宁夏网站建设优化/竞价托管外包费用
文章目录
- 1.树
- 树的表示
- 左孩子右兄弟表示法
- 双亲表示法
- 2.二叉树
- 满二叉树&完全二叉树
- 性质
- 存储方式
- 顺序存储
- 链式存储
- 遍历顺序
- TreeSize
- TreeLeafSize
- TreeKLevelSize
- BinaryTreeDestroy
- DFS
- BFS
- BinaryTreeComplete
- 3.堆
- 堆排序的实现
- AdjustDown
- 建堆算法
- HeapSort
- 堆的实现
- Heap.h
- Test.c
- Init&Destroy
- AdjustUp
- Push
- Pop
- Top
- Size
- Empty
- 练习
- [剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zui-xiao-de-kge-shu-lcof/)
- [104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
- [965. 单值二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/univalued-binary-tree/)
- [144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/)
- [100. Same Tree](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/same-tree/)
- [226. Invert Binary Tree](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
- [101. Symmetric Tree](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/)
- [572. Subtree of Another Tree](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/)
- [110. Balanced Binary Tree](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
- 清华大学复试二叉树遍历
1.树
非线性数据结构
树是递归定义的
每一棵树,都是由根+多个子树构成,子树结构亦是如此
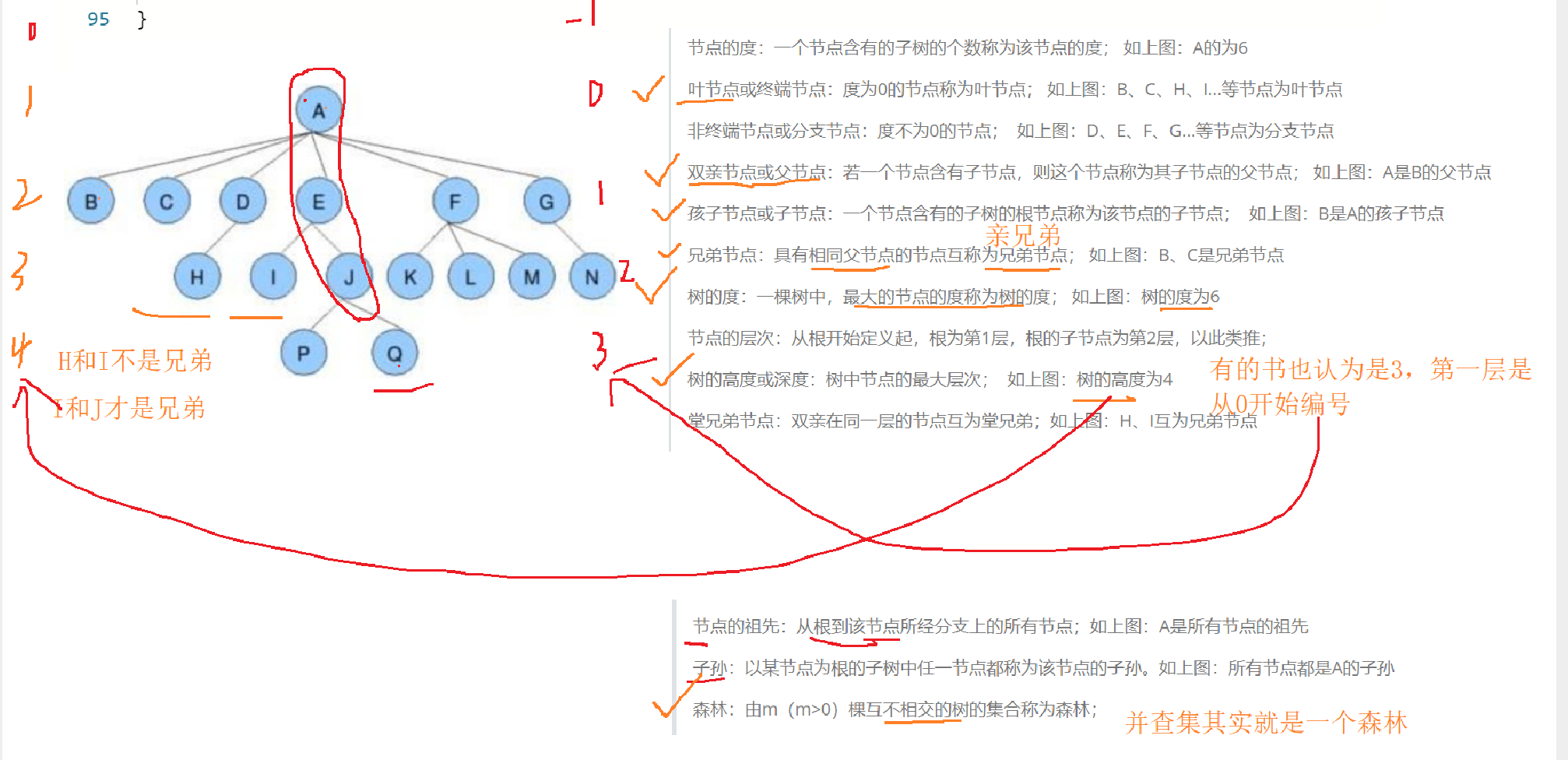
树的表示
树没有规定,他有多少个孩子
C++会好写一点

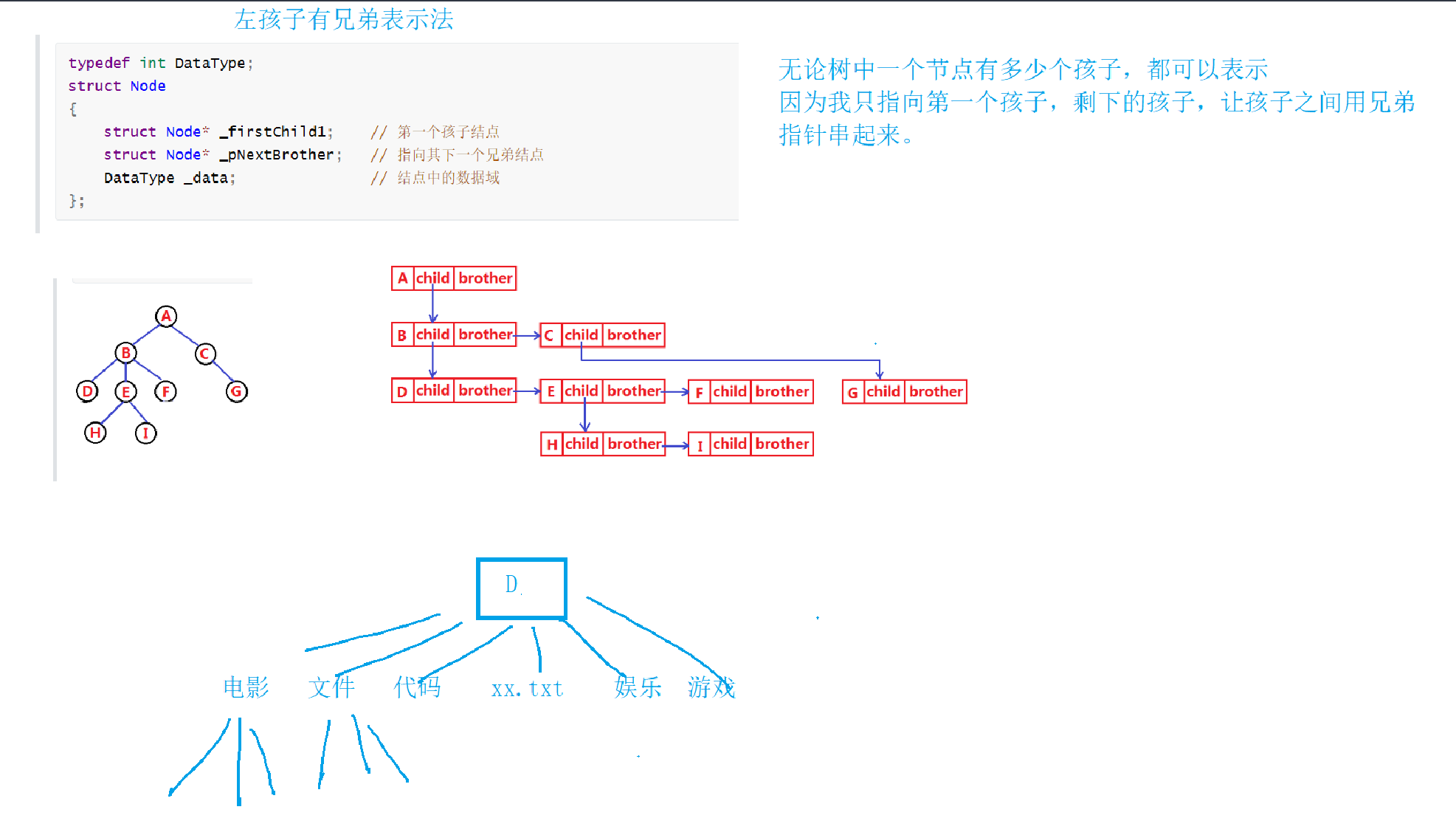
左孩子右兄弟表示法
struct Node
{struct Node* _firstChild1;//第一个孩子结点struct Node* _pNextBrother;//指向其下一个兄弟结点int _data;}
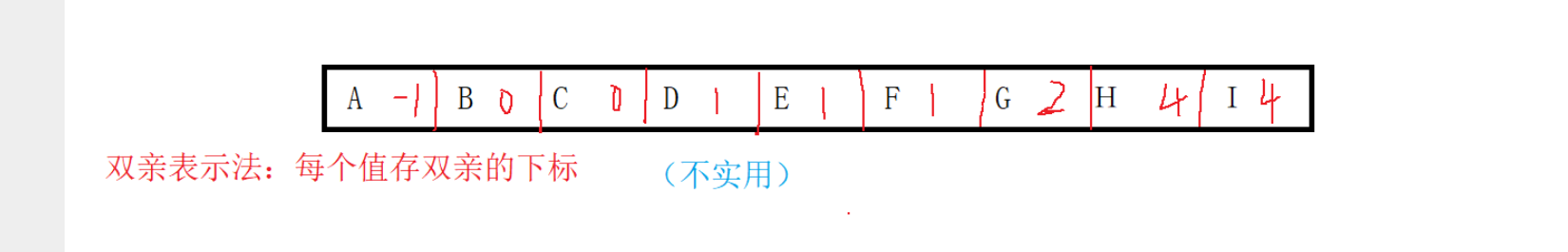
双亲表示法
每个值存双亲的下标
存到数组里,存一个个结构体
A的父亲是-1
B,C的父亲是0
2.二叉树
二叉树的度<=2
满二叉树&完全二叉树
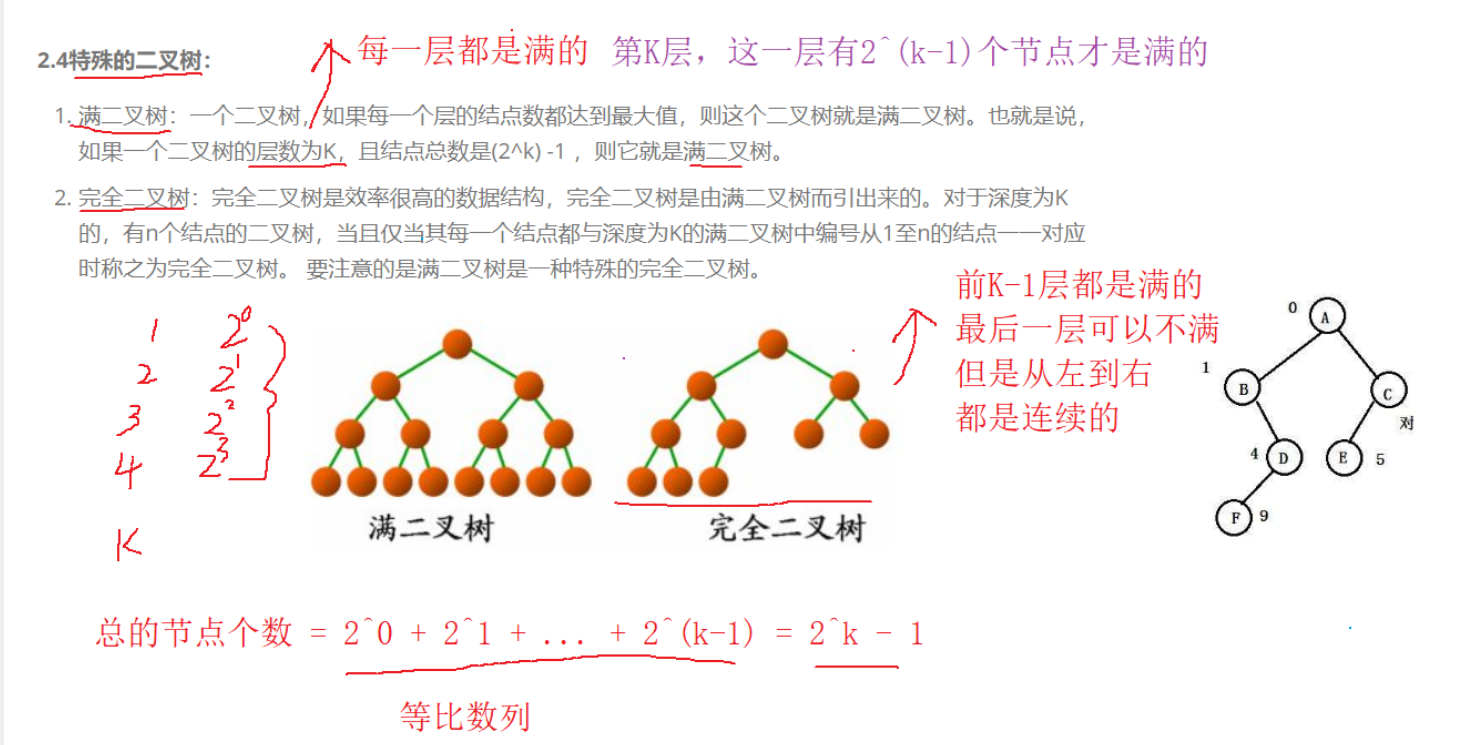
完全二叉树前k-1层都是满的,最后一层从左到右连续
性质

度为0的比度为2的多一个
🏷n0 = n2 +1
二叉树总结点: n0+n1+n2
完全二叉树中度为1的节点最多有一个,即a1=0或a1=0
😆
存储方式
顺序存储
使用数组存储:适用于完全二叉树
如果是非完全二叉树,用数组存储,可能存在很多空间浪费
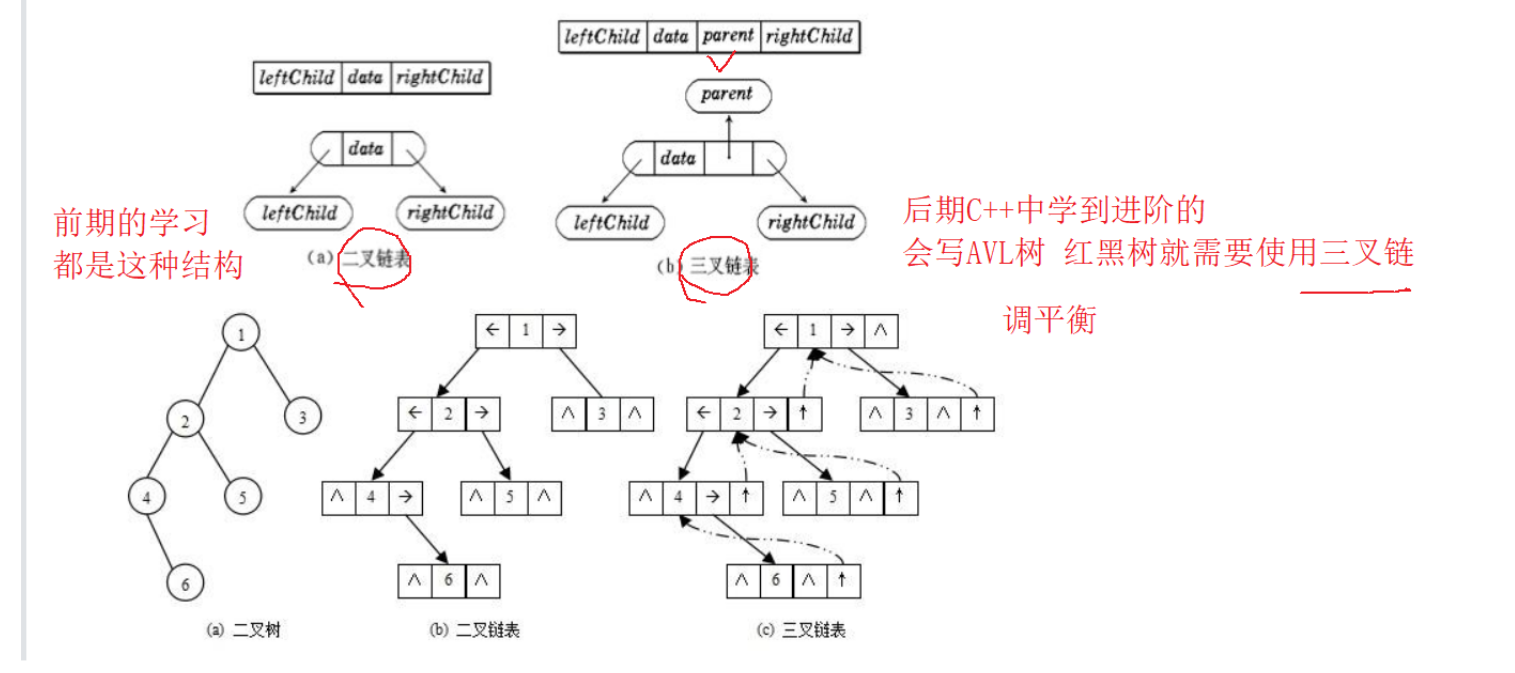
链式存储
二叉链
三叉链
遍历顺序
- 前序遍历 先根遍历(根左右)
- 中序遍历 中根遍历(左根右)
- 后序遍历 后根遍历(左右根)
- 层序遍历 一层一层走
//函数调用完毕 回到调用它的地方
普通二叉树的增删查改没有意义
如果为了存储数据,应该用线性表,二叉树反而复杂了
并且插入删除还不好定义在哪个位置去插入删除
二叉树应用
哈夫曼树
搜索树:AVL树,红黑树
排序二叉树极端情况下,搜索二叉树效率退化为O(N),跟链表差不多,大打折扣,如何解决:
AVL树,红黑树==>平衡树
TreeSize
//思路一,遍历计数器
void TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)
{if (root == NULL){return;}++(*psize);TreeSize(root->left, psize);TreeSize(root->right, psize);
}int size = 0;
TreeSize(A, &size);
printf("TreeSize::%d\n", size);//6
size = 0;
TreeSize(A, &size);
printf("TreeSize::%d\n", size);//6
动用全局变量或静态变量的结果
//分治算法思想,把大问题拆成小问题
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{//结点个数 = 左+右+我自己return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}printf("TreeSize::%d\n", TreeSize(A));//6printf("TreeSize::%d\n", TreeSize(A));//6
TreeLeafSize
//叶子结点个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){return 1;}return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
printf("TreeSize::%d\n", TreeLeafSize(A));//3TreeKLevelSize
//第k层结点个数
//左子树的第k-1层+右子树的第k-1层
int TreeKLevelSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (1 == k){return 1;}return TreeKLevelSize(root->left, k - 1) +TreeKLevelSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
BinaryTreeDestroy
后序烧毁比较合适,左右根
//一般选择一级指针,为了保持接口一致性,使用者要注意置空
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestroy(root->left);BinaryTreeDestroy(root->right);free(root);
}
BinaryTreeDestroy(A);
A = NULL;
//或者C++中使用引用来解决
//void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode*& root)
DFS
二叉树的前中后序遍历就是深度优先遍历
深度优先一般借助递归
BFS
一圈一圈往外展开
二叉树的广度优先遍历一般借助队列实现广度优先一般借助队列
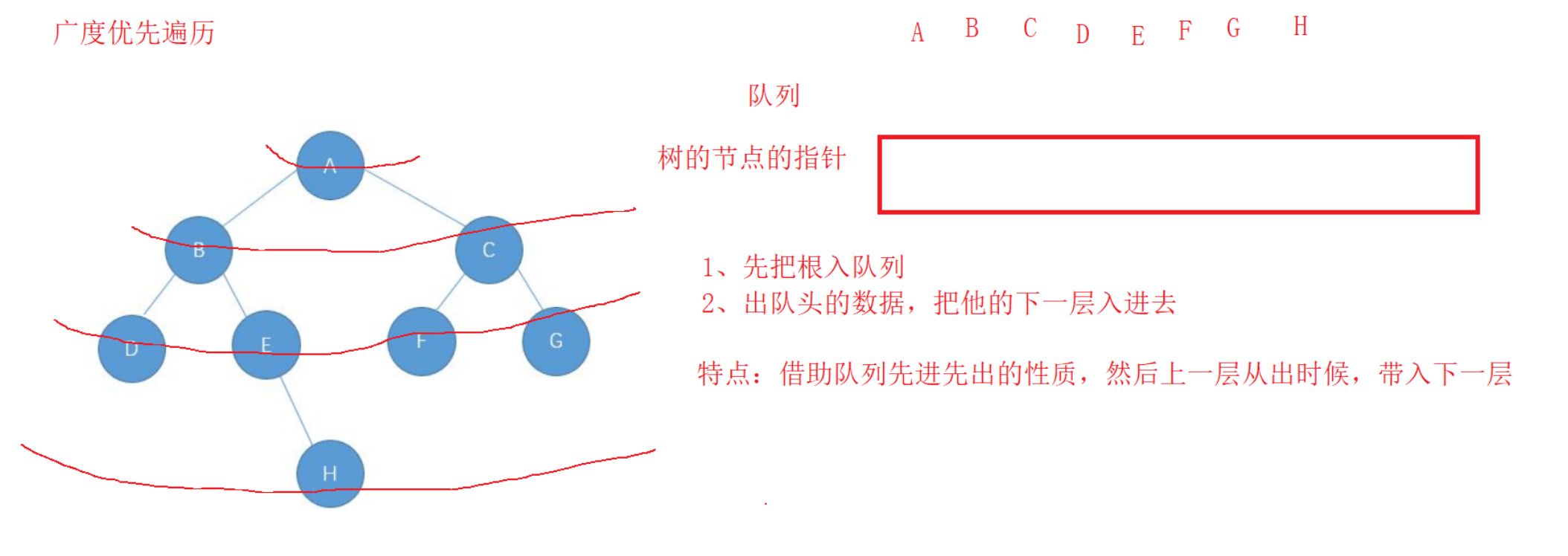
A先进去,A出来时把BC带进去,D出来的时候把DE带进去,C出来时把FG带进去…
//广度优先遍历
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//只是把结点指针pop出去,没有销毁结点printf("%c ", front->data);//如果左不为空,把左边的带进去if (front->left != NULL){QueuePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right != NULL){QueuePush(&q, front->right);}}QueueDestroy(&q);
}
//广度优先遍历
TreeLevelOrder(A);//A B C D E F
记得要在Queue.h里面添加树的前置声明,否则编译不过去
//前置声明
struct BinaryTreeNode;//在其他地方定义,链接的时候再去找它
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
BinaryTreeComplete
//判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
//借助层序遍历,层序走,结点是连续的,当出到空之后,后面全空就是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root != NULL){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到第一个NULL 跳出来去检查剩下的是否全为空if (front == NULL){break;}//不为空就继续传进去QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}//检查剩下的是否全为空while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front != NULL){//不全为空就不是完全二叉树return false;}}QueueDestroy(&q);//后面全是空return true;
}
3.堆
物理结构是一个数组
逻辑结构是完全二叉树把数组看成完全二叉树
大根堆:父亲 >= 孩子
小根堆:父亲 <= 孩子
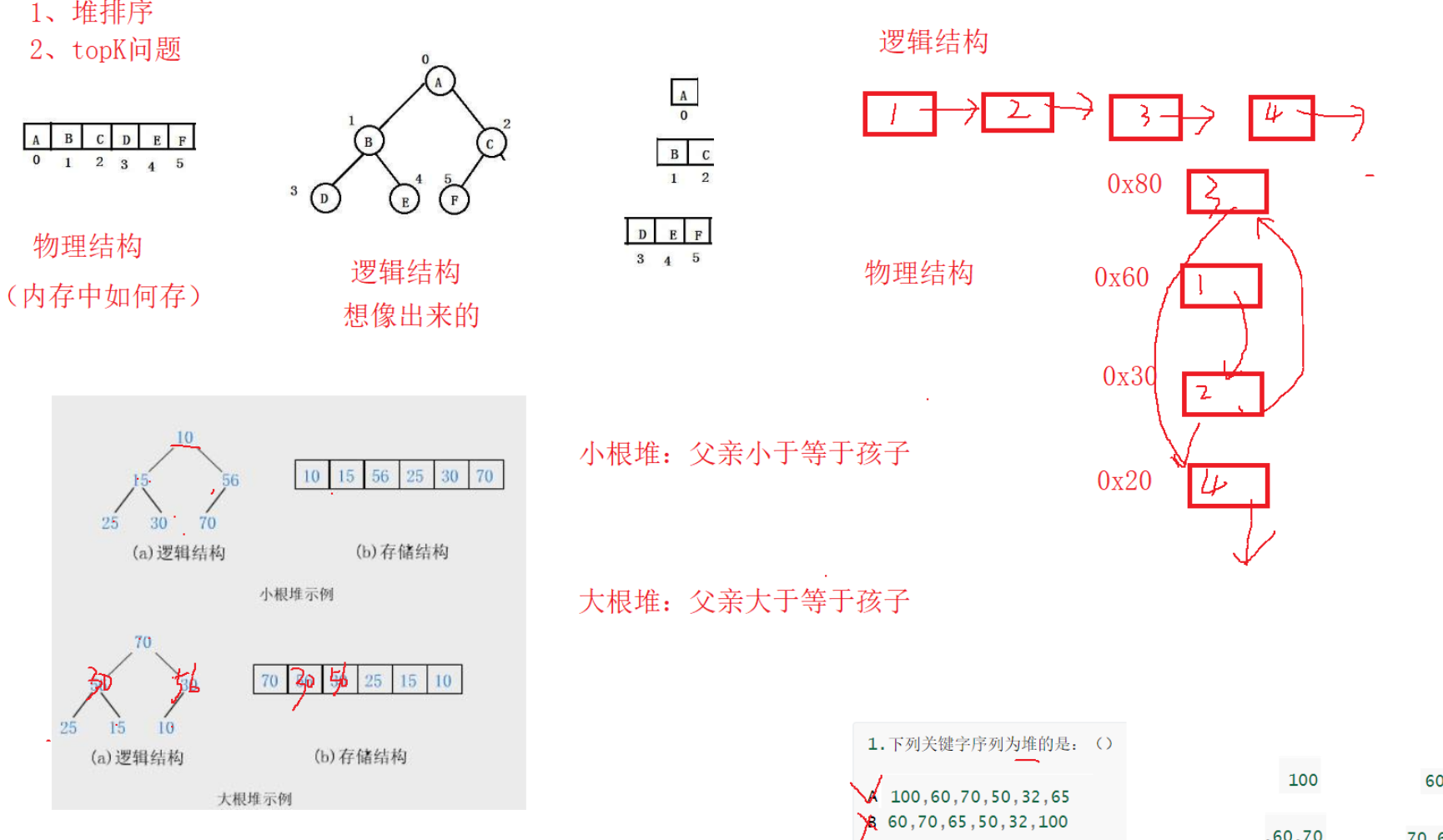
假设父亲下标是parent
leftchild = parent*2 + 1;
rightchild= parent*2 + 2;
可以推出==>parent = (child-1) / 2(6-1) / 2 => 2
堆排序的实现
如果左右子树恰好是小堆,如何把整棵树调成小堆
向下调整算法
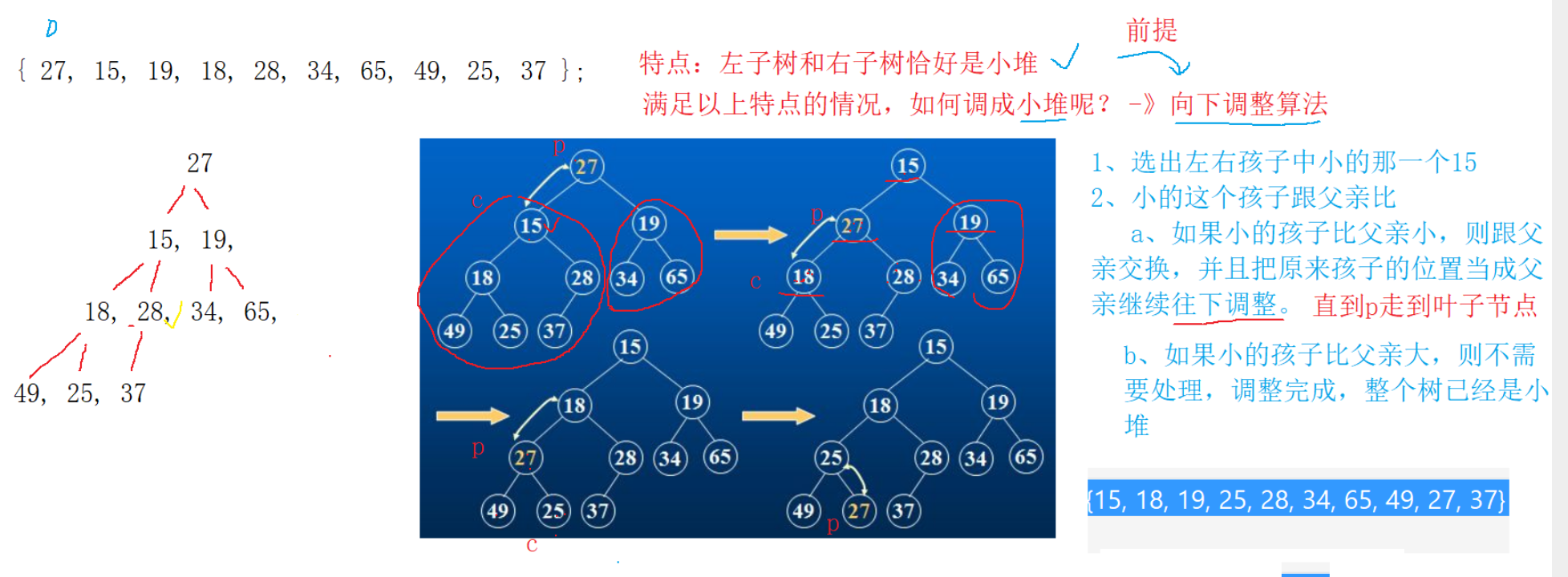
AdjustDown
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{int tmp = *p1;*p1 = *p2;*p2 = tmp;
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;//parent走到叶子节点就终止,也就是child坐标>=nwhile (child < n){//选出左右孩子小的那一个if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child]){//child + 1 < n 防止访问最后一个右孩子时(假设没有最后的右孩子)发生越界child++;}if (a[child] < a[parent]){Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{//a[child] >= a[parent]break;}}
}
建堆算法
如果左右子树不是小堆怎么办?
从倒数的第一个非叶子节点(最后一个节点的父亲),从后往前,按照编号,依次作为子树向下取调整
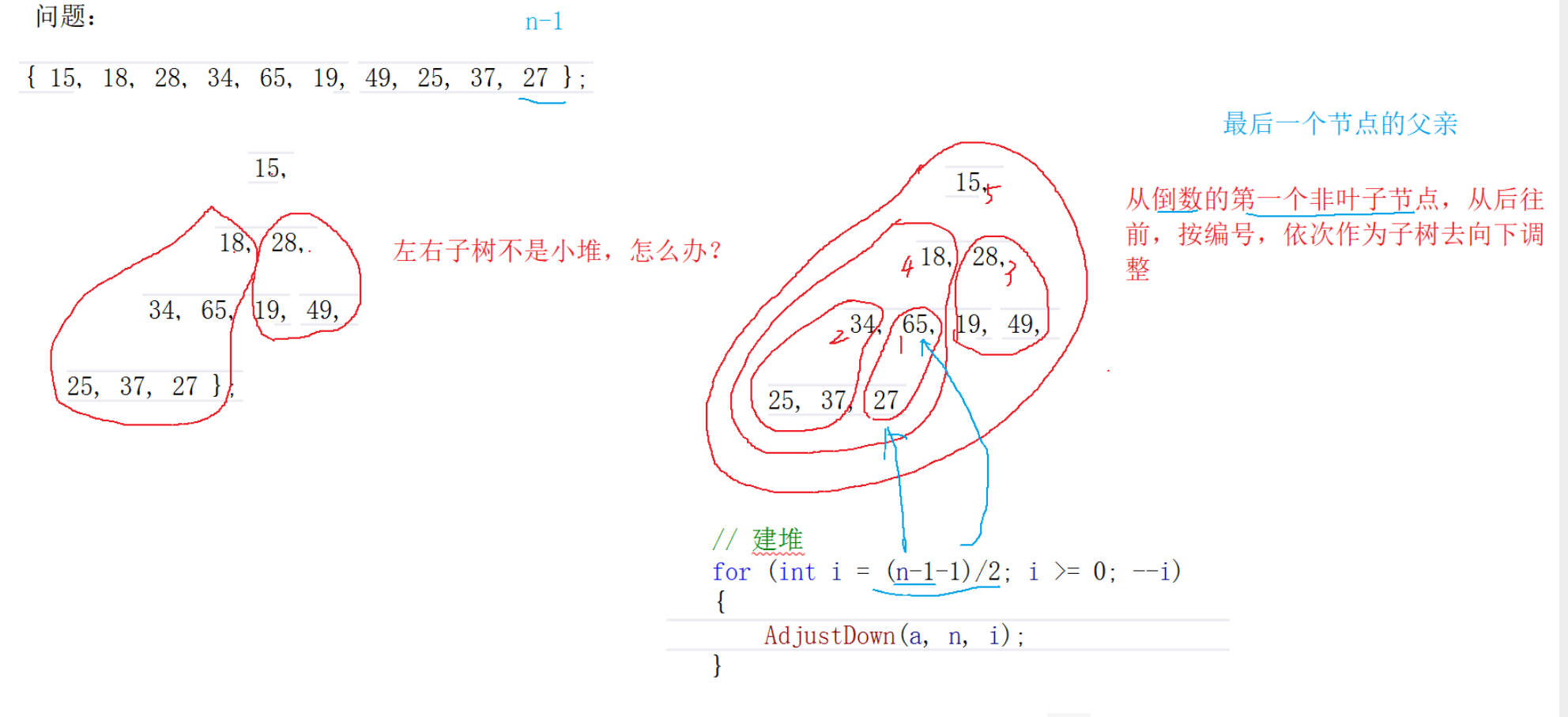
//建堆算法
//n-1是最后一个节点的下标
//建堆for (int i = (sz - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)//最后一个节点的父亲//parent = (child-1) / 2{AdjustDown(arr, sz, i);}
//建堆时间复杂度O(N)


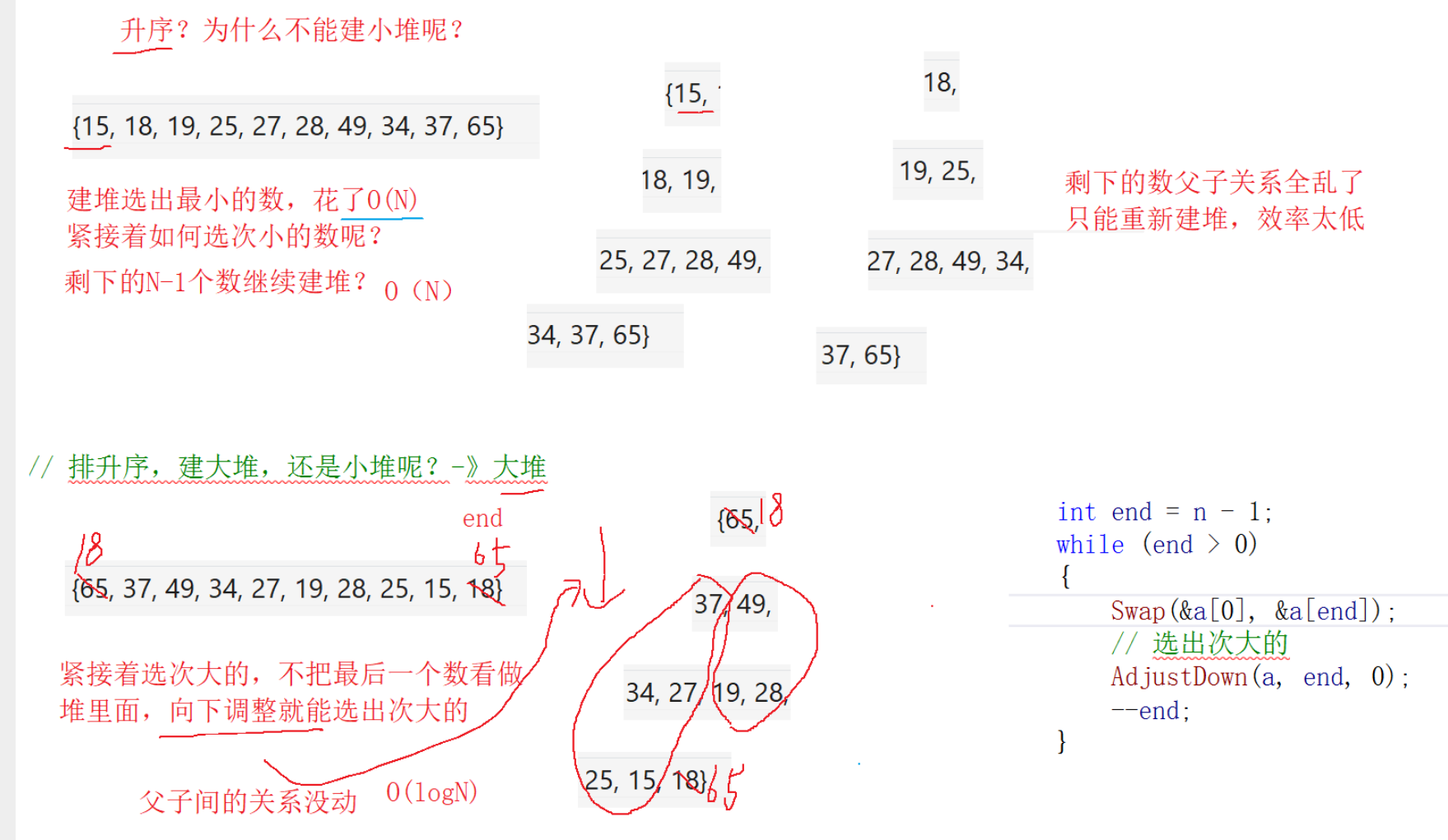
HeapSort
堆排序优于直接选择排序O(N^2) 才有价值
堆升序,应该建大堆,如果建小堆,会改变父子关系,需要重新建堆,每次建堆时间复杂度是O(N),效率太低最终堆排序时间复杂度O(N*logN)
HeapSort(int* arr, int sz)
{for (int i = (sz - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){//只需向下调整即可选出次大的数,时间复杂度O(logN)AdjustDown(arr, sz, i);}int end = sz - 1;//选出最大的数,交换到最后去while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);//选次大的//左右子树均为大堆,只需一次向下调整就能从n-1选出原来n里面次大的数AdjustDown(arr, end, 0);end--;}
}
int main()
{int arr[] = { 15,18,28,34,65,19,49,25,37,27 };int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);HeapSort(arr, sz);return 0;
}
堆的实现
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
struct Heap
{HPDataType* a;int size;int capacity;
};
//假设采用大堆
typedef struct Heap HP;
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2);
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child);
void HeapInit(HP* php, HPDataType* a, int n);
void HeapDestroy(HP* php);
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HeapPop(HP* php);
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php);
int HeapSize(HP* php);
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php);
void HeapPrint(HP* php);
Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Heap.h"
void Test()
{int a[] = { 15,18,28,34,65,19,49,25,37,27 };int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);HP hp;HeapInit(&hp, a, n);HeapPrint(&hp);HeapPush(&hp, 8);HeapPrint(&hp);HeapPush(&hp, 88);HeapPrint(&hp);HeapPop(&hp);HeapPrint(&hp);HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
void TopK()
{//TopK问题
}
int main()
{Test();return 0;
}
Init&Destroy
void HeapInit(HP* php, HPDataType* a, int n)
{assert(php);php->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);if (php->a == NULL){printf("malloc fail\n");exit(-1);}//把传进来的数组拷贝起来memcpy(php->a, a, sizeof(HPDataType) * n);php->size = n;php->capacity = n;//建堆for (int i = (php->size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, i);}
}
void HeapDestroy(HP* php)
{assert(php);free(php->a);php->a = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}
void HeapPrint(HP* php)
{for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++){printf("%d ", php->a[i]);}printf("\n");int num = 0;int levelSize = 1;for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++){printf("%d ", php->a[i]);num++;if (num == levelSize){printf("\n");levelSize *= 2;num = 0;}}printf("\n");printf("\n");
}
AdjustUp
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;//while (parent >= 0) chile=0时,算出来的parent也还是0 parent不会<0while (child > 0){if (a[child] > a[parent]){Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}
Push
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);//满了需要增容if (php->size == php->capacity){HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, php->capacity * 2 * sizeof(HPDataType));if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);}php->a = tmp;php->capacity *= 2;}php->a[php->size] = x;//插入数据后,需要相应改变路径,向上调整算法php->size++;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);
}
Pop
void HeapPop(HP* php)
{assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);Swap(&php->a[php->size - 1], &php->a[0]);//删掉换到最后的这个原堆顶数据php->size--;//从0开始向下调整AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);//类似堆排序的思想,只不过这里是删除掉最后一个位置上的数据,而堆排序是无视
}
Top
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php)
{assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);return php->a[0];
}
Size
int HeapSize(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size;
}
Empty
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}
练习
剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数
Top-K问题
思路一:排序
最好的排序时间复杂度O(N*logN)
思路二:建堆
把N个数建成小堆,选一个删一个,不断选出前k个最小
时间复杂度O(N+logN*k)
空间复杂度O(N)
思路三:(海量数据处理)
假设N很大,100亿,k是100
如果此时还用排序或堆,需要40GB空间,不合适
先把数组前k个数建成大堆
然后剩下N-K个数,跟堆顶的数据比较,如果比堆顶的数据小,则替换堆顶的数据,调堆,遍历100亿次,最后堆里就是最小的k个数
时间复杂度O(N*logK)
空间复杂度O(K)
int* getLeastNumbers(int* arr, int arrSize, int k, int* returnSize){//建立小堆即可HP hp;HeapInit(&hp, arr, arrSize);int* retArr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);for(int i=0; i<k; i++){retArr[i] = HeapTop(&hp);HeapPop(&hp);}HeapDestroy(&hp);*returnSize = k;return retArr;
}
//s
int* getLeastNumbers(int* arr, int arrSize, int k, int* returnSize){//k=0时单独处理if(k == 0){*returnSize = 0;return NULL;}int* retArr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);//前k个数建立大堆for(int i=0; i<k; i++){retArr[i] = arr[i];}for(int j=(k-1-1)/2; j>=0; j--){AdjustDown(retArr,k,j);}//剩下的N-k个数,比堆顶的小,就替换堆顶的数据,进堆for(int i=k; i<arrSize;++i){if(arr[i] < retArr[0]){retArr[0] = arr[i];//替换之后调整AdjustDown(retArr,k,0);}}*returnSize = k;return retArr;
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
//递归调用 左子树和右子树最大的+1
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL){return 0;}return maxDepth(root->left)>maxDepth(root->right)?maxDepth(root->left)+1:maxDepth(root->right)+1;
}
//时间复杂度太高,跑不过
//算了左右的最大深度却没保存,后面就得再去算O(N^2)
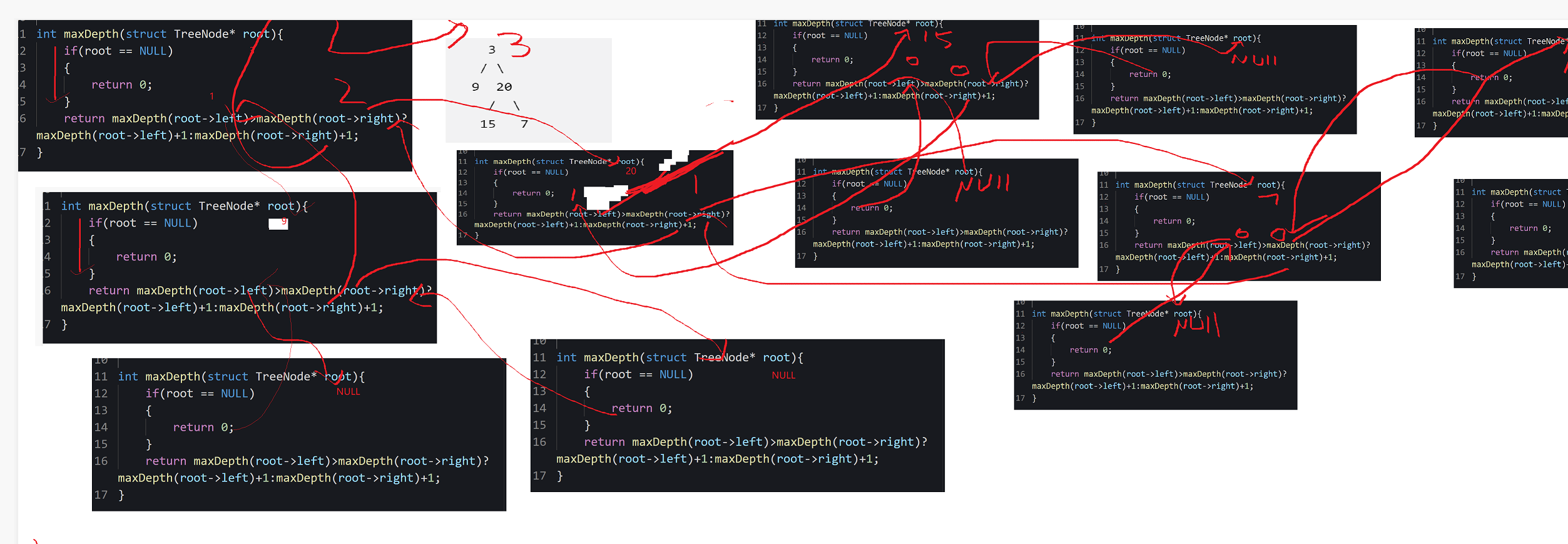
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL){return 0;}int lMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->left);int rMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->right);return lMaxDepth>rMaxDepth?lMaxDepth+1:rMaxDepth+1;
}
//只需将求好的左右最大深度保存起来再去比较就行
//调用fmax函数也行 (C中的)
//C++中是max函数
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL){return 0;}return fmax(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}
//函数调用形参是实参的临时拷贝
965. 单值二叉树
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL){return true;}//左不为空且左边的val不等于root的val就不是单值if(root->left != NULL && root->left->val != root->val){return false;}//右不为空且右边的val不等于root的val就不是单值if(root->right != NULL && root->right->val != root->val){return false;}//看左边是否是单值且右边是否也是单值return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{return root == NULL ? 0:TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
struct TreeNode* _preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* arr, int* pi)
{if(root==NULL)return;//根左右arr[(*pi)++] = root->val;_preorderTraversal(root->left,arr,pi);_preorderTraversal(root->right,arr,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){*returnSize = TreeSize(root);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));int i = 0;_preorderTraversal(root,arr,&i);//i需传址调用,不然每次栈帧开辟使用的i都是不同的i//子函数可以加个_return arr;
}
100. Same Tree
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){if(p==NULL && q==NULL)return true;if(p==NULL || q==NULL)return false;if(p->val != q->val)return false;return isSameTree(p->left, q->left)&& isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
226. Invert Binary Tree
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL)return NULL;//从根节点开始,递归地对树进行遍历,并从叶子节点先开始翻转struct TreeNode* left = invertTree(root->left);struct TreeNode* right = invertTree(root->right);root->left = right;root->right = left;return root;
}
101. Symmetric Tree
思路一:递归遍历
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* left,struct TreeNode* right)
{if(left == NULL && right == NULL)return true;if(left == NULL || right == NULL)return false;if(left->val != right->val)return false;return _isSymmetric(left->right, right->left)&& _isSymmetric(left->left, right->right);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL)return true;bool ret = _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right);return ret;
}
思路二: 先翻转再判断是否相等
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL)return true;//只需要翻转一边root->right = invertTree(root->right);bool ret = isSameTree(root->left, root->right);return ret;
}
572. Subtree of Another Tree
T是S的子树,也就是T和S某一棵子树相等
只要T跟S的所有子树比较一遍即可
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){if(root == NULL)return false;//遍历树的每一个结点,每个结点做子树的根去和subRoot比较是否相等//前序遍历//这里每次都会出现根if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))return true;return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)|| isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
110. Balanced Binary Tree
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){if(root == NULL)return true;//前序遍历int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->left);int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->right);return abs(leftDepth-rightDepth) < 2&& isBalanced(root->left)&& isBalanced(root->right);
}
时间复杂度分析 O(N^2)假设是满二叉树(最坏情况下)
isBalanced递归了N次(其实就是深度优先)每次递归:N N/2 N/2 N/4 N/4 ...要求:优化到O(N)
由于是自顶向下递归,因此对于同一个节点,函数maxDepth会被重复调用,导致时间复杂度较高。
bool _isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root, int* ph)
{if(root == NULL){*ph = 0;return true;}//后序遍历 先判断左再判断右//左边不平衡int leftHeight = 0;if(_isBalanced(root->left,&leftHeight) == false)return false;//右边不平衡int rightHeight = 0;if(_isBalanced(root->right,&rightHeight) == false)return false;//左右都平衡,把高度带回上一层*ph = fmax(leftHeight,rightHeight) + 1;return fabs(leftHeight-rightHeight) < 2;
}bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){int height = 0;return _isBalanced(root, &height);
}
清华大学复试二叉树遍历
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。 例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
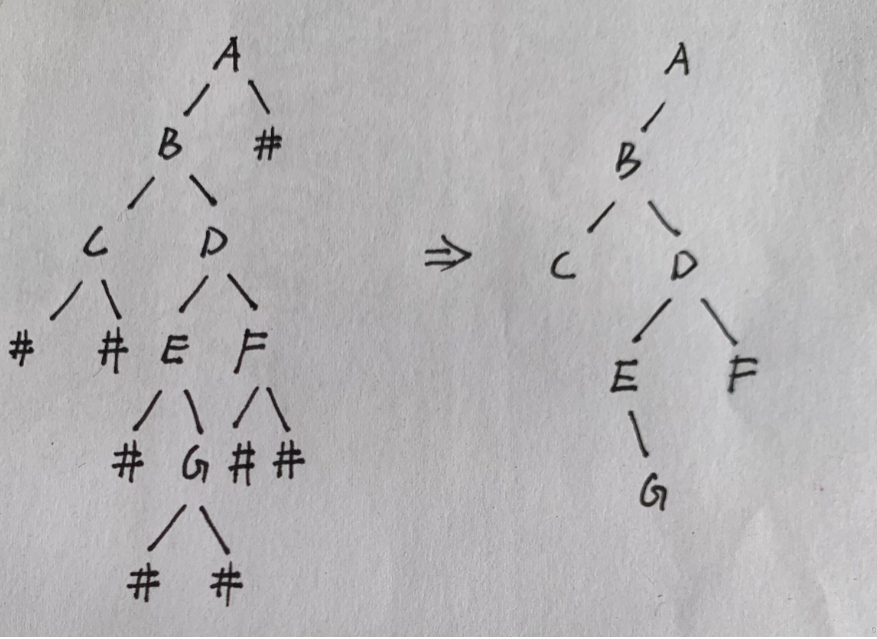
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct TreeNode
{char val;struct TreeNode* left;struct TreeNode* right;
}TNode;TNode* CreateTree(char* a, int* pi)
{if (a[*pi] == '#')//空树不需要递归构建,但是需要i++{(*pi)++;return NULL;}//不是空树就需要递归构建树TNode* root = (TNode*)malloc(sizeof(TNode));if (root == NULL){printf("malloc fail\n");exit(-1);}else{root->val = a[*pi];//将当前数组中的值作为根节点值(*pi)++;root->left = CreateTree(a, pi);//递归构建左子树root->right = CreateTree(a, pi);//递归构建右子树return root;}
}void InOrder(TNode* root)//中序递归遍历
{if (root == NULL){return;}InOrder(root->left);printf("%c ", root->val);InOrder(root->right);
}int main()
{char arr[30] = { 0 };gets(arr);int i = 0;TNode* root = CreateTree(arr, &i);InOrder(root);return 0;
}
