交通建设工程质量监督局网站/汕头seo不错
Android进阶 四大组件的工作过程(三):广播的注册,发送和接收过程

导语
本篇文章是介绍四大组件工作过程的第三篇文章,在前两篇文章里我们已经介绍了Activity和Service的工作流程。而本篇文章,我们将介绍广播相关的工作流程。与Activity和Service相比,广播的使用频率在一般情况下远远低于前两者,但是作为四大组件之一,我们仍然需要了解其工作原理。我们就将其工作过程分为注册,发送和接收三个个过程来分别介绍。
前两篇文章:
- Android进阶 四大组件的工作过程(一):Activity的工作过程
- Android进阶 四大组件的工作过程(二):Service的工作过程
广播的注册
广播又可以分为静态广播的注册和动态广播的注册,静态广播是通过PackageManagerService解析XML清单文件来安装的,也就是在安装APK的时候进行的,这涉及到PackageManagerService,由于对这一块我还不是特别熟悉,这里就主要来介绍动态广播的注册了。
动态广播的注册
我们注册动态广播时,需要调用registerReceiver方法,这个方法是在ContextWrapper中实现的,其实具体来说和Service的启动十分相似,我们来看代码:
public Intent registerReceiver(@Nullable BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter,int flags) {return mBase.registerReceiver(receiver, filter, flags);}
这里会调用到mBase的方法,这个mBase的实现类实际上看过Service的过程的话会十分熟悉,就是ContextImpl类,我们接着跳转到ContextImpl的方法中,最终会调用到ContextImpl的registerInternal方法:
private Intent registerReceiverInternal(BroadcastReceiver receiver, int userId,IntentFilter filter, String broadcastPermission,Handler scheduler, Context context, int flags) {IIntentReceiver rd = null;if (receiver != null) {if (mPackageInfo != null && context != null) {if (scheduler == null) {scheduler = mMainThread.getHandler();}rd = mPackageInfo.getReceiverDispatcher(receiver, context, scheduler,mMainThread.getInstrumentation(), true); //1------1} else {if (scheduler == null) {scheduler = mMainThread.getHandler();}rd = new LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher(receiver, context, scheduler, null, true).getIIntentReceiver();//2------2}}try {ActivityThread thread = ActivityThread.currentActivityThread();Instrumentation instrumentation = thread.getInstrumentation();if (instrumentation.isInstrumenting()&& ((flags & Context.RECEIVER_NOT_EXPORTED) == 0)) {flags = flags | Context.RECEIVER_EXPORTED;}final Intent intent = ActivityManager.getService().registerReceiverWithFeature(mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mBasePackageName, getAttributionTag(),AppOpsManager.toReceiverId(receiver), rd, filter, broadcastPermission, userId, //3------3flags);if (intent != null) {intent.setExtrasClassLoader(getClassLoader());// TODO: determine at registration time if caller is// protecting themselves with signature permissionintent.prepareToEnterProcess(ActivityThread.isProtectedBroadcast(intent),getAttributionSource());}return intent;} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();}}
这里我们分析一下这段代码,先看注释一处,如果mPackageInfo != null && context != null成立的话,就会获取拥有的IIntentReceiver对象,否则就会创建一个IIntentReceiver对象。从这个命名也可以看出来这个是用于跨进程通信,具体来说,这是用于广播的跨进程通信的。接着让我们直接跳到注释三处,这里非常熟悉,又会跳到AMS的registerReceiverWithFeature方法之中,并且会将之前获取到的IIntentReceiver对象给传入进去。所以接下来看AMS中的方法。
public Intent registerReceiverWithFeature(IApplicationThread caller, String callerPackage,String callerFeatureId, String receiverId, IIntentReceiver receiver,IntentFilter filter, String permission, int userId, int flags) {..........ArrayList<Intent> stickyIntents = null;ProcessRecord callerApp = null;final boolean visibleToInstantApps= (flags & Context.RECEIVER_VISIBLE_TO_INSTANT_APPS) != 0;int callingUid;int callingPid;boolean instantApp;synchronized(this) {if (caller != null) {callerApp = getRecordForAppLOSP(caller);//1--------1..........Iterator<String> actions = filter.actionsIterator();//2---------2...........int[] userIds = { UserHandle.USER_ALL, UserHandle.getUserId(callingUid) };while (actions.hasNext()) {String action = actions.next();for (int id : userIds) {ArrayMap<String, ArrayList<Intent>> stickies = mStickyBroadcasts.get(id);if (stickies != null) {ArrayList<Intent> intents = stickies.get(action);//3--------3if (intents != null) {if (stickyIntents == null) {stickyIntents = new ArrayList<Intent>();}stickyIntents.addAll(intents);//4---------4}}}...........}............}ArrayList<Intent> allSticky = null;if (stickyIntents != null) {final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();// Look for any matching sticky broadcasts...for (int i = 0, N = stickyIntents.size(); i < N; i++) {Intent intent = stickyIntents.get(i);// Don't provided intents that aren't available to instant apps.if (instantApp &&(intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_VISIBLE_TO_INSTANT_APPS) == 0) {continue;}if (filter.match(resolver, intent, true, TAG) >= 0) {if (allSticky == null) {allSticky = new ArrayList<Intent>();}allSticky.add(intent);//5---------5}}}............synchronized (this) {IApplicationThread thread;if (callerApp != null && ((thread = callerApp.getThread()) == null|| thread.asBinder() != caller.asBinder())) {// Original caller already diedreturn null;}ReceiverList rl = mRegisteredReceivers.get(receiver.asBinder());//6----------6if (rl == null) {rl = new ReceiverList(this, callerApp, callingPid, callingUid,userId, receiver);if (rl.app != null) {final int totalReceiversForApp = rl.app.mReceivers.numberOfReceivers();if (totalReceiversForApp >= MAX_RECEIVERS_ALLOWED_PER_APP) {throw new IllegalStateException("Too many receivers, total of "+ totalReceiversForApp + ", registered for pid: "+ rl.pid + ", callerPackage: " + callerPackage);}rl.app.mReceivers.addReceiver(rl);} else {try {receiver.asBinder().linkToDeath(rl, 0);} catch (RemoteException e) {return sticky;}rl.linkedToDeath = true;}mRegisteredReceivers.put(receiver.asBinder(), rl);} ...........}BroadcastFilter bf = new BroadcastFilter(filter, rl, callerPackage, callerFeatureId,receiverId, permission, callingUid, userId, instantApp, visibleToInstantApps,exported);if (rl.containsFilter(filter)) {Slog.w(TAG, "Receiver with filter " + filter+ " already registered for pid " + rl.pid+ ", callerPackage is " + callerPackage);} else {rl.add(bf);//7----------7if (!bf.debugCheck()) {Slog.w(TAG, "==> For Dynamic broadcast");}mReceiverResolver.addFilter(getPackageManagerInternal().snapshot(), bf);//8--------8}...........return sticky;}}
这个方法的注释一处获得了调用方的进程接着在注释二处获得了过滤器的迭代器,很显然是之后用于遍历的。在注释三所在的While循环中,就使用这个迭代器遍历了过滤器中的每一个action标签并且获取到了对应的粘性Intent并在注释四处将其添加到AMS的粘性Intent列表中。注释五处则是将符合过滤器要求的粘性Intent添加到了粘性广播的Intent列表之中。
接着来到第二部分,注释六处根据传入的Binder获取到了ReceiverList接收器列表。这个ReceiverList是一个继承了
ArrayList< BroadcastFilter >的类,主要是来存储广播接收者和BroadcastFilter的。之后又会创建一个BroadcastFilter并且会在注释注释七处将其添加入ReceiverList中。最后在注释八处将BroadcastFilter也添加进自身(AMS)的mReceiverResolver,这样当AMS接收到广播时就可以从mReceiverResolver中找到对应的广播接收者。这个变量时IntentResolver类型的,通过它就可以识别Intent意图并执行响应的回调,具体我们在下一节介绍这个类。
IntentResolver类
IntentResolver是Android框架中的一个类,用于解析和匹配意图(Intent)。它在Android系统中起着关键的作用,用于处理各种组件之间的通信和交互。
IntentResolver的主要功能是根据给定的意图(Intent)进行组件匹配。它维护了一组注册的组件(如活动、服务、广播接收器),并根据意图的属性(如动作、类别、数据等)来匹配合适的组件。
具体来说,IntentResolver的主要任务包括:
-
注册组件:当应用程序声明了活动、服务或广播接收器时,它们会通过注册机制将自己注册到IntentResolver中,以便能够被其他应用程序或系统发现和调用。
-
匹配意图:当一个意图(Intent)被发送或启动时,IntentResolver会根据意图的属性对注册的组件进行匹配。它会遍历已注册的组件列表,逐个检查每个组件的过滤器(IntentFilter),并判断是否与意图匹配。
-
返回匹配结果:IntentResolver会返回匹配的组件列表,供调用方选择合适的组件进行交互。根据不同的场景,可能会有多个组件与意图匹配,因此调用方可以根据自己的需求选择最合适的组件进行启动、发送广播等操作。
IntentResolver在Android系统的各个组件之间起着桥梁的作用,它使得不同应用程序之间能够进行组件间的通信和交互。它是实现Android组件之间高效通信的重要组成部分。
广播的发送过程
发送广播也可以有多种形式,这里我们以发送普通广播为例来介绍广播的发送过程。发送普通广播调用的是sendBroadcast方法,它同样是在ContextWrapper中实现的,同样是会由ContextImpl最终调用:
public void sendBroadcast(Intent intent) {warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();String resolvedType = intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver());try {intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);ActivityManager.getService().broadcastIntentWithFeature(mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getAttributionTag(), intent, resolvedType,null, Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null, null, null /*excludedPermissions=*/,null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false, getUserId());} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();}}
显然又是会跳转到AMS中,来看AMS中的方法:
public final int broadcastIntentWithFeature(IApplicationThread caller, String callingFeatureId,Intent intent, String resolvedType, IIntentReceiver resultTo,int resultCode, String resultData, Bundle resultExtras,String[] requiredPermissions, String[] excludedPermissions,String[] excludedPackages, int appOp, Bundle bOptions,boolean serialized, boolean sticky, int userId) {enforceNotIsolatedCaller("broadcastIntent");synchronized(this) {intent = verifyBroadcastLocked(intent);//1--------1final ProcessRecord callerApp = getRecordForAppLOSP(caller);final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {return broadcastIntentLocked(callerApp,//2---------2callerApp != null ? callerApp.info.packageName : null, callingFeatureId,intent, resolvedType, resultTo, resultCode, resultData, resultExtras,requiredPermissions, excludedPermissions, excludedPackages, appOp, bOptions,serialized, sticky, callingPid, callingUid, callingUid, callingPid, userId);} finally {Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);}}}
这里注释一处的verifyBroadcastLocked方法将会验证广播的合法性,通过合法性验证后将会继续跳转到注释二的方法处:
final int broadcastIntentLocked(ProcessRecord callerApp, String callerPackage,@Nullable String callerFeatureId, Intent intent, String resolvedType,IIntentReceiver resultTo, int resultCode, String resultData,Bundle resultExtras, String[] requiredPermissions,String[] excludedPermissions, String[] excludedPackages, int appOp, Bundle bOptions,boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int callingPid, int callingUid,int realCallingUid, int realCallingPid, int userId,boolean allowBackgroundActivityStarts,@Nullable IBinder backgroundActivityStartsToken,@Nullable int[] broadcastAllowList) {intent = new Intent(intent);final boolean callerInstantApp = isInstantApp(callerApp, callerPackage, callingUid);...............if ((receivers != null && receivers.size() > 0)|| resultTo != null) {BroadcastQueue queue = broadcastQueueForIntent(intent); //1---------1BroadcastRecord r = new BroadcastRecord(queue, intent, callerApp, callerPackage,callerFeatureId, callingPid, callingUid, callerInstantApp, resolvedType,requiredPermissions, excludedPermissions, excludedPackages, appOp, brOptions,receivers, resultTo, resultCode, resultData, resultExtras,ordered, sticky, false, userId, allowBackgroundActivityStarts,backgroundActivityStartsToken, timeoutExempt);if (DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.v(TAG_BROADCAST, "Enqueueing ordered broadcast " + r);final BroadcastRecord oldRecord =replacePending ? queue.replaceOrderedBroadcastLocked(r) : null;if (oldRecord != null) {// Replaced, fire the result-to receiver.if (oldRecord.resultTo != null) {final BroadcastQueue oldQueue = broadcastQueueForIntent(oldRecord.intent);try {oldQueue.performReceiveLocked(oldRecord.callerApp, oldRecord.resultTo,oldRecord.intent,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null, null,false, false, oldRecord.userId, oldRecord.callingUid, callingUid);} catch (RemoteException e) {Slog.w(TAG, "Failure ["+ queue.mQueueName + "] sending broadcast result of "+ intent, e);}}} else {queue.enqueueOrderedBroadcastLocked(r);queue.scheduleBroadcastsLocked();//2--------2}} else {if (intent.getComponent() == null && intent.getPackage() == null&& (intent.getFlags()&Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY) == 0) {// This was an implicit broadcast... let's record it for posterity.addBroadcastStatLocked(intent.getAction(), callerPackage, 0, 0, 0);}}return ActivityManager.BROADCAST_SUCCESS;}
这个方法主要就是在注释一处获得了广播列表然后在注释二处调用scheduleBroadcastLocked方法,这个方法会向BroadcastQueue自身的Handler发送BROADCAST_INTENT_MSG的信息,然后触发其processNextBroadcast方法,最后会调用其processNextBroadcastLocked方法,这个方法就是为了将广播发送给广播接收者的。
广播的发送和接收过程
其实接下来就会涉及到广播的接收了,我们接上文,看processNextBroadcastLocked方法:
final void processNextBroadcastLocked(boolean fromMsg, boolean skipOomAdj) {BroadcastRecord r;..........if (fromMsg) {mBroadcastsScheduled = false;}// First, deliver any non-serialized broadcasts right away.while (mParallelBroadcasts.size() > 0) {r = mParallelBroadcasts.remove(0);r.dispatchTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();r.dispatchRealTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();r.dispatchClockTime = System.currentTimeMillis();............final int N = r.receivers.size();...........for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {Object target = r.receivers.get(i);if (DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.v(TAG_BROADCAST,"Delivering non-ordered on [" + mQueueName + "] to registered "+ target + ": " + r);deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(r,(BroadcastFilter) target, false, i); //1---------1}addBroadcastToHistoryLocked(r);if (DEBUG_BROADCAST_LIGHT) Slog.v(TAG_BROADCAST, "Done with parallel broadcast ["+ mQueueName + "] " + r);}............}
这里我们直接看注释一处的代码,这里会遍历广播的接收者列表,然后调用注释一处的deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked方法将广播依次发送给接收者。
private void deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(BroadcastRecord r,BroadcastFilter filter, boolean ordered, int index) {boolean skip = false;............try {if (DEBUG_BROADCAST_LIGHT) Slog.i(TAG_BROADCAST,"Delivering to " + filter + " : " + r);if (filter.receiverList.app != null && filter.receiverList.app.isInFullBackup()) {// Skip delivery if full backup in progress// If it's an ordered broadcast, we need to continue to the next receiver.if (ordered) {skipReceiverLocked(r);}} else {r.receiverTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();maybeAddAllowBackgroundActivityStartsToken(filter.receiverList.app, r);maybeScheduleTempAllowlistLocked(filter.owningUid, r, r.options);maybeReportBroadcastDispatchedEventLocked(r, filter.owningUid);performReceiveLocked(filter.receiverList.app, filter.receiverList.receiver,//1--------1new Intent(r.intent), r.resultCode, r.resultData,r.resultExtras, r.ordered, r.initialSticky, r.userId,filter.receiverList.uid, r.callingUid);// parallel broadcasts are fire-and-forget, not bookended by a call to// finishReceiverLocked(), so we manage their activity-start token hereif (filter.receiverList.app != null&& r.allowBackgroundActivityStarts && !r.ordered) {postActivityStartTokenRemoval(filter.receiverList.app, r);}}if (ordered) {r.state = BroadcastRecord.CALL_DONE_RECEIVE;}.........} }
如果通过了前面的权限检查,这里就会继续调用注释一处的performReceiveLocked方法:
void performReceiveLocked(ProcessRecord app, IIntentReceiver receiver,Intent intent, int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras,boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser,int receiverUid, int callingUid) throws RemoteException {// Send the intent to the receiver asynchronously using one-way binder calls.if (app != null) {final IApplicationThread thread = app.getThread();if (thread != null) {// If we have an app thread, do the call through that so it is// correctly ordered with other one-way calls.try {thread.scheduleRegisteredReceiver(receiver, intent, resultCode, //1------1data, extras, ordered, sticky, sendingUser,app.mState.getReportedProcState());// TODO: Uncomment this when (b/28322359) is fixed and we aren't getting// DeadObjectException when the process isn't actually dead.//} catch (DeadObjectException ex) {// Failed to call into the process. It's dying so just let it die and move on.// throw ex;} catch (RemoteException ex) {// Failed to call into the process. It's either dying or wedged. Kill it gently.synchronized (mService) {Slog.w(TAG, "Can't deliver broadcast to " + app.processName+ " (pid " + app.getPid() + "). Crashing it.");app.scheduleCrashLocked("can't deliver broadcast",CannotDeliverBroadcastException.TYPE_ID, /* extras=*/ null);}throw ex;}} else {// Application has died. Receiver doesn't exist.throw new RemoteException("app.thread must not be null");}} else {receiver.performReceive(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered,sticky, sendingUser);}..........}
这里如果广播接收者所在的应用程序进程存在且正在运行,就会调用注释一处的scheduleRegisteredReceiver方法,这个thread是IApplicationThread类型的,显然又是远程调用具体就是ApplicationThread,也就是ActivityThread,最后会用广播接收者所在的进程来接收广播,来看ApplicationThread的对应方法:
public void scheduleRegisteredReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver, Intent intent,int resultCode, String dataStr, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,boolean sticky, int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException {updateProcessState(processState, false);receiver.performReceive(intent, resultCode, dataStr, extras, ordered,sticky, sendingUser);}
这里又会调用到receiver的performReceive方法,这个receiver是IIntentReceiver 类型的,具体是会在LoadedApk的ReceiverDispatcher类的InnerReceiver实现的,我们看它的performReceive方法:
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data,Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {final LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher rd;if (intent == null) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Null intent received");rd = null;} else {rd = mDispatcher.get();}if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) {int seq = intent.getIntExtra("seq", -1);Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG, "Receiving broadcast " + intent.getAction()+ " seq=" + seq + " to " + (rd != null ? rd.mReceiver : null));}if (rd != null) {rd.performReceive(intent, resultCode, data, extras, //1------1ordered, sticky, sendingUser);} else {// The activity manager dispatched a broadcast to a registered// receiver in this process, but before it could be delivered the// receiver was unregistered. Acknowledge the broadcast on its// behalf so that the system's broadcast sequence can continue.if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG,"Finishing broadcast to unregistered receiver");IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();try {if (extras != null) {extras.setAllowFds(false);}mgr.finishReceiver(this, resultCode, data, extras, false, intent.getFlags());} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();}}}}
来看注释一处,这里会调用到LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher的performReceive方法:
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data,Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {final Args args = new Args(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered,sticky, sendingUser); //1---------1if (intent == null) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Null intent received");} else {if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) {int seq = intent.getIntExtra("seq", -1);Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG, "Enqueueing broadcast " + intent.getAction()+ " seq=" + seq + " to " + mReceiver);}}if (intent == null || !mActivityThread.post(args.getRunnable())) {//2--------2if (mRegistered && ordered) {IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG,"Finishing sync broadcast to " + mReceiver);args.sendFinished(mgr);}}}
注释一处,将方法传入的一系列参数进行封装,形成一个Args对象,然后会在注释二处将args的runnable发送到ActivityThread的Handler中,那我们该关心的就是这个getRunnable方法返回了什么内容了:
public final Runnable getRunnable() {return () -> {final BroadcastReceiver receiver = mReceiver;final boolean ordered = mOrdered;if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) {int seq = mCurIntent.getIntExtra("seq", -1);Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG, "Dispatching broadcast " + mCurIntent.getAction()+ " seq=" + seq + " to " + mReceiver);Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG, " mRegistered=" + mRegistered+ " mOrderedHint=" + ordered);}final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();final Intent intent = mCurIntent;if (intent == null) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Null intent being dispatched, mDispatched=" + mDispatched+ (mRunCalled ? ", run() has already been called" : ""));}mCurIntent = null;mDispatched = true;mRunCalled = true;if (receiver == null || intent == null || mForgotten) {if (mRegistered && ordered) {if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG,"Finishing null broadcast to " + mReceiver);sendFinished(mgr);}return;}if (Trace.isTagEnabled(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER)) {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,"broadcastReceiveReg: " + intent.getAction());}try {ClassLoader cl = mReceiver.getClass().getClassLoader();intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);// TODO: determine at registration time if caller is// protecting themselves with signature permissionintent.prepareToEnterProcess(ActivityThread.isProtectedBroadcast(intent),mContext.getAttributionSource());setExtrasClassLoader(cl);receiver.setPendingResult(this);receiver.onReceive(mContext, intent);//1-------1} catch (Exception e) {if (mRegistered && ordered) {if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG,"Finishing failed broadcast to " + mReceiver);sendFinished(mgr);}if (mInstrumentation == null ||!mInstrumentation.onException(mReceiver, e)) {Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);throw new RuntimeException("Error receiving broadcast " + intent+ " in " + mReceiver, e);}}if (receiver.getPendingResult() != null) {finish();}Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);};}}
这里直接看注释一处,就会触发接收器的onReceive回调方法,从而广播接收器正式接收到了广播的消息。到这里为止,广播的接收过程也结束了。
总结
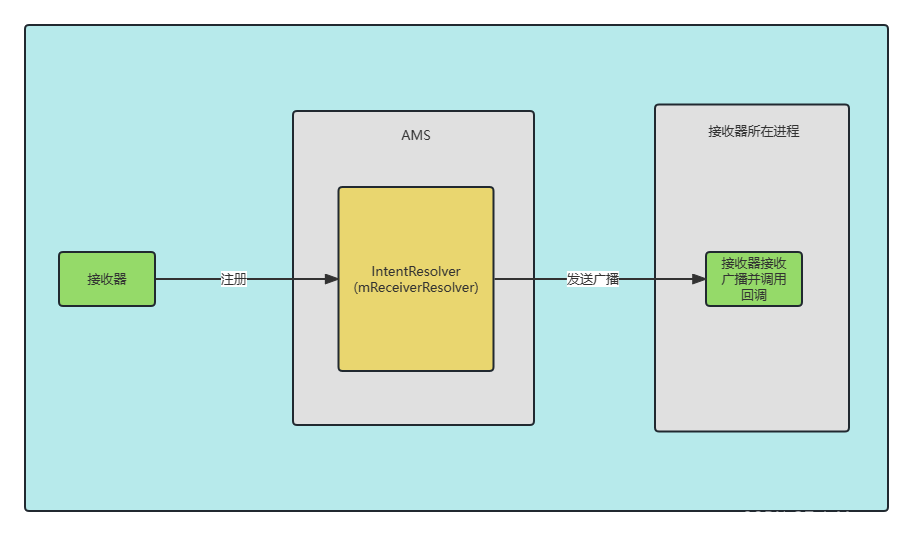
相比Activity和Service的工作过程,Broadcast的工作过程还是比较好懂的,主要就是以AMS为媒介,注册时将接收器注册进AMS中存储接收器的列表中;然后发送过程中也通过AMS来实现发送,调用其存储的接收器的onReceive方法,这样就实现了Broadcast的注册,发送和接收。
下面是一张简要的总结图,省略了大部分细节: