |
| | | | ^ | | + | | |
| | | | | | | + | | | |
| | | +---------------------------+ | | | | | |
| | +--------------------------------+ | v | | |
| | | | state.restore() | | |
| | | | + | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | +------------------+ <------------------+ | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | 1) v v | | |
| | +----------------------------------------+ reset() | | |
| | | | |
| | state.on_reset() | | |
| | | | |
| | + | | |
| | | | | |
| | +-----------------------------------> | |
| | | |
| +----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+手机如下:
至此,弹性训练如何恢复就分析完毕,以后可能结合 Pytorch 分布式 optimizer 来继续分析。
0xEE 个人信息
★★★★★★关于生活和技术的思考★★★★★★
微信公众账号:罗西的思考
如果您想及时得到个人撰写文章的消息推送,或者想看看个人推荐的技术资料,敬请关注。

0xFF 参考
PyTorch 中文手册(2)-自动求导
pytorch中优化器optimizer.param_groups
PyTorch学习笔记6–案例2:PyTorch神经网络(MNIST CNN)
https://github.com/chenyuntc/pytorch-book
